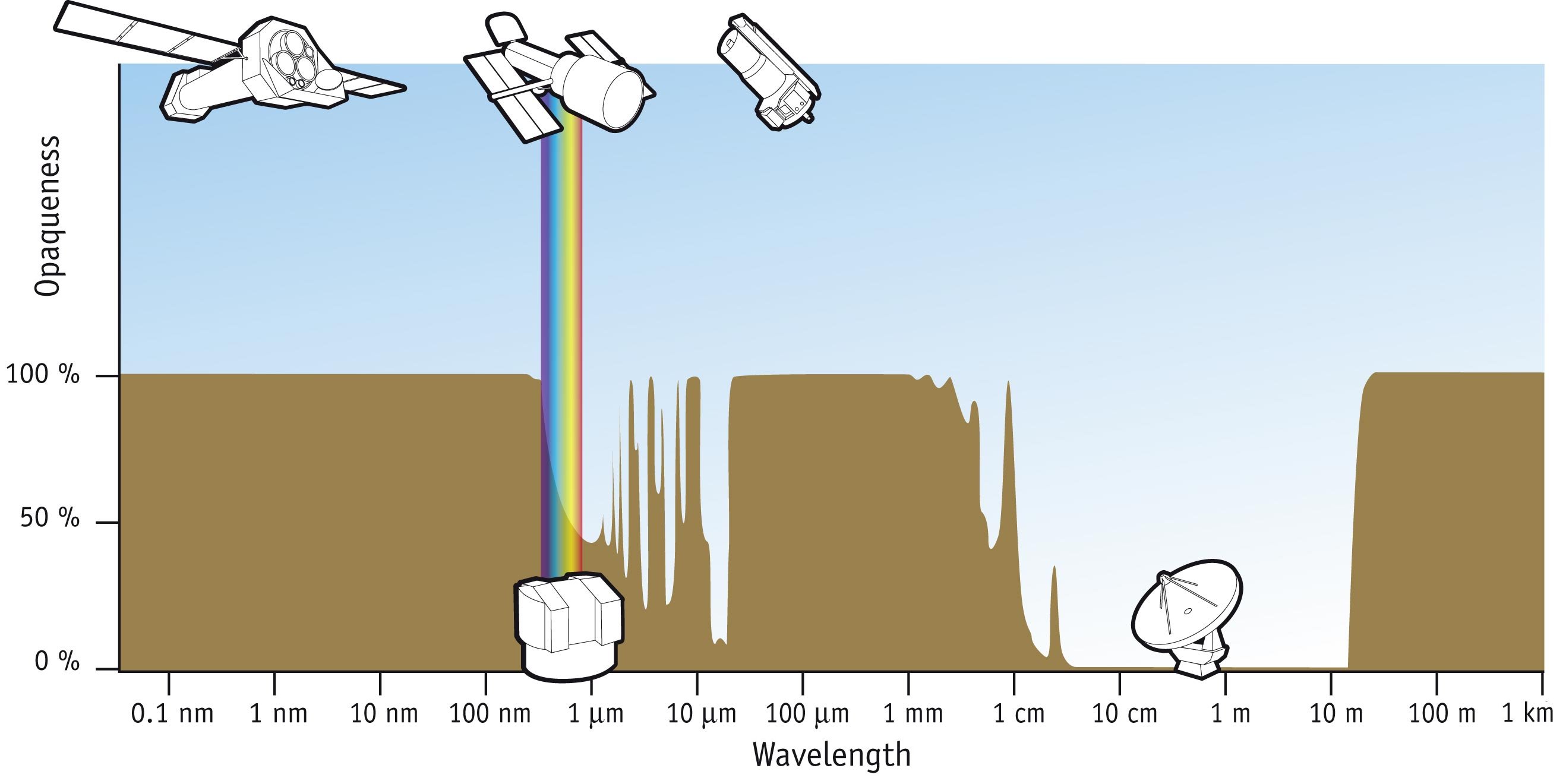
|
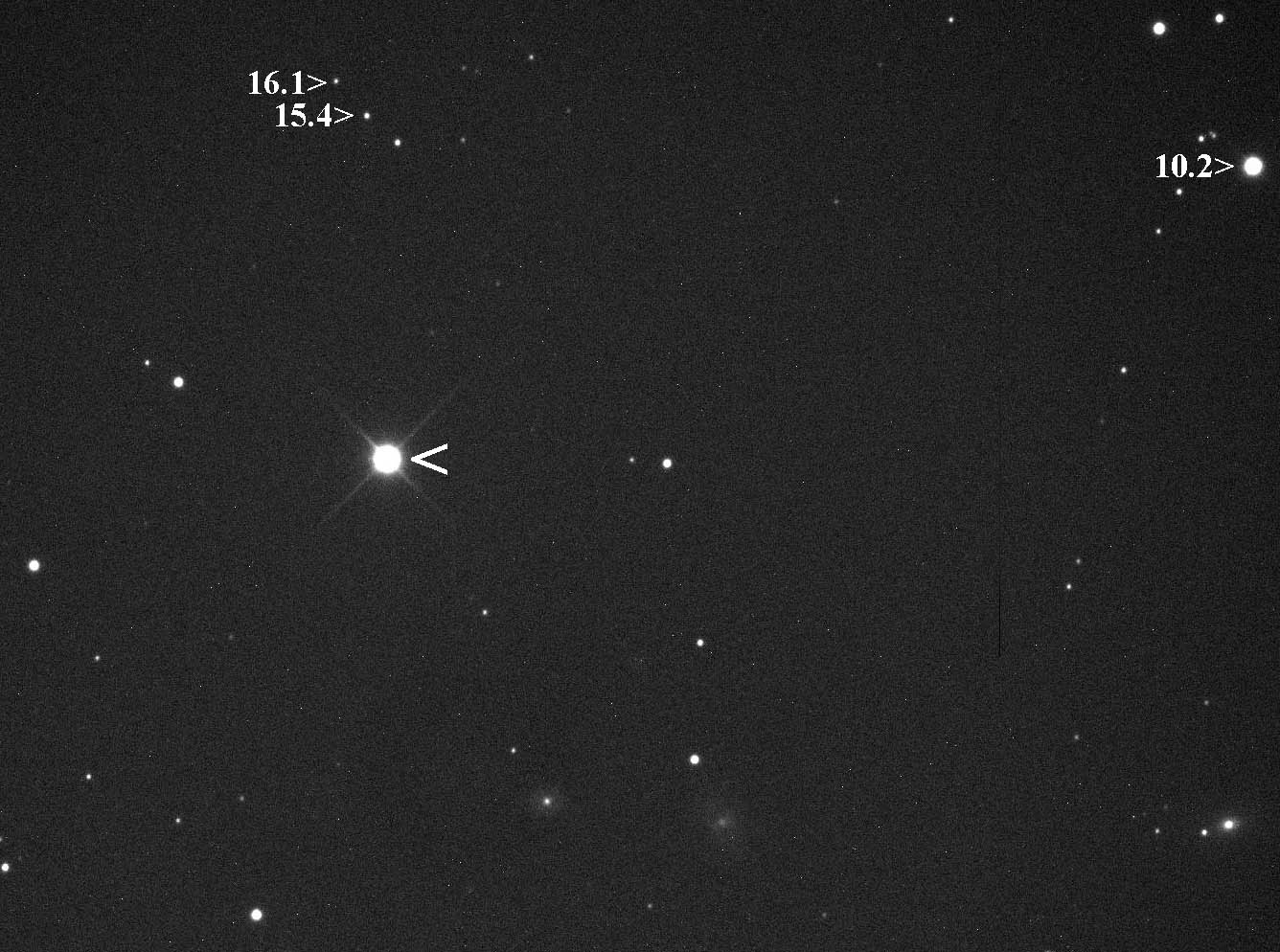
SGR J1550−5418
SGR J1550−5418 is a soft gamma repeater (SGR), the sixth to be discovered, located in the constellation Norma. Long known as an X-ray source, it was noticed to have become active on 23 October 2008, and then after a relatively quiescent interval, became much more active on 22 January 2009. It has been observed by the Swift satellite, and by the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, launched in 2008, as well as in X-ray and radio emission. It has been observed to emit intense bursts of gamma rays at a rate of up to several per minute. At its estimated distance of 30,000 light years (~10 kpc), the most intense flares equal the total energy emission of the Sun in ~20 years. The underlying object is believed to be a rotating neutron star, of the type known as ''magnetars'', which have magnetic fields up to 1015 gauss, about 1000 times that of more typical neutron star X-ray sources. See orders of magnitude (magnetic field) for examples of other magnetic field strengths. The rotation per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Gamma Repeater
A soft gamma repeater (SGR) is an astronomical object which emits large bursts of gamma-rays and X-rays at irregular intervals. It is conjectured that they are a type of magnetar or, alternatively, neutron stars with fossil disks around them. History On March 5, 1979 a powerful gamma-ray burst was noted. As a number of receivers at different locations in the Solar System saw the burst at slightly different times, its direction could be determined, and it was shown to originate from near a supernova remnant in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Over time it became clear that this was not a normal gamma-ray burst. The photons were less energetic in the soft gamma-ray and hard X-ray range, and repeated bursts came from the same region. Astronomer Chryssa Kouveliotou of the Universities Space Research Association (USRA) at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center decided to test the theory that soft gamma repeaters were magnetars. According to the theory, the bursts would cause the object t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norma (constellation)
Norma is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere between Ara and Lupus, one of twelve drawn up in the 18th century by French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille and one of several depicting scientific instruments. Its name is Latin for normal, referring to a right angle, and is variously considered to represent a rule, a carpenter's square, a set square or a level. It remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Four of Norma's brighter stars—Gamma, Delta, Epsilon and Eta—make up a square in the field of faint stars. Gamma2 Normae is the brightest star with an apparent magnitude of 4.0. Mu Normae is one of the most luminous stars known, with a luminosity between a quarter million and one million times that of the Sun. Four star systems are known to harbour planets. The Milky Way passes through Norma, and the constellation contains eight open clusters visible to observers with binoculars. The constellation also hosts Abell 3627, also called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical X-ray Source
Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays. Several types of astrophysical objects emit X-rays. They include galaxy clusters, black holes in active galactic nuclei (AGN), galactic objects such as supernova remnants, stars, and binary stars containing a white dwarf (cataclysmic variable stars and super soft X-ray sources), neutron star or black hole (X-ray binaries). Some Solar System bodies emit X-rays, the most notable being the Moon, although most of the X-ray brightness of the Moon arises from reflected solar X-rays. Furthermore, celestial entities in space are discussed as celestial X-ray sources. The origin of all observed astronomical X-ray sources is in, near to, or associated with a coronal cloud or gas at coronal cloud temperatures for however long or brief a period. A combination of many unresolved X-ray sources is thought to produce the observed X-ray background. The X-ray continuum can arise f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission
Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, previously called the Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Explorer, is a NASA three-telescope space observatory for studying gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) and monitoring the afterglow in X-ray, and UV/Visible light at the location of a burst. It was launched on 20 November 2004, aboard a Delta II launch vehicle. Headed by principal investigator Neil Gehrels until his death in February 2017, the mission was developed in a joint partnership between Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) and an international consortium from the United States, United Kingdom, and Italy. The mission is operated by Pennsylvania State University as part of NASA's Medium Explorer program (MIDEX). The burst detection rate is 100 per year, with a sensitivity ~3 times fainter than the BATSE detector aboard the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory. The Swift mission was launched with a nominal on-orbit lifetime of two years. Swift is a NASA MIDEX (medium-class Explorer) mission. It was the third to be la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope (FGST, also FGRST), formerly called the Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope (GLAST), is a space observatory being used to perform gamma-ray astronomy observations from low Earth orbit. Its main instrument is the Large Area Telescope (LAT), with which astronomers mostly intend to perform an all-sky survey studying astrophysical and cosmological phenomena such as active galactic nuclei, pulsars, other high-energy sources and dark matter. Another instrument aboard Fermi, the Gamma-ray Burst Monitor (GBM; formerly GLAST Burst Monitor), is being used to study gamma-ray bursts and solar flares. Fermi, named for high-energy physics pioneer Enrico Fermi, was launched on 11 June 2008 at 16:05 UTC aboard a Delta II 7920-H rocket. The mission is a joint venture of NASA, the United States Department of Energy, and government agencies in France, Germany, Italy, Japan, and Sweden, becoming the most sensitive gamma-ray telescope on orbit, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequency, frequencies above 30 exahertz (), it imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Ulrich Villard, Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation ''gamma rays'' based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900 he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha particle, alpha rays and beta particle, beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power. Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy range from a few kiloelectronvolts (keV) to approximately 8 megaelectronvolts (MeV), corres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. white holes, quark stars, and strange stars), neutron stars are the smallest and densest currently known class of stellar objects. Neutron stars have a radius on the order of and a mass of about 1.4 solar masses. They result from the supernova explosion of a massive star, combined with gravitational collapse, that compresses the core past white dwarf star density to that of atomic nuclei. Once formed, they no longer actively generate heat, and cool over time; however, they may still evolve further through collision or accretion. Most of the basic models for these objects imply that neutron stars are composed almost entirely of neutrons (subatomic particles with no net electrical charge and with slightly larger mass than protons); ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetar
A magnetar is a type of neutron star with an extremely powerful magnetic field (∼109 to 1011 T, ∼1013 to 1015 G). The magnetic-field decay powers the emission of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, particularly X-rays and gamma rays.Ward; Brownlee, p.286 The existence of magnetars was proposed in 1992 by Robert Duncan and . Their proposal sought to explain the properties of transient sources of gamma rays, now known as soft gamma repeaters (SGRs). Over the following decade, the magnetar hypothesis became widely accepted, and was extended to explain anomalous X-ray pulsars (AXPs). , 24 confirmed magnetars were known. It has been suggested that magnetars are the source of fast radio bursts (FRB), in particular as a result of findings in 2020 by scientists using the Australian Square Kilometre Array. Description Like other neutron stars, magnetars are around in diameter, and have a mass about 1.4 solar masses. They are formed by the collapse of a star with a mass 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orders Of Magnitude (magnetic Field)
This page lists examples of magnetic induction B in teslas and gauss produced by various sources, grouped by orders of magnitude. Note: * Traditionally, magnetizing field H, is measured in amperes per meter. * Magnetic induction B (also known as magnetic flux density) has the SI unit tesla or Wb/m2 * One tesla is equal to 104 gauss. * Magnetic field drops off as the cube of the distance from a dipole source. Examples These examples attempt to make the measuring point clear, usually the surface of the item mentioned. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Orders Of Magnitude (Magnetic Field) Magnetic Field A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and t ... Magnetism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Echo
309x309px, Reflected light following path B arrives shortly after the direct flash following path A but before light following path C. B and C have the same Earth.html" ;"title="apparent distance from the star as seen from Earth">apparent distance from the star as seen from Earth. A light echo is a physical phenomenon caused by light reflection (physics), reflected off surfaces distant from the source, and arriving at the observer with a delay relative to this distance. The phenomenon is analogous to an echo (phenomenon), echo of sound, but due to the much faster speed of light, it mostly only manifests itself over astronomical distances. For example, a light echo is produced when a sudden flash from a nova is reflected off a cosmic dust cloud, and arrives at the viewer after a longer duration than it otherwise would have taken with a direct path. Because of their geometries, light echoes can produce the illusion of superluminal motion. Explanation Light echoes are produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramatic appearance of a nova vary, depending on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars. All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems. The main sub-classes of novae are classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. They are all considered to be cataclysmic variable stars. Classical nova eruptions are the most common type. They are likely created in a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and either a main sequence, subgiant, or red giant star. When the orbital period falls in the range of several days to one day, the white dwarf is close enough to its companion star to start drawing accreted matter onto the surface of the white dwarf, which creates a dense but shallow atmosphere. This atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalous X-ray Pulsar
Anomalous X-ray pulsars (AXPs) are an observational manifestation of magnetars—young, isolated, highly magnetized neutron stars. These energetic X-ray pulsars are characterized by slow rotation periods of ~2–12 seconds and large magnetic fields of ~1013–1015 gauss (1 to 100 gigatesla The tesla (symbol: T) is the unit of magnetic flux density (also called magnetic B-field strength) in the International System of Units (SI). One tesla is equal to one weber per square metre. The unit was announced during the General Conference ...s). , there were 12 confirmed and 2 candidate AXPs known. (An online catalog of SGR/AXP properties maintained by the pulsar group at McGill University) The identification of AXPs with magnetars was motivated by their similarity to [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |