|
Salisbury Branch Line (Great Western Railway)
The Salisbury branch line of the Great Western Railway from to Salisbury in Wiltshire, England, was completed in 1856. Most of the smaller stations were closed in 1955 but the line remains in use as part of the Wessex Main Line. History Wilts and Somerset Railway In 1844 the Great Western Railway (GWR) and the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) were engaged in a struggle to secure territory, known as the gauge war: the GWR lines were broad gauge and the LSWR were standard gauge, sometimes called "narrow gauge" for contrast. When the LSWR proposed a new line from Basingstoke to Newbury and Swindon, the GWR sought to fend it off with their own proposal, a branch line from their main line at Thingley Junction, west of Chippenham, to Salisbury. In this period the government's policy was that any general area could only support one railway line, and a commission appointed by the Board of Trade would appraise rival proposals and determine which should be permitted. In this c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838 with the initial route completed between London and Bristol in 1841. It was engineered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who chose a broad gauge of —later slightly widened to —but, from 1854, a series of Consolidation (business), amalgamations saw it also operate Standard gauge, standard-gauge trains; the last broad-gauge services were operated in 1892. The GWR was the only company to keep its identity through the Railways Act 1921, which amalgamated it with the remaining independent railways within its territory, and it was finally merged at the end of 1947 when it was Nationalization, nationalised and became the Western Region of British Railways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sherborne
Sherborne is a market town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in north west Dorset, in South West England. It is sited on the River Yeo (South Somerset), River Yeo, on the edge of the Blackmore Vale, east of Yeovil. The parish includes the hamlets of Nether Coombe and Lower Clatcombe. The A30 road, which connects London to Penzance, runs through the town. In the United Kingdom Census 2021, 2021 census the population of Sherborne was 10,361. Sherborne's historic buildings include Sherborne Abbey, its Sherborne House, Dorset, manor house, independent schools, and two castles: the ruins of a 12th-century fortified palace and the 16th-century mansion known as Sherborne Castle built by Sir Walter Raleigh. Much of the old town, including the abbey and many medieval and Georgian architecture, Georgian buildings, is built from distinctive ochre-coloured ham stone. The town is served by Sherborne railway station. Toponymy The town was named ''scir burne'' by the Anglo-Saxons, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
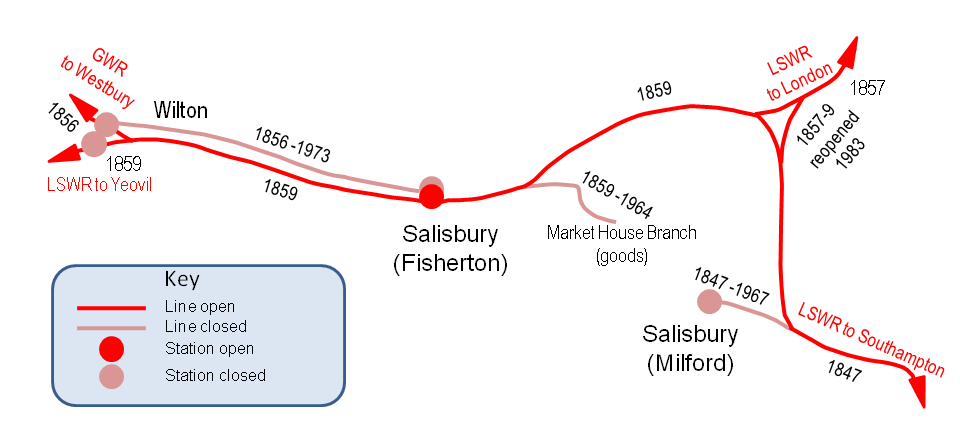
Fisherton Street
Fisherton Street is in the city of Salisbury in the English county of Wiltshire. On the western side of the city, it is primarily a commercial street. It runs eastwards from Wilton Road towards the city centre. After crossing the River Avon it becomes Bridge Street. The street's name derives from the fact that it connected Salisbury city with the nearby village of Fisherton Anger, then a mile or so from the city centre but now part of the city. Notable buildings include the former Georgian era Salisbury Infirmary, now in residential use as Pembroke House; the Victorian Clock Tower; the King's Head Hotel; and St Paul's Church. Salisbury railway station Salisbury railway station serves the cathedral city of Salisbury in Wiltshire, England. It is from on the West of England line to . This is crossed by the Wessex Main Line from Bristol Temple Meads to Southampton Central. The station is ope ... is close to the street and was at first known as Fisherton Street to distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salisbury Railway Station
Salisbury railway station serves the cathedral city of Salisbury in Wiltshire, England. It is from on the West of England line to . This is crossed by the Wessex Main Line from Bristol Temple Meads to Southampton Central. The station is operated and served by South Western Railway (SWR), and is also served by Great Western Railway (GWR). History Three railway station sites have been used in Salisbury, owned by the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) from 1847 and the Great Western Railway (GWR) from 1856, as well as two further stations at Wilton, west. London and South Western Railway The LSWR opened their Milford station on the east side of the city on 1 March 1847, with the opening of their branch line from Eastleigh to passenger traffic. This was the city's only railway until 30 June 1856, when the GWR opened the Salisbury branch from Westbury. On 1 May 1857, the LSWR opened the extended main line from London and Andover, at first to the Milford station. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milford, Wiltshire
Laverstock is a village and civil parish on the north-east and east outskirts of Salisbury in the ceremonial county of Wiltshire, England. The parish is shaped like a figure 7 and incorporates Ford hamlet, the eastern half of the former manor of Milford, the area near the ancient settlement of Old Sarum, and part of the Hampton Park district on the edge of Salisbury. Laverstock, the parish's main settlement, lies on the east bank of the River Bourne and is approximately east of Salisbury city centre, due south of Swindon and west-southwest of London. History Flint mines and signs of barrows have been discovered on Burrough's Hill, indicating settlement back to Neolithic time. There is also evidence of settlement during the Iron and Bronze Age. A Roman cemetery and settlement has been found on Cocky's Hill. Laverstock has two entries in the Domesday Book which indicate the settlement was then owned by Wilton Abbey with some parts owned by officers of the king. Milford Mill B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milford Railway Station (Wiltshire)
Milford railway station was the first railway station to be built in the city of Salisbury, Wiltshire, England, in 1847. The Bishopstoke to Salisbury line approached from the south-east, and terminated in the Milford area of the city by the Church of St Martin. In 1859, passenger services were transferred away to the newer station located at Fisherton (now the main station in Salisbury), with Milford retained as a goods depot until the 1960s. History The station opened to traffic in 1847, when the London and South Western Railway's branch from Southampton and Bishopstoke was built into the east side of Salisbury. Goods traffic started between Bishopstoke () and Salisbury in January 1847, with passenger trains starting in March of the same year. The railway's arrival resulted in terraced housing being built in the area around St Martin's Church for the railway workers. A journey to London took at least four hours with a change at Bishopstoke, until the direct line to London w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pigeon post is not. Ancient signalling systems, although sometimes quite extensive and sophisticated as in China, were generally not capable of transmitting arbitrary text messages. Possible messages were fixed and predetermined, so such systems are thus not true telegraphs. The earliest true telegraph put into widespread use was the Chappe telegraph, an optical telegraph invented by Claude Chappe in the late 18th century. The system was used extensively in France, and European nations occupied by France, during the Napoleonic era. The electric telegraph started to replace the optical telegraph in the mid-19th century. It was first taken up in Britain in the form of the Cooke and Wheatstone telegraph, initially used mostly as an aid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilton, Wiltshire
Wilton is a town and Civil parishes in England, civil parish in Wiltshire, England. Lying about west of the city of Salisbury, and until 1889 the county town of Wiltshire, it has a rich heritage dating back to the Anglo-Saxons. The parish had a population of 4,305 at the 2021 census, an increase from the 3,579 recorded in 2011. Carpets have been manufactured at Wilton since the 18th century. The town is home to Wilton House, country seat of the Earls of Pembroke, and has a large Romanesque Revival parish church. The rivers River Wylye, Wylye and River Nadder, Nadder meet at Wilton. History The history of Wilton dates back to the Anglo-Saxons in the 8th century, and by the late 9th century it was the capital of ''Wiltunscire'', a shire of the Wessex, Kingdom of Wessex. It remained the administrative centre of Wiltshire until the 11th century. Wilton was of significant importance to the church, with the founding of Wilton Abbey in 771 amongst other establishments. In 871 Alfre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wylye
Wylye () is a village and civil parish on the River Wylye in Wiltshire, England. The village is about northwest of Salisbury and a similar distance southeast of Warminster. The parish extends north and south of the river, and includes the hamlet of Deptford. Today Deptford is at the junction of two primary roads, the A303 (London to the southwest) and the A36 (Southampton to Bristol). In 1934 half of Fisherton parish was added to Wylye, including the small village of Fisherton Delamere. History A collection of Bronze Age jewellery found near the village by metal detectorists in 2012, known as the Wylye Hoard, is held by Salisbury Museum. Bilbury Rings, on the southern slope of the valley, is an Iron Age hillfort. Nearby is a prehistoric field system. A Roman road from Winchester to the Mendips passes through the southern edge of the parish. The boundaries of Wyle manor, and possibly also of Deptford manor, were defined in the 10th century. Domesday Book in 1086 recorded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathampton
Bathampton () is a village and Civil parishes in England, civil parish east of Bath, Somerset, Bath, England on the south bank of the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon. The parish has a population of 1,603. The Kennet and Avon Canal passes through the village and a Bathampton Toll Bridge, toll bridge links Bathampton to Batheaston on the north bank of the canal. History Bathampton Camp is a univallate Iron Age hill fort situated approximately east from the village. The site was excavated in 1904–05 and in 1952–54. Results found human and animal remains, pottery and flint flakes. The parish was part of the Hundred (county subdivision), hundred of Hampton (hundred), Hampton. The village used to be served by Bathampton railway station, but it was closed following the destructive Beeching cuts. Plasticine was manufactured in the village between 1900 and 1983 by a company founded by William Harbutt, who also lived in Bathampton. Governance The Parish councils of England, pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen's Bench Division Of The High Court Of Justice Of England And Wales
The High Court of Justice in London, known properly as His Majesty's High Court of Justice in England, together with the Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, are the Senior Courts of England and Wales. Its name is abbreviated as EWHC (England and Wales High Court) for legal citation purposes. The High Court deals at first instance with all high-value and high-importance civil law (non-criminal) cases; it also has a supervisory jurisdiction over all subordinate courts and tribunals, with a few statutory exceptions, though there are debates as to whether these exceptions are effective. The High Court consists of three divisions: the King's Bench Division, the Chancery Division and the Family Division. Their jurisdictions overlap in some cases, and cases started in one division may be transferred by court order to another where appropriate. The differences of procedure and practice between divisions are partly historical, derived from the separate courts which were merged into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandamus
A writ of (; ) is a judicial remedy in the English and American common law system consisting of a court order that commands a government official or entity to perform an act it is legally required to perform as part of its official duties, or to refrain from performing an act the law forbids it from doing. Writs of mandamus are usually used in situations where a government official has failed to act as legally required or has taken a legally prohibited action. Decisions that fall within the discretionary power of public officials cannot be controlled by the writ. For example, mandamus can not force a lower court to take a specific action on applications that have been made. However, if the court refuses to rule at all, then mandamus can be used to order the court to rule on the applications. Mandamus may be a command to take or not take a particular action, and it is supplemented by legal rights. In the American legal system it must be a judicially enforceable and legally pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |