|
Samotherium
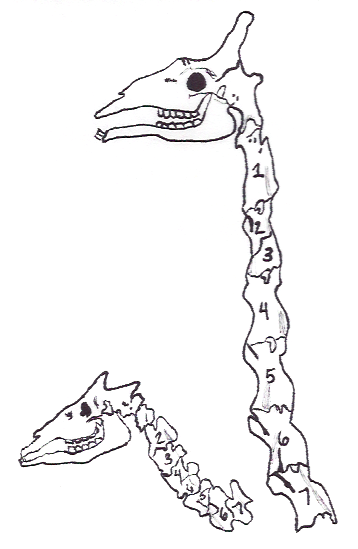
''Samotherium'' ("beast of Samos") is an extinct genus of Giraffidae from the Miocene and Pliocene of Eurasia and Africa. ''Samotherium'' had two ossicones on its head, and long legs. The ossicones usually pointed upward, and were curved backwards, with males having larger, more curved ossicones, though in the Chinese species, ''S. sinense'', the straight ossicones point laterally, not upwards. The genus is closely related to '' Shansitherium''. Fossil evidence suggests that ''Samotherium'' had a rounded muzzle, which would suggest a grazing lifestyle and a habitat composed of grassland. One common predator of this animal was the '' Amphimachairodus''. Biologist Richard Ellis has proposed that the skull of ''Samotherium'' is portrayed on an ancient Greek vase as a monster that Heracles Heracles ( ; ), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a Divinity, divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of ZeusApollodorus1.9.16/ref> and Alcmene, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samotherium Species
''Samotherium'' ("beast of Samos") is an extinct genus of Giraffidae from the Miocene and Pliocene of Eurasia and Africa. ''Samotherium'' had two ossicones on its head, and long legs. The ossicones usually pointed upward, and were curved backwards, with males having larger, more curved ossicones, though in the Chinese species, ''S. sinense'', the straight ossicones point laterally, not upwards. The genus is closely related to '' Shansitherium''. Fossil evidence suggests that ''Samotherium'' had a rounded muzzle, which would suggest a grazing lifestyle and a habitat composed of grassland. One common predator of this animal was the ''Amphimachairodus''. Biologist Richard Ellis has proposed that the skull of ''Samotherium'' is portrayed on an ancient Greek vase as a monster that Heracles is fighting. However, other authors have argued that it is more likely to be the skull of a monitor lizard instead. Description A 2015 study found that ''Samotherium'' had a neck intermediate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giraffidae
The Giraffidae are a family (biology), family of ruminant artiodactyl mammals that share a recent common ancestor with deer and bovids. This family, once a diverse group spread throughout Eurasia and Africa, presently comprises only two extant genera, the giraffe (between one and eight, usually four, species of ''Giraffa'', depending on taxonomic interpretation) and the okapi (the only known species of ''Okapia''). Both are confined to sub-Saharan Africa: the giraffe to the open savannas, and the okapi to the dense rainforest of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Congo. The two genera look very different on first sight, but share a number of common features, including a long, dark-coloured tongue, lobed canine teeth, and horns covered in skin, called ossicones. Taxonomy Evolutionary background The giraffids are ruminants of the clade Pecora. Other extant pecorans are the families Antilocapridae (pronghorns), Cervidae (deer), Moschidae (musk deer), and Bovidae (Bovini, cattl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giraffe
The giraffe is a large Fauna of Africa, African even-toed ungulate, hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa.'' It is the Largest mammals#Even-toed Ungulates (Artiodactyla), tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. It is classified under the Family (biology), family Giraffidae, along with its closest extant relative, the okapi. Traditionally, giraffes have been thought of as one species, ''Giraffa camelopardalis'', with nine subspecies. Most recently, researchers proposed dividing them into four Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant species which can be distinguished by their fur Animal coat, coat patterns. Six valid Lists of extinct species, extinct species of ''Giraffa'' are known from the fossil record. The giraffe's distinguishing characteristics are its extremely long neck and legs, horn-like ossicones, and spotted coat patterns. Its scattered range extends from Chad in the north to South Africa in the south and from Niger in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okapi
The okapi (; ''Okapia johnstoni''), also known as the forest giraffe, Congolese giraffe and zebra giraffe, is an artiodactyl mammal that is endemic to the northeast Democratic Republic of the Congo in central Africa. However, non-invasive genetic identification has suggested that a population has occurred south-west of the Congo River as well. It is the only species in the genus ''Okapia''. Although the okapi has striped markings reminiscent of zebras, it is most closely related to the giraffe. The okapi and the giraffe are the only living members of the family Giraffidae. The okapi stands about tall at the shoulder and has a typical body length around . Its weight ranges from . It has a long neck, and large, flexible ears. Its coat is a chocolate to reddish brown, much in contrast with the white horizontal stripes and rings on the legs, and white ankles. Male okapis have short, distinct horn-like protuberances on their heads called ossicones, less than in length. Female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossicone
Ossicones are columnar or conical skin-covered bone structures on the heads of giraffes, male okapi, and some of their extinct relatives. Ossicones are distinguished from the superficially similar structures of Horn (anatomy), horns and antlers by their unique development and a permanent covering of skin and fur. Structure Giraffe ossicones consist of a highly vascularized and innervated bone core covered with similarly vascularized and innervated skin. They are attached to the skull with vascularized, innervated connective tissue. Ossicones are formed at late gestation, but in early development they are not bony and not fused to the skull yet. Ossicones usually fuse to the skull at sexual maturity. All male and female giraffes have a pair of parietal ossicones on the parietal bones of the skull. Males also usually have a single median ossicone on the frontal bone that is larger in northern animals and smaller in southern giraffes. Giraffes can also have small additional paire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shansitherium
''Shansitherium'' ("beast of Shanxi")Killgus, H., 1922. Die unterpliocaenen chinesischen Säugetierreste der Tafelschen Sammlung zu Tübingen (Doctoral dissertation) is an extinct genus of superficially moose-like or antelope-like giraffids from the late Miocene epoch of Shanxi Province, China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after .... They are closely related to the genus '' Samotherium''. Species The genus consists of the following species: * '' Shansitherium fuguensis'' * '' Shansitherium tafeli'' * '' Shansitherium quadricornis''Bohlin, B., 1926. Die Familie Giraffidae mit besonderen Berucksichtgung der fossilen Formen aus China. ''Palaeontologia Sinica'', ser C. 4. The Geological Survey of China, Peking. References External links * Prehistoric giraffes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitional Fossils
A transitional fossil is any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group. This is especially important where the descendant group is sharply differentiated by gross anatomy and mode of living from the ancestral group. These fossils serve as a reminder that taxonomic divisions are human constructs that have been imposed in hindsight on a continuum of variation. Because of the incompleteness of the fossil record, there is usually no way to know exactly how close a transitional fossil is to the point of divergence. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that transitional fossils are direct ancestors of more recent groups, though they are frequently used as models for such ancestors. In 1859, when Charles Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species'' was first published, the fossil record was poorly known. Darwin described the perceived lack of transitional fossils as "the most obvious and gravest objection which can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogene Mammals Of Asia
The Neogene ( ,) is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period million years ago. It is the second period of the Cenozoic and the eleventh period of the Phanerozoic. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by Paleogene and Neogene and, despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. During this period, mammals and birds continued to evolve into modern forms, while other groups of life remained relatively unchanged. The first humans (''H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene Artiodactyla
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Artiodactyla
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the connections between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |