SIMM on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
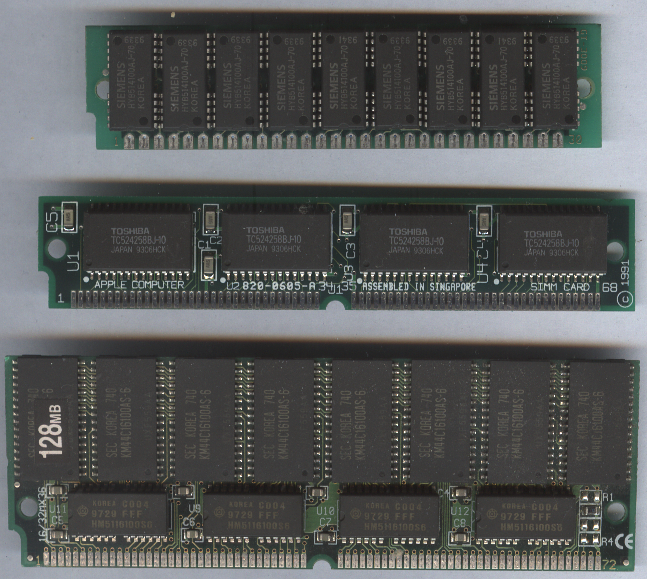 A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It is a printed circuit board upon which multiple
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It is a printed circuit board upon which multiple
Low-cost, high-density memory packaging: A 64K X 9 DRAM SIP module
''The International journal for hybrid microelectronics''. at

 Standard sizes: 256 KB, 1 MB, 4 MB, 16 MB.
30-pin SIMMs have 12 address lines, which can provide a total of 24 address bits. With an 8-bit data width, this leads to an absolute maximum capacity of 16 MB for both parity and non-parity modules (the additional redundancy-bit chip usually does not contribute to the usable capacity).
* Pins 26, 28 and 29 are not connected on non-parity SIMMs.
Standard sizes: 256 KB, 1 MB, 4 MB, 16 MB.
30-pin SIMMs have 12 address lines, which can provide a total of 24 address bits. With an 8-bit data width, this leads to an absolute maximum capacity of 16 MB for both parity and non-parity modules (the additional redundancy-bit chip usually does not contribute to the usable capacity).
* Pins 26, 28 and 29 are not connected on non-parity SIMMs.
† /RAS1 and /RAS3 are only used on two-rank SIMMS: 2, 8, 32, and 128 MB.
# These lines are only defined on 3.3 V modules.
x Presence-detect signals are detailed in JEDEC standard.
General SIMM Installation Guide
{{DRAM Computer memory form factor
 A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It is a printed circuit board upon which multiple
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It is a printed circuit board upon which multiple random-access memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of Computer memory, electronic computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working Data (computing), data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows ...
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
chips are attached to one or both sides. It differs from a dual in-line memory module
A DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) is a popular type of memory module used in computers. It is a printed circuit board with one or both sides (front and back) holding DRAM integrated circuit, chips and Pin (electronics), pins. The vast majority ...
(DIMM), the most predominant form of memory module since the late 1990s, in that the contacts on a SIMM are redundant on both sides of the module. SIMMs were standardised under the JEDEC JESD-21C standard.
Most early PC motherboard
A motherboard, also called a mainboard, a system board, a logic board, and informally a mobo (see #Nomenclature, "Nomenclature" section), is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It ho ...
s ( 8088-based PCs, XTs, and early ATs) used socketed DIP chips for DRAM
Dram, DRAM, or drams may refer to:
Technology and engineering
* Dram (unit), a unit of mass and volume, and an informal name for a small amount of liquor, especially whisky or whiskey
* Dynamic random-access memory, a type of electronic semicondu ...
. As computer memory capacities grew, memory modules were used to save motherboard space and ease memory expansion. Instead of plugging in eight or nine single DIP chips, only one additional memory module was needed to increase the memory of the computer.
History
SIMMs were invented in 1983 by James E. ClaytonClayton, James E. (1983)Low-cost, high-density memory packaging: A 64K X 9 DRAM SIP module
''The International journal for hybrid microelectronics''. at
Wang Laboratories
Wang Laboratories, Inc., was an American computer company founded in 1951 by An Wang and G. Y. Chu. The company was successively headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts (1954–1963), Tewksbury, Massachusetts (1963–1976), Lowell, Massachuse ...
with subsequent patents granted in 1987.
Wang Laboratories litigated both patents against multiple companies. The original memory modules were built upon ceramic substrates with 64K Hitachi "flip chip" parts and had pins, i.e. single in-line package (SIP) packaging
Packaging is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of designing, evaluating, and producing packages. Packaging can be described as a coo ...
. SIMMs using pins are usually called SIP or SIPP memory modules to distinguish them from the more common modules using edge connectors.
The first variant of SIMMs has 30 pins and provides 8 bits of data (plus a 9th error-detection bit in parity SIMMs). They were used in AT-compatible ( 286-based, e.g., Wang APC), 386
__NOTOC__
Year 386 (Roman numerals, CCCLXXXVI) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Honorius and Euodius (or, less frequently, year 1139 ''Ab urbe condita''). ...
-based, 486-based, Macintosh Plus, Macintosh II, Quadra, Atari STE microcomputers, Wang VS minicomputers and Roland
Roland (; ; or ''Rotholandus''; or ''Rolando''; died 15 August 778) was a Frankish military leader under Charlemagne who became one of the principal figures in the literary cycle known as the Matter of France. The historical Roland was mil ...
electronic samplers.
The second variant of SIMMs has 72 pins and provides 32 bits of data (36 bits in parity and ECC versions). These appeared first in the early 1990s in later models of the IBM PS/2
The Personal System/2 or PS/2 is IBM's second generation of personal computers. Released in 1987, it officially replaced the IBM Personal Computer, IBM PC, IBM Personal Computer XT, XT, IBM Personal Computer/AT, AT, and IBM PC Convertible, PC Co ...
, and later in systems based on the 486, Pentium
Pentium is a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel from 1993 to 2023. The Pentium (original), original Pentium was Intel's fifth generation processor, succeeding the i486; Pentium was Intel's flagship proce ...
, Pentium Pro
The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel and introduced on November 1, 1995. It implements the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture (sometimes termed i686), and was the first x86 Intel C ...
, early Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
, and contemporary/competing chips of other brands. By the mid-90s, 72-pin SIMMs had replaced 30-pin SIMMs in new-build computers, and were starting to themselves be replaced by DIMMs.
Non-IBM PC computers such as UNIX workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or computational science, scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating syste ...
s may use proprietary non-standard SIMMs. The Macintosh IIfx uses proprietary non-standard SIMMs with 64 pins.
DRAM technologies used in SIMMs include FPM (Fast Page Mode memory, used in all 30-pin and early 72-pin modules), and the higher-performance EDO DRAM (used in later 72-pin modules).
Due to the differing data bus widths of the memory modules and some processors, sometimes several modules must be installed in identical pairs or in identical groups of four to fill a memory bank. The rule of thumb is a ''286'', ''386SX'', 68000 or low-end 68020 / 68030 (e.g. Atari Falcon, Mac LC) system (using a 16 bit wide data bus) would require two 30-pin SIMMs for a memory bank. On ''386DX'', ''486'', and full-spec 68020 through 68060 (e.g. Atari TT, Amiga 4000, Mac II) systems (32 bit data bus), either four 30-pin SIMMs or one 72-pin SIMM are required for one memory bank. On Pentium
Pentium is a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel from 1993 to 2023. The Pentium (original), original Pentium was Intel's fifth generation processor, succeeding the i486; Pentium was Intel's flagship proce ...
systems (data bus width of 64 bits), two 72-pin SIMMs are required. However, some Pentium systems have support for a "half bank mode", in which the data bus would be shortened to only 32 bits to allow operation of a single SIMM. Conversely, some 386 and 486 systems use what is known as "memory interleaving", which requires twice as many SIMMs and effectively doubles the bandwidth.
The earliest SIMM sockets were conventional push-type sockets. These were soon replaced by ZIF sockets in which the SIMM was inserted at an angle, then tilted into an upright position. To remove one, the two metal or plastic clips at each end must be pulled to the side, then the SIMM must be tilted back and pulled out (low-profile sockets reversed this convention somewhat, like SODIMMs - the modules are inserted at a "high" angle, then pushed ''down'' to become more flush with the motherboard). The earlier sockets used plastic retainer clips which were found to break, so steel clips replaced them.
Some SIMMs support presence detect (PD). Connections are made to some of the pins that encode the capacity and speed of the SIMM, so that compatible equipment can detect the properties of the SIMM. PD SIMMs can be used in equipment which does not support PD; the information is ignored. Standard SIMMs can easily be converted to support PD by fitting jumpers, if the SIMMs have solder pads to do so, or by soldering wires on.
30-pin SIMMs

 Standard sizes: 256 KB, 1 MB, 4 MB, 16 MB.
30-pin SIMMs have 12 address lines, which can provide a total of 24 address bits. With an 8-bit data width, this leads to an absolute maximum capacity of 16 MB for both parity and non-parity modules (the additional redundancy-bit chip usually does not contribute to the usable capacity).
* Pins 26, 28 and 29 are not connected on non-parity SIMMs.
Standard sizes: 256 KB, 1 MB, 4 MB, 16 MB.
30-pin SIMMs have 12 address lines, which can provide a total of 24 address bits. With an 8-bit data width, this leads to an absolute maximum capacity of 16 MB for both parity and non-parity modules (the additional redundancy-bit chip usually does not contribute to the usable capacity).
* Pins 26, 28 and 29 are not connected on non-parity SIMMs.
72-pin SIMMs
Standard sizes: 1 MB, 2 MB, 4 MB, 8 MB, 16 MB, 32 MB, 64 MB, 128 MB (the standard also defines 3.3 V modules with additional address lines and up to 2 GB) With 12 address lines, which can provide a total of 24 address bits, two ranks of chips, and 32-bit data output, the absolute maximum capacity is 227 = 128 MB. * Pins 35, 36, 37 and 38 are not connected on non-parity SIMMs.† /RAS1 and /RAS3 are only used on two-rank SIMMS: 2, 8, 32, and 128 MB.
# These lines are only defined on 3.3 V modules.
x Presence-detect signals are detailed in JEDEC standard.
Proprietary SIMMs
GVP 64-pin
Several CPU cards from Great Valley Products for the CommodoreAmiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers produced by Commodore International, Commodore from 1985 until the company's bankruptcy in 1994, with production by others afterward. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16-b ...
used special 64-pin SIMMs (32 bits wide, 1, 4 or 16 MB, 60 ns).
Apple 64-pin
Dual-ported 64-pin SIMMs were used inApple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
Macintosh IIfx computers to allow overlapping read/write cycles (1, 4, 8, 16 MB, 80 ns).
HP LaserJet
72-pin SIMMs with non-standard presence detect (PD) connections.See also
* Dual in-line package (DIP) * Single in-line package (SIP) * Zig-zag in-line package (ZIP) *Dual in-line memory module
A DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) is a popular type of memory module used in computers. It is a printed circuit board with one or both sides (front and back) holding DRAM integrated circuit, chips and Pin (electronics), pins. The vast majority ...
(DIMM)
References
External links
General SIMM Installation Guide
{{DRAM Computer memory form factor