|
SMS Prinz Eugen (1877)
SMS ''Prinz Eugen'' was an ironclad warship built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy in the 1870s, the third and final member of the . The ship was supposedly the SMS Don Juan d'Austria (1862), same vessel that had been laid down in 1861, and had simply been reconstructed. In reality, the head of the Austro-Hungarian Navy could not secure funding for new ships, but reconstruction projects were uncontroversial, so he "rebuilt" the three earlier s. Only the engines and parts of the armor plate were reused in the new ''Prinz Eugen'', which was laid down in October 1874, launched in September 1877, and commissioned in November 1878. The ship spent significant periods out of service, in part due to slender naval budgets that prevented much active use. In 1880, she took part in an international naval demonstration against the Ottoman Empire, and she went to Spain in 1888 for the 1888 Barcelona Universal Exposition, Barcelona Universal Exposition. ''Prinz Eugen'' was stricken in 1904 and conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Eugene Of Savoy
Prince Eugene Francis of Savoy-Carignano (18 October 1663 – 21 April 1736), better known as Prince Eugene, was a distinguished Generalfeldmarschall, field marshal in the Army of the Holy Roman Empire and of the Austrian Habsburg dynasty during the 17th and 18th centuries. Renowned as one of the greatest military commanders of his era, Prince Eugene also rose to the highest offices of state at the Imperial court in Vienna spending six decades in the service of three emperors. Born in Paris, to the son of a French count and a niece of Cardinal Mazarin, Eugene was raised at the court of King Louis XIV. Initially destined for the priesthood as the youngest son of a noble family, he chose to pursue a military career at 19. Due to his poor physique and possibly a scandal involving his mother, Louis XIV denied him a commission in the French Royal Army and forbade him from enlisting elsewhere. Embittered, Eugene fled France and entered the service of Emperor Leopold I, Holy Roman Empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1888 Barcelona Universal Exposition
The 1888 Barcelona Universal Exposition (in Catalan language, Catalan: ''Exposició Universal de Barcelona'' and ''Exposición Universal de Barcelona'' in Spanish language, Spanish) was Spain's first International World's Fair and ran from 8 April to 9 December 1888. The second one in Barcelona was held in 1929 Barcelona World Fair, 1929. Summary :es:Eugenio Serrano de Casanova, Eugenio Serrano de Casanova (journalist, writer and entrepreneur) tried to launch an exposition in 1886, and when that failed, the Mayor of Barcelona, Francesc de Paula Rius i Taulet, Francesc Rius i Taulet, took over the planning of the project. The fair was hosted on the reconstructed site of the city's main public park, the Parc de la Ciutadella, with Josep Vilaseca i Casanovas, Vilaseca's Arc de Triomf forming the entrance. More than 2 million people from Spain, the rest of Europe, and other international points of embarkation visited the exhibition, which made the equivalent of $1,737,000 USD. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliber (artillery)
In artillery, caliber or calibre''Caliber'' is the American English spelling, while ''calibre'' is used in British English. is the internal diameter of a gun barrel, or, by extension, a relative measure of the barrel length. Rifled barrels Rifled barrels introduce ambiguity to measurement of caliber. A rifled bore consists of alternating grooves and lands. The distance across the bore from groove to groove is greater than the distance from land to land. Projectiles fired from rifled barrels must be of the full groove-to-groove diameter to be effectively rotated by the rifling, but the caliber has sometimes been specified as the land-to-land diameter before rifling grooves were cut. The depth of rifling grooves (and the consequent ambiguity) increases in larger calibers. Steel artillery projectiles may have a forward bourrelet section machined to a diameter slightly smaller than the original land-to-land dimension of the barrel and a copper driving band somewhat larger than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Battery
A main battery is the primary weapon or group of weapons around which a warship is designed. As such, a main battery was historically a naval gun or group of guns used in volleys, as in the broadsides of cannon on a ship of the line. Later, this came to be turreted groups of similar large-caliber naval rifles. With the evolution of technology the term has come to encompass guided missiles and torpedoes as a warship's principal offensive weaponry, deployed both on surface ships and submarines. A main battery features common parts, munition and fire control system across the weapons which it comprises. Description In the age of cannon at sea, the main battery was the principal group of weapons around which a ship was designed, usually its heavies. With the coming of naval rifles and subsequent revolving gun turrets, the main battery became the principal group of heaviest guns, regardless of how many turrets they were placed in. As missiles displaced guns both above and belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casemate Ship
The central battery ship, also known as a centre battery ship in the United Kingdom and as a casemate ship in European continental navies, was a development of the (high- freeboard) broadside ironclad of the 1860s, given a substantial boost due to the inspiration gained from the Battle of Hampton Roads, the first battle between ironclads fought in 1862 during the American Civil War. One of the participants was the Confederate casemate ironclad , essentially a central battery ship herself, albeit a low-freeboard one. The central battery ships had their main guns concentrated in the middle of the ship in an armoured citadel. The concentration of armament amidships meant the ship could be shorter and handier than a broadside type like previous warships. In this manner the design could maximize the thickness of armour in a limited area while still carrying a significant broadside. These ships meant the end of the armoured frigates with their full-length gun decks. In the UK, the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mast (sailing)
The mast of a sailing vessel is a tall spar, or arrangement of spars, erected more or less vertically on the median line of a ship or boat. Its purposes include carrying sails, spars, and derricks, giving necessary height to a navigation light, look-out position, signal yard, control position, radio aerial, or signal lamp. Large ships have several masts, with the size and configuration depending on the style of ship. Nearly all sailing masts are guyed. Until the mid-19th century, all vessels' masts were made of wood formed from a single or several pieces of timber which typically consisted of the trunk of a conifer tree. From the 16th century, vessels were often built of a size requiring masts taller and thicker than from single tree trunks. On these larger vessels, to achieve the required height, the masts were built from up to four sections (also called masts). From lowest to highest, these were called: lower, top, topgallant, and royal masts. Giving the lower section ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funnel (ship)
A funnel is the smokestack or chimney on a ship used to expel boiler steam and smoke or engine exhaust gas, exhaust. They are also commonly referred to as stacks. Purpose The primary purpose of a ship's funnel(s) is to lift the exhaust gases clear of the deck, in order not to foul the ship's structure or decks, and to avoid impairing the ability of the crew to carry out their duties. In steam ships the funnels also served to help induce a boiler draught, convection draught through the boilers. Design Since the introduction of steam-power to ships in the 19th century, the funnel has been a distinctive feature of the silhouette of a vessel, and used for recognition purposes. Funnel area The required funnel cross-sectional area is determined by the volume of exhaust gases produced by the propulsion plant. Often this area is too great for a single funnel. Early steam vessels needed multiple funnels ( had 5 when launched), but as efficiency increased new machinery needed fewe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Ram
A ram on the bow of ''Olympias'', a modern reconstruction of an ancient Athenian trireme A naval ram is a weapon fitted to varied types of ships, dating back to antiquity. The weapon comprised an underwater prolongation of the bow of the ship to form an armoured beak, usually between in length. This would be driven into the hull of an enemy ship to puncture, sink or disable it. Antiquity It was possibly developed in late Bronze Age Egypt, but it only became widely used in later Iron Age Mediterranean galleys. The ram was a naval weapon in the Greek/ Roman antiquity and was used in such naval battles as Salamis and Actium. Naval warfare in the Mediterranean rarely used sails, and the use of rams specifically required oarsmen rather than sails in order to maneuver with accuracy and speed, and particularly to reverse the movement of a ramming ship to disentangle it from its sinking victim, lest it be pulled down when its victim sank. The Athenians were especially known fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p. 5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks". A merchant vessel has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
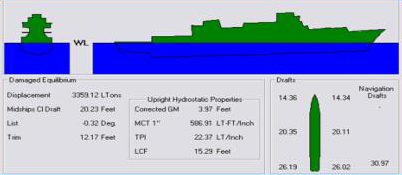
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship is a determined depth of the vessel below the waterline, measured vertically to its hull's lowest—its propellers, or keel, or other reference point. Draft varies according to the loaded condition of the ship. A deeper draft means the ship will have greater vertical depth below the waterline. Draft is used in under keel clearance calculations, where the draft is calculated with the available depth of water (from Electronic navigational charts) to ensure the ship can navigate safely, without grounding. Navigators can determine their draught by calculation or by visual observation (of the ship's painted load lines). Related terminology A ship's draft/draught is the "depth of the vessel below the waterline measured vertically to the lowest part of the hull, propellers, or other reference point". That is, the draft or draught is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer sides of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship (or boat), the more initial stability it has, at the expense of secondary stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position. A ship that heels on her ''beam ends'' has her deck beams nearly vertical. Typical values Typical length-to-beam ratios ( aspect ratios) for small sailboats are from 2:1 (dinghies to trailerable sailboats around ) to 5:1 (racing sailboats over ). Large ships have widely varying beam ratios, some as large as 20:1. Rowing shells designed for flatwater racing may have length to beam ratios as high as 30:1, while a cora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |