|
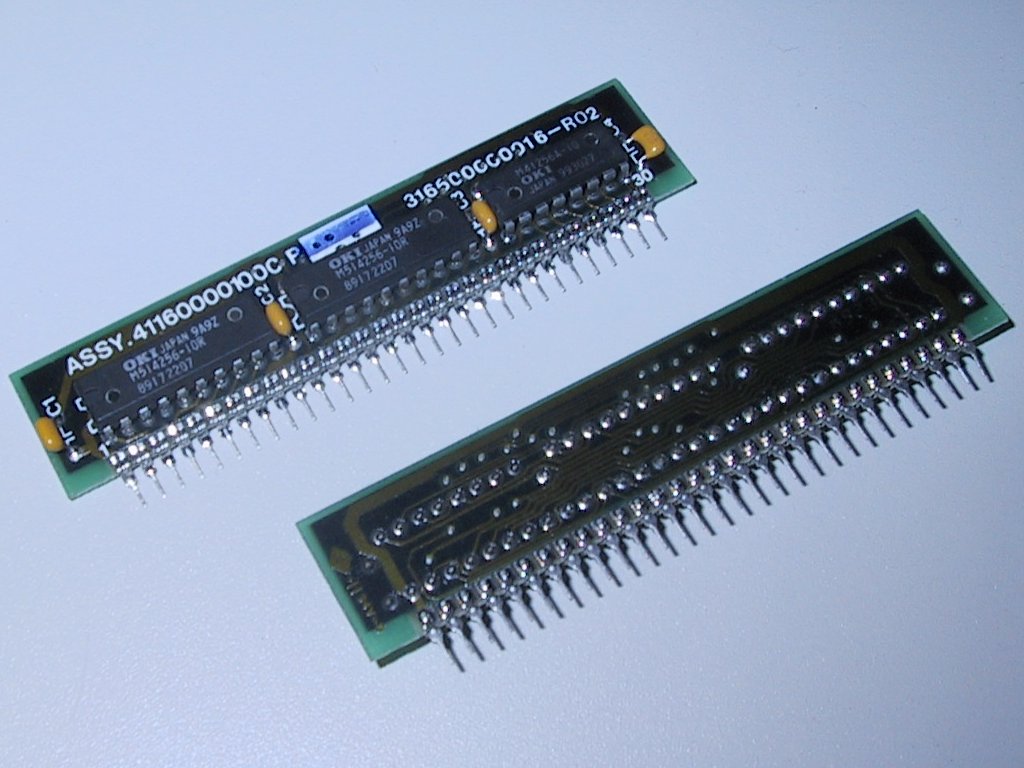
SIPP Memory
A SIPP (single in-line pin package) or SIP (single in-line package) was a short-lived variant of the 30-pin SIMM random-access memory. It consisted of a small printed circuit board upon which were mounted a number of memory chips. It had 30 pins along one edge which mated with matching holes in the motherboard of the computer. This type of memory was used in some 80286 and 80386 (80386SX) systems. It was soon replaced by SIMMs using edge connectors, which proved to be more economical and durable. 30-pin SIPP modules were pin compatible with 30-pin SIMM modules explaining why some SIPP modules were in fact SIMM modules with pins soldered onto the connectors. See also * Zig-zag in-line package The zig-zag in-line package (ZIP) is a packaging technology for integrated circuits. It was intended as a replacement for dual in-line packaging (DIL or DIP). A ZIP is an integrated circuit encapsulated in a slab of plastic with 16, 20, 28 or 40 ... References {{Compu-hardware-stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIPP initiative from Intel
{{disambig ...
SIPP may refer to: * Self-invested personal pension, a type of United Kingdom pension plan * Simple Internet Protocol Plus, former name of IPv6 * SIPP memory, single in-line pin package, a type of computer memory * Standard Interline Passenger Procedure, ACRISS vehicle category codes * Survey of Income and Program Participation, a survey of household income and transfer payments * SIPp, test tool / traffic generator for Session Initiation Protocol * "The Sipp" or Sipp, shortened form of Mississippi, a state of the United States of America * Stable Image Platform Program Stable Image Platform Program or Stable IT Platform Program is the name of an initiative introduced by Intel. The idea is that a pre-configured disk image will work on any of the certified hardware combinations. Intel states the program guarantees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
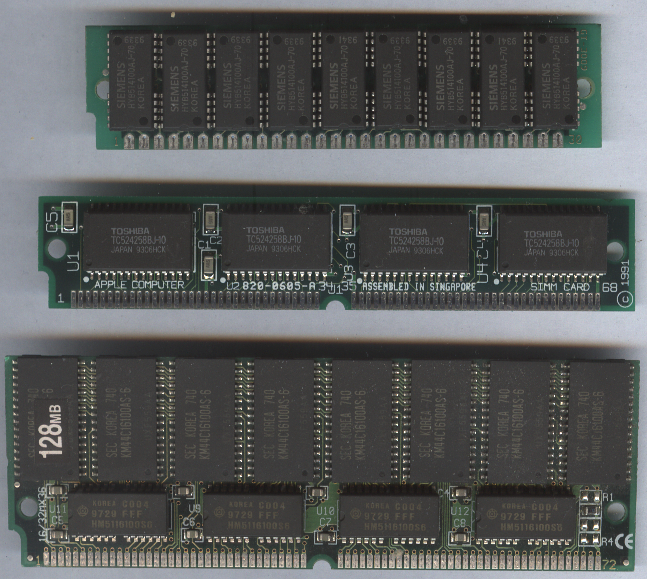
SIMM
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It is a printed circuit board upon which multiple random-access memory Integrated circuit chips are attached to one or both sides. It differs from a dual in-line memory module (DIMM), the most predominant form of memory module since the late 1990s, in that the contacts on a SIMM are redundant on both sides of the module. SIMMs were standardised under the JEDEC JESD-21C standard. Most early PC motherboards ( 8088-based PCs, XTs, and early ATs) used socketed DIP chips for DRAM. As computer memory capacities grew, memory modules were used to save motherboard space and ease memory expansion. Instead of plugging in eight or nine single DIP chips, only one additional memory module was needed to increase the memory of the computer. History SIMMs were invented in 1983 by James E. ClaytonClayton, James E. (1983)Low-cost, high-density memory packaging: A 64K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random-access Memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of Computer memory, electronic computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working Data (computing), data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read (computer), read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media (such as hard disks and Magnetic tape data storage, magnetic tape), where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement. In today's technology, random-access memory takes the form of integrated circuit (IC) chips with MOSFET, MOS (metal–oxide–semiconductor) Memory cell (computing), memory cells. RAM is normally associated with Volatile memory, volatile types of memory where s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printed Circuit Board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) Chemical milling, etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. PCBs are used to connect or Electrical wiring, "wire" Electronic component, components to one another in an electronic circuit. Electrical components may be fixed to conductive pads on the outer layers, generally by soldering, which both electrically connects and mechanically fastens the components to the board. Another manufacturing process adds Via (electronics), vias, metal-lined drilled holes that enable electrical interconnections between conductive layers, to boards with more than a single side. Printed circuit boards are used in nearly all e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motherboard
A motherboard, also called a mainboard, a system board, a logic board, and informally a mobo (see #Nomenclature, "Nomenclature" section), is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and computer memory, memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as the CPU, the chipset's input/output and Memory controller, memory controllers, interface (computing), interface connectors, and other components integrated for general use. Nomenclature ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of the word ''motherboard'' to 1965, its earliest-found attestation occurring in the magazine ''Electronics (magazine), Electronics''. The term alludes to its importance and size compared to the components attached to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
80286
The Intel 80286 (also marketed as the iAPX 286 and often called Intel 286) is a 16-bit microprocessor that was introduced on February 1, 1982. It was the first 8086-based CPU with separate, non-multiplexed address and data buses and also the first with memory management and wide protection abilities. It had a data size of 16 bits, and had an address width of 24 bits, which could address up to 16M of memory with a suitable operating system such as Windows compared to 1M for the 8086. The 80286 used approximately 134,000 transistors in its original nMOS (HMOS) incarnation and, just like the contemporary 80186, it can correctly execute most software written for the earlier Intel 8086 and 8088 processors. The 80286 was employed for the IBM PC/AT, introduced in 1984, and then widely used in most PC/AT compatible computers until the early 1990s. In 1987, Intel shipped its five-millionth 80286 microprocessor. History and performance Intel's first 80286 chips were specified for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
80386
The Intel 386, originally released as the 80386 and later renamed i386, is the third-generation x86 architecture microprocessor from Intel. It was the first 32-bit processor in the line, making it a significant evolution in the x86 architecture. Pre-production samples of the 386 were released to select developers in 1985, while mass production commenced in 1986. The 386 was the central processing unit (CPU) of many workstations and high-end personal computers of the time. The 386 began to fall out of public use starting with the release of the i486 processor in 1989, while in embedded systems the 386 remained in widespread use until Intel finally discontinued it in 2007. Compared to its predecessor the Intel 80286 ("286"), the 80386 added a three-stage instruction pipeline which it brings up to total of 6-stage instruction pipeline, extended the architecture from 16-bits to 32-bits, and added an on-chip memory management unit. This paging translation unit made it much easier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
80386SX
The Intel 386, originally released as the 80386 and later renamed i386, is the third-generation x86 architecture microprocessor from Intel. It was the first 32-bit computing, 32-bit processor in the line, making it a significant evolution in the x86 architecture. Pre-production samples of the 386 were released to select developers in 1985, while mass production commenced in 1986. The 386 was the central processing unit, central processing unit (CPU) of many workstations and high-end personal computers of the time. The 386 began to fall out of public use starting with the release of the i486 processor in 1989, while in embedded systems the 386 remained in widespread use until Intel finally discontinued it in 2007. Compared to its predecessor the Intel 80286 ("286"), the 80386 added a three-stage instruction pipelining, instruction pipeline which it brings up to total of 6-stage instruction pipeline, extended the architecture from 16-bits to 32-bits, and added an on-chip memory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge Connector
An edge connector is the portion of a printed circuit board (PCB) consisting of signal trace, traces leading to the edge of the board that are intended to plug into a matching jack (connector), socket. The edge connector is a money-saving device because it only requires a single discrete female connector (the male connector is formed out of the edge of the PCB), and they also tend to be fairly robust and durable. They are commonly used in computers for expansion slots for peripheral cards, such as Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI, PCI Express, and Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP cards. Socket design Edge connector sockets consist of a plastic "box" open on one side, with pins on one or both sides of the longer edges, sprung to push into the middle of the open center. Connectors are often Key (engineering), keyed to ensure the correct Electrical polarity, polarity, and may contain bumps or notches both for polarity and to ensure that the wrong type of device is not inserte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zig-zag In-line Package
The zig-zag in-line package (ZIP) is a packaging technology for integrated circuits. It was intended as a replacement for dual in-line packaging (DIL or DIP). A ZIP is an integrated circuit encapsulated in a slab of plastic with 16, 20, 28 or 40 pins, measuring (for the ZIP-20 package) about 3 mm x 30 mm x 10 mm. The package's pins protrude in two rows from one of the long edges. The two rows are staggered by 1.27 mm (0.05"), giving them a zig-zag appearance, and allowing them to be spaced more closely than a rectangular grid would allow. The pins are inserted into holes in a printed circuit board, with the packages standing at right-angles to the board, allowing them to be placed closer together than DIPs of the same size. ZIPs have now been superseded by surface-mount packages such as the thin small-outline packages ( TSOPs), but are still in use. The quad in-line package uses a similar staggered semiconductor package design, but on two sides instead of on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |