|
SERVQUAL
SERVQUAL is a multi-dimensional research instrument designed to capture consumer expectations and perceptions of a service along five dimensions (originally ten), which are said to represent service quality. SERVQUAL is built on the expectancy–disconfirmation paradigm, which, in simple terms, means that service quality is understood as the extent to which consumers' pre-consumption expectations of quality are confirmed or disconfirmed by their actual perceptions of the service experience. The SERVQUAL questionnaire was first published in 1985 by a team of academic researchers in the United States, A. Parasuraman, Valarie Zeithaml and Leonard L. Berry, to measure quality in the service sector. In its introduction, the survey represented a breakthrough in the measurement methods used for service quality research. The diagnostic value of the instrument is supported by the ''model of service quality'' which forms the conceptual framework for the development of the scale (i.e. i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Services Marketing
Services marketing is a specialized branch of marketing which emerged as a separate field of study in the early 1980s, following the recognition that the unique characteristics of Service (economics), services required different strategies compared with the marketing of physical goods. Services marketing typically refers to both business to consumer (B2C) and business-to-business (B2B) services, and includes the marketing of services such as telecommunications services, transportation and distribution services, all types of hospitality, tourism leisure and entertainment services, car rental services, health care services, professional services and trade services. Service marketers often use an expanded marketing mix which consists of the seven Ps: product, price, place, Promotion (marketing), promotion, people, physical evidence and process. A contemporary approach, known as ''service-dominant logic'', argues that the demarcation between products and services that persisted throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valarie Zeithaml
Valarie A. Zeithaml is a marketing professor and author. She is the David S. Van Pelt Family Distinguished Professor of Marketing at Kenan-Flagler Business School, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Zeithaml is an expert in the area of services marketing and service quality. Early life and education Zeithaml earned her Bachelor of Arts degree from Gettysburg College before pursuing further education at the University of Maryland, where she obtained both her Master of Business Administration (MBA) and Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degrees. Career In the 1980s, Zeithaml and her co-authors developed SERVQUAL, a multidimensional scale of perceived service quality. She was named a Thomson Reuters Highly Cited Researcher in the report on “The World’s Most Influential Scientific Minds.” Zeithaml held positions at the University of North Carolina’s Kenan-Flagler Business School, including Associate Dean of the MBA Program, Senior Associate Dean for Academic Affairs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
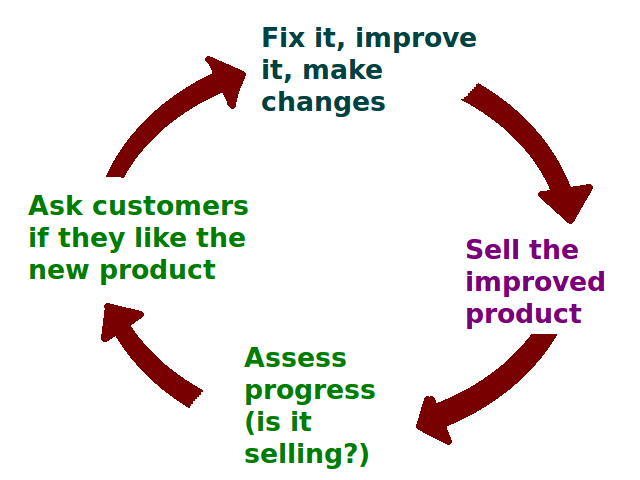
Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is a term frequently used in marketing to evaluate customer experience. It is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation. Customer satisfaction is defined as "the number of customers, or percentage of total customers, whose reported experience with a firm, its products, or its services (ratings) exceeds specified Contentment, satisfaction goals".. Enhancing customer satisfaction and fostering customer loyalty are pivotal for businesses, given the significant importance of improving the balance between customer Attitude (psychology), attitudes before and after the consumption process. Expectation confirmation theory, Expectancy disconfirmation theory is the most widely accepted theoretical framework for explaining customer satisfaction. However, other frameworks, such as equity theory, attribution theory, Contrast theory of meaning, contrast theory, assimilation theory, and various others, are also used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customer Satisfaction Research
Customer satisfaction research is that area of marketing research, customer intelligence, and customer analytics which focuses on customers' perceptions with their shopping or purchase experience. Companies are interested in understanding what their customers think about their shopping or purchase experience, because finding new customers is generally more costly and difficult than servicing existing or repeat customers. Types of research Descriptive or documentary research Many customer satisfaction studies are intentionally or unintentionally only descriptive in nature because they give a snapshot in time of customer attitudes. If the study instrument is administered to groups of customers periodically, then a descriptive picture of customer satisfaction through time can be developed ("tracking" or cohort study).http://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol74No3/2Vol74No3.pdf Inferential or models-based research Beyond documentary types of work are studies that attempt to provide an unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disconfirmed Expectancy
Disconfirmed expectancy is a psychological term for what is commonly known as a failed prophecy. According to the American social psychologist Leon Festinger's theory of cognitive dissonance, disconfirmed expectancies create a state of psychological discomfort because the outcome contradicts expectancy. Upon recognizing the falsification of an expected event an individual will experience the competing cognitions, "I believe " and, "I observed " The individual must either discard the now disconfirmed belief or justify why it has not actually been disconfirmed. As such, disconfirmed expectancy and the factors surrounding the individual's consequent actions have been studied in various settings. Initial study Disconfirmed expectancy was famously illustrated in the 1956 book ''When Prophecy Fails'' by Leon Festinger, Henry W. Riecken, and Stanley Schachter. The book gave an inside account of a doomsday cult led by Dorothy Martin (given the alias "Marion Keech" to preserve her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Berry (professor)
Leonard L. "Len" Berry (born 1942) is a University Distinguished Professor of Marketing of Mays Business School at Texas A&M University, and a senior fellow at the Patient_safety_organization#Institute_for_Healthcare_Improvement, Institute for Healthcare Improvement. Berry is a past president of the American Marketing Association. He has studied service delivery in healthcare at the Mayo Clinic and in cancer care settings. Berry is Texas A&M's most cited faculty member on Google Scholar, with over 235,000 citations. Biography Berry earned bachelor's and master's degrees at the University of Denver and a Ph.D. at Arizona State University. A longtime professor at Texas A&M University, Berry founded the school's Center for Retailing Studies in 1982 and directed it for 18 years. In 1983, Berry coined the term relationship marketing, which emphasizes the need for organizations to maintain (rather than simply acquire) customers. He is a founder of the services marketing discipline. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. For example, it is possible that variations in six observed variables mainly reflect the variations in two unobserved (underlying) variables. Factor analysis searches for such joint variations in response to unobserved latent variables. The observed variables are modelled as linear combinations of the potential factors plus "error" terms, hence factor analysis can be thought of as a special case of errors-in-variables models. Simply put, the factor loading of a variable quantifies the extent to which the variable is related to a given factor. A common rationale behind factor analytic methods is that the information gained about the interdependencies between observed variables can be used later to reduce the set of variables in a dataset. Factor analysis is commonly used in psychometrics, pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principal Components Analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a Linear map, linear dimensionality reduction technique with applications in exploratory data analysis, visualization and Data Preprocessing, data preprocessing. The data is linear map, linearly transformed onto a new coordinate system such that the directions (principal components) capturing the largest variation in the data can be easily identified. The principal components of a collection of points in a real coordinate space are a sequence of p unit vectors, where the i-th vector is the direction of a line that best fits the data while being orthogonal to the first i-1 vectors. Here, a best-fitting line is defined as one that minimizes the average squared perpendicular distance, perpendicular Distance from a point to a line, distance from the points to the line. These directions (i.e., principal components) constitute an orthonormal basis in which different individual dimensions of the data are Linear correlation, linearly uncorrelated. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competence (human Resources)
Competence is the set of demonstrable personal characteristics or KSAOs (Knowledge, Skills, Abilities, and Other characteristics) that enable job performance at a high level with consistency and minimal difficulty. Competency in human resources is a series of knowledge, abilities, skills, experiences and behaviors, which leads to effective performance in an individual's activities. Competency is measurable and can be developed through training. It can also be broken down into smaller criteria. Some scholars see "competence" as an aspect that can be developed through training because it is a combination of practical & theoretical knowledge which involves cognitive skills, behavior, and values used to improve performance. Competency is the state or quality of being adequately or well qualified, possessing the ability to perform a specific, measurable job. For instance, competency needed for management, depending on the sector, might include system thinking and emotional intellig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Buttle
Francis Buttle is a retired Professor of Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Management, Relationship Marketing, and Marketing, and a customer management consultant based. He is author of more than 160 peer-reviewed scientific papers and 16 books which have been cited over 20,000 times earning him an h-index of 51. Buttle was born in the UK in 1948, and educated at Lancaster Royal Grammar School. He later earned degrees from the University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology (B.Sc. Hons), University of Lancaster (M.A.) and the University of Massachusetts (Ph.D.). He worked in a number of private sector roles before becoming a university academic. He taught and researched at the University of West of England (at that time named Bristol Polytechnic), Massey University (New Zealand), University of Surrey (UK), University of Massachusetts (USA), Manchester Business School (UK) and Macquarie Graduate School of Management (Australia). His research interests ranged acro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disconfirmed Expectancy
Disconfirmed expectancy is a psychological term for what is commonly known as a failed prophecy. According to the American social psychologist Leon Festinger's theory of cognitive dissonance, disconfirmed expectancies create a state of psychological discomfort because the outcome contradicts expectancy. Upon recognizing the falsification of an expected event an individual will experience the competing cognitions, "I believe " and, "I observed " The individual must either discard the now disconfirmed belief or justify why it has not actually been disconfirmed. As such, disconfirmed expectancy and the factors surrounding the individual's consequent actions have been studied in various settings. Initial study Disconfirmed expectancy was famously illustrated in the 1956 book ''When Prophecy Fails'' by Leon Festinger, Henry W. Riecken, and Stanley Schachter. The book gave an inside account of a doomsday cult led by Dorothy Martin (given the alias "Marion Keech" to preserve her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |