|
Ruuben Kaalep
Ruuben Kaalep (born on 21 September 1993 in Tallinn) is an Estonian politician, poet and a far-right (self-styled ethnofuturist) philosopher. He has been member of XIV Riigikogu. He is a founder of the Conservative People's Party of Estonia's youth organization Sinine Äratus ('Blue Awakening'). Since 2012, he is a member of Estonian Conservative People's Party. Philosophy In 2020, Arktos Media published the book "Rebirth of Europe: The Ethnofuturist Manifesto" by Kaalep and August Meister, in which the authors outline their ethnofuturist philosophy. They envision in ethnofuturism a "nationalism of a completely new type", which would be open to global nationalist cooperation and help to find "a balance between the old traditions and the dynamic energy that propels us into the future". Essential to their philosophy is something Kaalep and Meister call "the Organic Principle," which involves a nondualist realization of existence, uniting seemingly opposite concepts of good and evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju '' maakond'' (county). Tallinn is the main financial, industrial, and cultural centre of Estonia. It is located northwest of the country's second largest city Tartu, however only south of Helsinki, Finland, also west of Saint Petersburg, Russia, north of Riga, Latvia, and east of Stockholm, Sweden. From the 13th century until the first half of the 20th century, Tallinn was known in most of the world by variants of its other historical name Reval. Tallinn received Lübeck city rights in 1248,, however the earliest evidence of human population in the area dates back nearly 5,000 years. The medieval indigenous population of what is now Tallinn and northern Estonia was one of the last " pagan" civilisations in Europe to adopt Christia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Good And Evil
In religion, ethics, philosophy, and psychology "good and evil" is a very common dichotomy. In cultures with Manichaean and Abrahamic religious influence, evil is perceived as the dualistic antagonistic opposite of good, in which good should prevail and evil should be defeated. In cultures with Buddhist spiritual influence, both good and evil are perceived as part of an antagonistic duality that itself must be overcome through achieving ''Śūnyatā'' meaning emptiness in the sense of recognition of good and evil being two opposing principles but not a reality, emptying the duality of them, and achieving a oneness. Evil is often used to denote profound immorality. Evil has also been described as a supernatural force. Definitions of evil vary, as does the analysis of its motives. However, elements that are commonly associated with evil involve unbalanced behavior involving expediency, selfishness, ignorance, or neglect. The modern philosophical questions regarding good and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Depressive Disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introduced by a group of US clinicians in the mid-1970s, the term was adopted by the American Psychiatric Association for this symptom cluster under mood disorders in the 1980 version of the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM-III), and has become widely used since. The diagnosis of major depressive disorder is based on the person's reported experiences, behavior reported by relatives or friends, and a mental status examination. There is no laboratory test for the disorder, but testing may be done to rule out physical conditions that can cause similar symptoms. The most common time of onset is in a person's 20s, with females affected about twice as often as males. The course of the disorder varies widely, from one e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Left
The New Left was a broad political movement mainly in the 1960s and 1970s consisting of activists in the Western world who campaigned for a broad range of social issues such as civil and political rights, environmentalism, feminism, gay rights, gender roles and drug policy reforms. Some see the New Left as an oppositional reaction to earlier Marxist and labor union movements for social justice that focused on dialectical materialism and social class, while others who used the term see the movement as a continuation and revitalization of traditional leftist goals. Some who self-identified as "New Left" rejected involvement with the labor movement and Marxism's historical theory of class struggle, although others gravitated to their own takes on established forms of Marxism and Marxism–Leninism, such as the New Communist movement (which drew from Maoism) in the United States or the K-GruppenThe K groups originally referred to the mainly Maoist-oriented small parties an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberalism
Liberalism is a political and moral philosophy based on the rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostility to autocracy, cultural distaste for conservatism and for tradition in general, tolerance, and ... individualism". John Dunn. ''Western Political Theory in the Face of the Future'' (1993). Cambridge University Press. . Liberals espouse various views depending on their understanding of these principles. However, they generally support private property, market economies, individual rights (including civil rights and human rights), liberal democracy, secularism, rule of law, economic and political freedom, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of assembly, and freedom of religion. Liberalism is frequently cited as the dominant ideology of modern times.Wolfe, p. 23.Adams, p. 11. Liberalism became a distinct movement in the Age of Enlightenment, gaining popularity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globalism
Globalism refers to various patterns of meaning beyond the merely international. It is used by political scientists, such as Joseph Nye, to describe "attempts to understand all the interconnections of the modern world—and to highlight patterns that underlie (and explain) them." While primarily associated with world-systems, it can be used to describe other global trends. The concept of globalism is also classically used to distinguish the ideologies of globalization (the subjective meanings) from the processes of globalization (the objective practices). In this sense, globalism is to globalization what nationalism is to nationality. The term is now frequently used as a pejorative by far-right movements and conspiracy theorists. False usage in this way has also been associated with antisemitism, as antisemites frequently appropriate ''globalist'' to refer to Jews. Definition Paul James defines ''globalism'' "at least in its more specific use ... as the dominant ideology an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentti Linkola
Kaarlo Pentti Linkola (7 December 1932 – 5 April 2020) was a prominent Finnish deep ecologist, ornithologist, polemicist, naturalist, writer, and fisherman. He wrote widely about his ideas and in Finland was a prominent thinker.George C. Schoolfield, "A history of Finland's literature", U of Nebraska Press, 1998p. 271 Linkola was a year-round fisherman from 1959 to 1995. He fished on Keitele, Päijänne and the Gulf of Finland, and since 1978 he fished on Vanajavesi. Linkola blamed humans for the continuous degradation of the environment. He promoted rapid population decline to combat the problems commonly attributed to overpopulation. Life Linkola was born on 7 December 1932. He grew up in Helsinki and summered in Kariniemi in Tyrväntö at the farm of his maternal grandfather, Hugo Suolahti. His father, Kaarlo Linkola, was a botanist, phytogeographer, and the Rector of University of Helsinki, and his grandfather Hugo had worked as the chancellor of that same univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
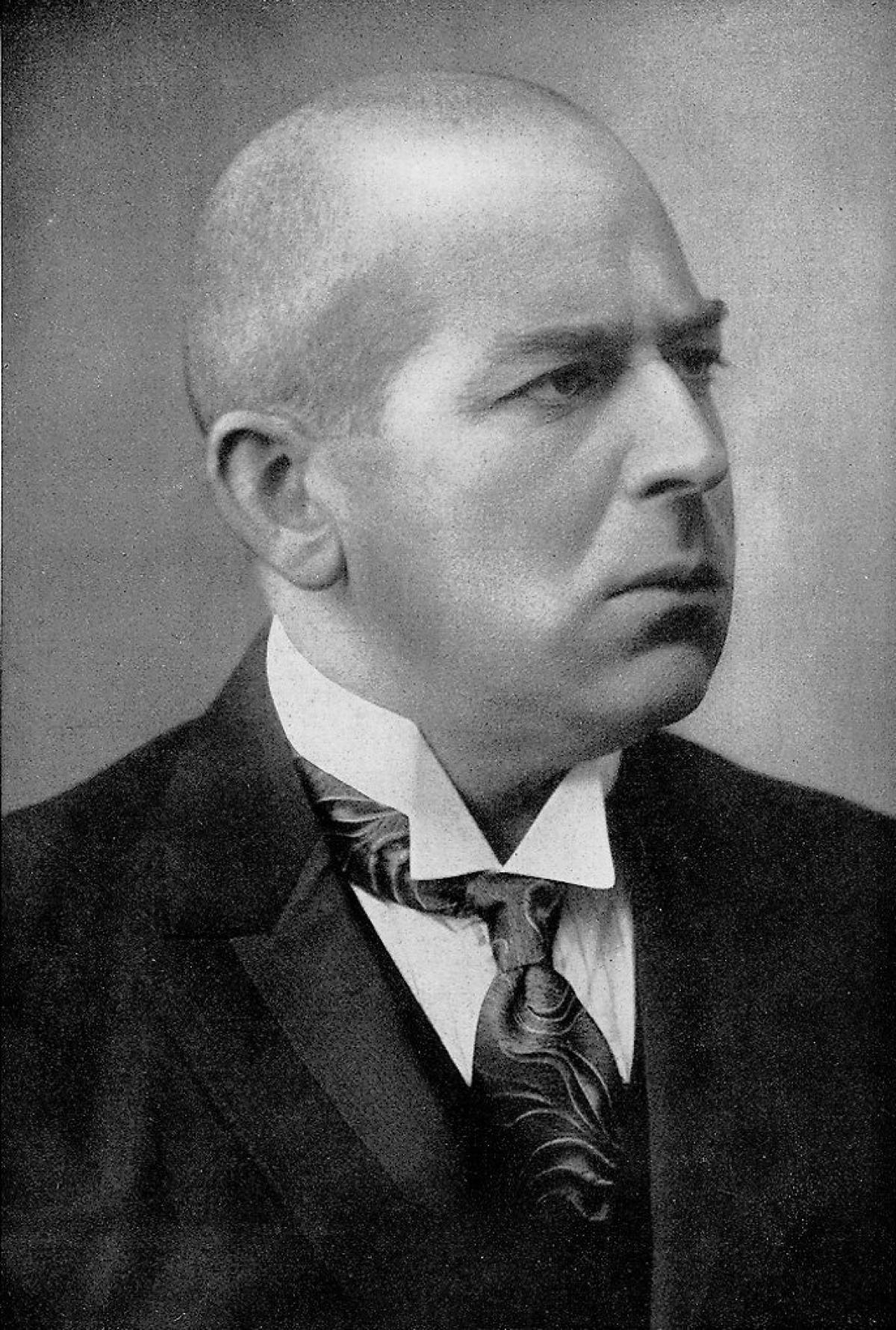
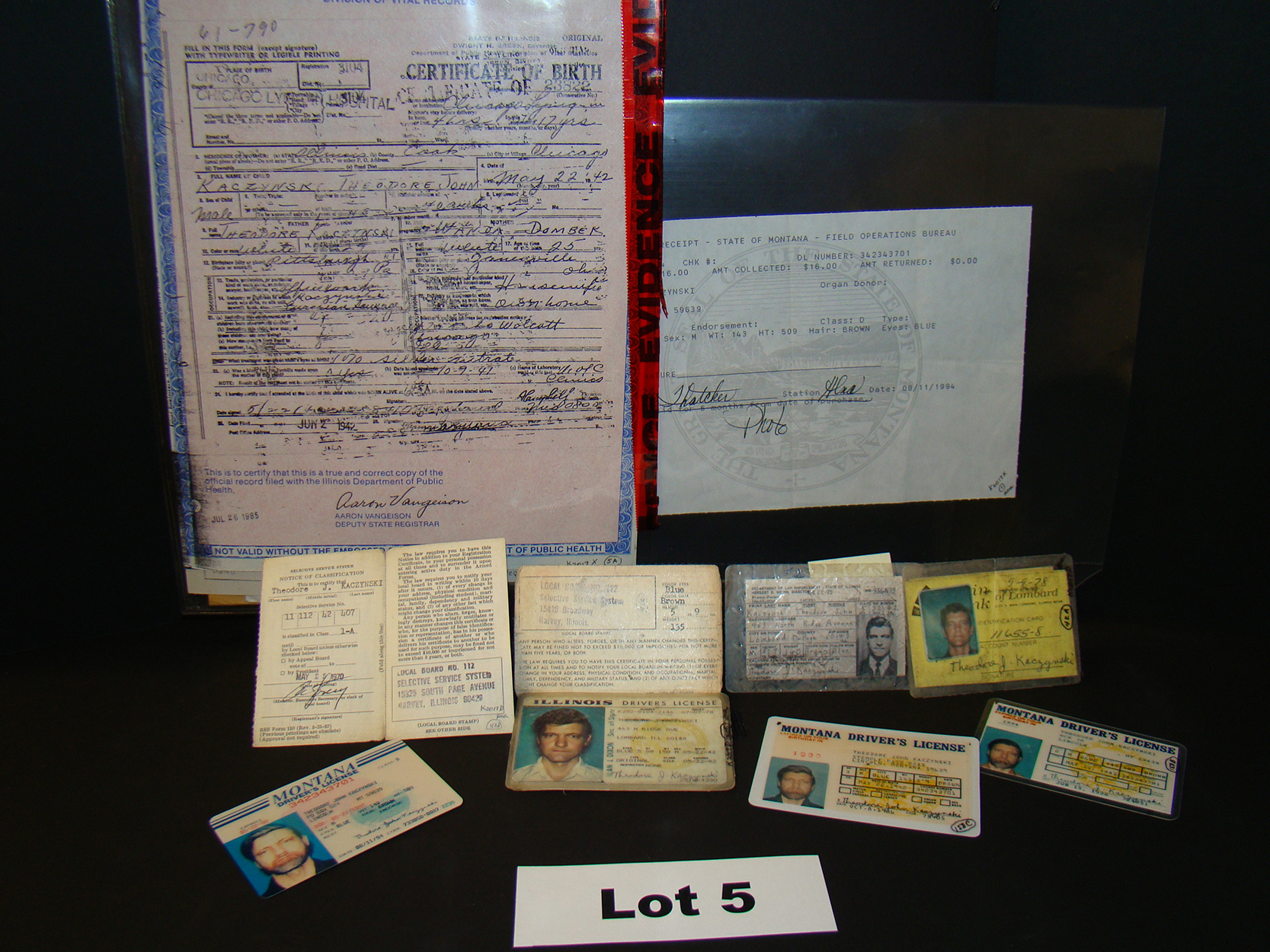
Ted Kaczynski
Theodore John Kaczynski ( ; born May 22, 1942), also known as the Unabomber (), is an American domestic terrorist and former mathematics professor. Between 1978 and 1995, Kaczynski killed three people and injured 23 others in a nationwide mail bombing campaign against people he believed to be advancing modern technology and the destruction of the environment. He authored '' Industrial Society and Its Future'', a 35,000-word manifesto and social critique opposing industrialization, rejecting leftism, and advocating for a nature-centered form of anarchism. A mathematics prodigy, Kaczynski attended Harvard University and the University of Michigan. In 1971, he abandoned his academic career to pursue a primitive life, moving to a remote cabin without electricity or running water near Lincoln, Montana, where he lived as a recluse while learning survival skills to become self-sufficient. After witnessing the destruction of the wilderness surrounding his cabin, he concluded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oswald Spengler
Oswald Arnold Gottfried Spengler (; 29 May 1880 – 8 May 1936) was a German historian and philosopher of history whose interests included mathematics, science, and art, as well as their relation to his organic theory of history. He is best known for his two-volume work, '' The Decline of the West'' (''Der Untergang des Abendlandes''), published in 1918 and 1922, covering human history. Spengler's model of history postulates that human cultures and civilizations are akin to biological entities, each with a limited, predictable, and deterministic lifespan. Spengler predicted that about the year 2000, Western civilization would enter the period of pre‑death emergency whose countering would lead to 200 years of Caesarism (extra-constitutional omnipotence of the executive branch of government) before Western civilization's final collapse. Spengler is regarded as a nationalist and an anti-democrat, and he was a prominent member of the Weimar-era Conservative Revolution. Alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unus Mundus
''Unus mundus'' (Latin for "One world") is an underlying concept of Western philosophy, theology, and alchemy, of a primordial unified reality from which everything derives. The term can be traced back to medieval Scholasticism though the notion itself dates back at least as far as Plato's allegory of the cave. The idea was popularized in the 20th century by the Swiss psychoanalyst Carl Gustav Jung, though the term can be traced back to scholastics such as Duns ScotusC. G. Jung ed, ''Man and his Symbols'' (1978) p. 402 and was taken up again in the 16th century by Gerhard Dorn, a student of the famous alchemist Paracelsus. Jung and Pauli Jung, in conjunction with the physicist Wolfgang Pauli, explored the possibility that his concepts of archetypes and synchronicity might be related to the ''unus mundus'' - the archetype being an expression of ''unus mundus''; synchronicity, or "meaningful coincidence", being made possible by the fact that both the observer and connected phen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Philosophy
Eastern philosophy or Asian philosophy includes the various philosophies that originated in East and South Asia, including Chinese philosophy, Japanese philosophy, Korean philosophy, and Vietnamese philosophy; which are dominant in East Asia, and Indian philosophy (including Hindu philosophy, Jain philosophy, Buddhist philosophy), which are dominant in South Asia, Southeast Asia, Tibet, and Mongolia. Indian philosophy Indian philosophy refers to ancient philosophical traditions ( sa, ; 'world views', 'teachings') of the Indian subcontinent. Jainism may have roots dating back to the times of the Indus Valley civilization. The major orthodox schools arose sometime between the start of the Common Era and the Gupta Empire. These Hindu schools developed what has been called the "Hindu synthesis" merging orthodox Brahmanical and unorthodox elements from Buddhism and Jainism. Hindu thought also spread east to the Indonesian Srivijaya empire and the Cambodian Khme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




.jpg)
