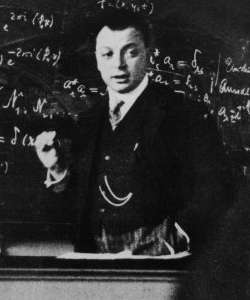|
Unus Mundus
''Unus mundus'' (Latin for "One world") is an underlying concept of Western philosophy, theology, and alchemy, of a primordial unified reality from which everything derives. The term can be traced back to medieval Scholasticism though the notion itself dates back at least as far as Plato's allegory of the cave. The idea was popularized in the 20th century by the Swiss psychoanalyst Carl Gustav Jung, though the term can be traced back to scholastics such as Duns ScotusC. G. Jung ed, ''Man and his Symbols'' (1978) p. 402 and was taken up again in the 16th century by Gerhard Dorn, a student of the famous alchemist Paracelsus. Jung and Pauli Jung, in conjunction with the physicist Wolfgang Pauli, explored the possibility that his concepts of archetypes and synchronicity might be related to the ''unus mundus'' - the archetype being an expression of ''unus mundus''; synchronicity, or "meaningful coincidence", being made possible by the fact that both the observer and connected p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Banks Rhine
Joseph Banks Rhine (September 29, 1895 – February 20, 1980), usually known as J. B. Rhine, was an American Botany, botanist who founded parapsychology as a branch of psychology, founding the parapsychology lab at Duke University, the ''Journal of Parapsychology'', the Rhine Research Center, Foundation for Research on the Nature of Man, and the Parapsychological Association. Rhine wrote the books ''Extrasensory Perception (book), Extrasensory Perception'' and ''Parapsychology: Frontier Science of the Mind''. Early life and education Rhine was the second of five children born to Samuel Ellis Rhine and Elizabeth Vaughan Rhine in Juniata County, Pennsylvania, Waterloo, Juniata County, Pennsylvania. Samuel Rhine had been educated in a Harrisburg business college, had taught school and later had been a farmer and merchant. The family moved to Marshallville, Ohio, when Joseph was in his early teens.Denis, Brian. (1982). ''The Enchanted Voyager''. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemical Concepts
Alchemy (from the Arabic word , ) is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in Chinese alchemy, China, Rasayana, India, the Alchemy and chemistry in medieval Islam, Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Egypt (Roman province), Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD.. Alchemy#Hellenistic Egypt, Greek-speaking alchemists often referred to their craft as "the Art" (τέχνη) or "Knowledge" (ἐπιστήμη), and it was often characterised as mystic (μυστική), sacred (ἱɛρά), or divine (θɛíα). Alchemists attempted to purify, mature, and perfect certain materials. Common aims were chrysopoeia, the transmutation of "base metals" (e.g., lead) into "noble metals" (particularly gold); the creation of an Elixir of life, elixir of immortality; and the creation of Panacea (medicine), panaceas ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenomenon
A phenomenon ( phenomena), sometimes spelled phaenomenon, is an observable Event (philosophy), event. The term came into its modern Philosophy, philosophical usage through Immanuel Kant, who contrasted it with the noumenon, which ''cannot'' be directly observed. Kant was heavily influenced by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz in this part of his philosophy, in which phenomenon and noumenon serve as interrelated technical terms. Far predating this, the Ancient Greek Philosophy, ancient Greek Pyrrhonism, Pyrrhonist philosopher Sextus Empiricus also used ''phenomenon'' and ''noumenon'' as interrelated technical terms. Common usage In popular usage, a ''phenomenon'' often refers to an extraordinary, unusual or notable event. According to the ''Dictionary of Visual Discourse'':In ordinary language 'phenomenon/phenomena' refer to any occurrence worthy of note and investigation, typically an untoward or unusual event, person or fact that is of special significance or otherwise notable. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observer (quantum Physics)
Some interpretations of quantum mechanics posit a central role for an observer of a quantum phenomenon. The quantum mechanical observer is tied to the issue of Observer effect (physics)#Quantum mechanics, observer effect, where a measurement necessarily requires interacting with the physical object being measured, affecting its properties through the interaction. The term "observable" has gained a technical meaning, denoting a Hermitian operator that represents a measurement. Foundation The theoretical foundation of the concept of measurement in quantum mechanics is a contentious issue deeply connected to the many interpretations of quantum mechanics. A key focus point is that of wave function collapse, for which several popular interpretations assert that measurement causes a ''discontinuous change'' into an Eigenvalues and eigenvectors#Schr.C3.B6dinger equation, eigenstate of the operator associated with the quantity that was measured, a change which is not time-reversible. More ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jungian Archetypes
Jungian archetypes are a concept from psychology that refers to a universal, inherited idea, pattern of thought, or image that is present in the collective unconscious of all human beings. As the psychic counterpart of instinct (i.e., archetypes are innate, symbolic, psychological expressions that manifest in response to patterned biological instincts), archetypes are thought to be the basis of many of the common themes and symbols that appear in stories, myths, and dreams across different cultures and societies. Some examples of archetypes include those of the mother, the child, the trickster, and Flood myth, the flood, among others. The concept of the collective unconscious was first proposed by Carl Jung, a Swiss Psychiatry, psychiatrist and Analytical Psychology, analytical psychologist. According to Jung, archetypes are innate patterns of thought and behavior that strive for Self-realization, realization within an individual's environment. This process of Self-actualization, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli ( ; ; 25 April 1900 – 15 December 1958) was an Austrian theoretical physicist and a pioneer of quantum mechanics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics "for the discovery of the Exclusion Principle, also called the Pauli exclusion principle, Pauli Principle". The discovery involved Spin (physics), spin theory, which is the basis of a theory of the Matter#Structure, structure of matter. To preserve the conservation of energy in beta decay, he posited the existence of a small neutral particle, dubbed the neutrino by Enrico Fermi. The neutrino was detected in 1956. Early life Pauli was born in Vienna to a chemist, (''né'' Wolf Pascheles, 1869–1955), and his wife, Bertha Camilla Schütz; his sister was Hertha Pauli, a writer and actress. Pauli's middle name was given in honor of his Godparent, godfather, physicist Ernst Mach. Pauli's paternal grandparents were from prominent Jewish families of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unus Mundus According To Jung (en)
Unus the Untouchable (also known as Gunther Bain, born Angelo Unuscione) is a supervillain appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Unus is a mutant, and is named for his ability to consciously project an invisible force field which protects him from harm. Publication history Unus first appeared in ''X-Men'' #8 (November 1964), and was created by Stan Lee and Jack Kirby. Fictional character biography Origin Angelo Unuscione was born in Milan, Italy. After his arrival in the United States, he legally changed his name to Gunther Bain. He became a wrestler, and, when Beast briefly left the X-Men, he was able to defeat him in a wrestling match.''X-Men'' #8 (November 1964) Once in America, he sought out the Brotherhood of Mutants to join them. He turned criminal, and joined with the Brotherhood as they fought the X-Men. During the battle, his powers were enhanced by a shot fired from Beast's gun, increasing his power beyond his ability to control it, and making ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parapsychological
Parapsychology is the study of alleged psychic phenomena (extrasensory perception, telepathy, teleportation, precognition, clairvoyance, psychokinesis (also called telekinesis), and psychometry) and other paranormal claims, for example, those related to near-death experiences, synchronicity, apparitional experiences, etc. Criticized as being a pseudoscience, the majority of mainstream scientists reject it. Parapsychology has been criticised for continuing investigation despite being unable to provide reproducible evidence for the existence of any psychic phenomena after more than a century of research. Parapsychology research rarely appears in mainstream scientific journals; a few niche journals publish most papers about parapsychology. Terminology The term ''parapsychology'' was coined in 1889 by philosopher Max Dessoir as the German . It was adopted by J. B. Rhine in the 1930s as a replacement for the term ''psychical research'' to indicate a significant shift toward exper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandala
A mandala (, ) is a geometric configuration of symbols. In various spiritual traditions, mandalas may be employed for focusing attention of practitioners and adepts, as a spiritual guidance tool, for establishing a sacred space and as an aid to meditation and trance induction. In the Eastern religions of Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Shinto it is used as a map representing deities, or especially in the case of Shinto, paradises, kami or actual shrines. Hinduism In Hinduism, a basic mandala, also called a '' yantra'', takes the form of a square with four gates containing a circle with a centre point. Each gate is in the general shape of a T. Mandalas often have radial balance. A '' yantra'' is similar to a mandala, usually smaller and using a more limited colour palette. It may be a two- or three-dimensional geometric composition used in '' sadhanas'', puja or meditative rituals, and may incorporate a mantra into its design. It is considered to represent the abode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronicity
Synchronicity () is a concept introduced by Carl Jung, founder of analytical psychology, to describe events that coincide in time and appear meaningfully related, yet lack a discoverable causal connection. Jung held that this was a healthy function of the mind, although it can become harmful within psychosis. Jung developed the theory as a hypothetical noncausal principle serving as the intersubjective or philosophically objective connection between these seemingly meaningful coincidences. After coining the term in the late 1920s Jung developed the concept with physicist Wolfgang Pauli through correspondence and in their 1952 work ''The Interpretation of Nature and the Psyche''. This culminated in the Pauli–Jung conjecture.Jung, Carl G. 9512005.Synchronicity. Pp. 91–98 in ''Jung on Synchronicity and the Paranormal'', edited by R. Main. London: Taylor & Francis. Jung and Pauli's view was that, just as causal connections can provide a meaningful understanding of the psyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertium Quid
Tertium quid refers to an unidentified third element that is in combination with two known ones.Tertium quid , ''Online Etymological Dictionary'' The phrase is associated with . It is for "third something" (literally, "third what"), a translation of the ''triton ti'' (τρίτον τί). The Greek phrase was used by ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |