|
Rule-set-based Access Control
Rule-set-based access control (RSBAC) is an open source access control framework for current Linux kernels, which has been in stable production use since January 2000 (version 1.0.9a). Features * Free open source GNU General Public License ( GPL) Linux kernel security extension * Independent of governments and big companies * Several well-known and new security models, e.g. mandatory access control ( MAC), access control list ( ACL), and role compatibility (RC) * On-access virus scanning with Dazuko interface * Detailed control over individual user and program network accesses * Fully access controlled kernel level user management * Any combination of security models possible * Easily extensible: write your own model for runtime registration * Support for latest kernels * Stable for production use * Easily portable to other operating systems The RSBAC system architecture has been derived and extended from the Generalized Framework for Access Control ( GFAC) by Marshall Abrams and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Access Control
In physical security and information security, access control (AC) is the action of deciding whether a subject should be granted or denied access to an object (for example, a place or a resource). The act of ''accessing'' may mean consuming, entering, or using. It is often used interchangeably with authorization, although the authorization may be granted well in advance of the access control decision. Access control on digital platforms is also termed admission control. The protection of external databases is essential to preserve digital security. Access control is considered to be a significant aspect of privacy that should be further studied. Access control policy (also access policy) is part of an organization’s security policy. In order to verify the access control policy, organizations use an access control model. General security policies require designing or selecting appropriate security controls to satisfy an organization's risk appetite - access policies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Security Modules
Linux Security Modules (LSM) is a framework allowing the Linux kernel to support, without bias, a variety of computer security models. LSM is licensed under the terms of the GNU General Public License and is a standard part of the Linux kernel since Linux 2.6. AppArmor, LoadPin, SELinux, Smack, TOMOYO, Yama, SafeSetID, Integrity Policy Enforcement (IPE), and Landlock are the currently approved security modules in the official kernel. Design LSM was designed in order to answer all the requirements for successfully implementing a mandatory access control module, while imposing the fewest possible changes to the Linux kernel. LSM avoids the approach of system call interposition used by Systrace because it doesn't scale to multiprocessor kernels and is subject to TOCTTOU (race) attacks. Instead, LSM inserts " hooks" (upcalls to the module) at every point in the kernel where a user-level system-call is about to result with an access to an important internal kernel-object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Security Software
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license. Thousands of Linux distributions exist, many based directly or indirectly on other distributions; popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, Linux Mint, Arch Linux, and Ubuntu, while commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise, and ChromeOS. Linux distributions are frequently used in server platforms. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses and recommends the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the use and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System Security
Operation or Operations may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity * Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory * ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Man Publishing's house organ for articles and discussion about its wargaming products * ''The Operation'' (film), a 1973 British television film * ''The Operation'' (1990), a crime, drama, TV movie starring Joe Penny, Lisa Hartman, and Jason Beghe * The Operation M.D., formerly The Operation, a Canadian garage rock band * "Operation", a song by Relient K from '' The Creepy EP'', 2001 Television Episodes * "The Operation", ''Sky Dancers'' episode 27 (1996) * "The Operation", ''The Golden Girls'' season 1, episode 18 (1986) * "The Operation", ''You're Only Young Twice'' (1997) series 2, episode 8 (1978) Shows * ''The Operation'' (1992–1998), a reality television series from TLC Business * Manufacturing operations, operation of a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Security
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and computer network, networks from Threat (security), threats that can lead to unauthorized information disclosure, theft or damage to computer hardware, hardware, software, or Data (computing), data, as well as from the disruption or misdirection of the Service (economics), services they provide. The significance of the field stems from the expanded reliance on computer systems, the Internet, and wireless network standards. Its importance is further amplified by the growth of smart devices, including smartphones, televisions, and the various devices that constitute the Internet of things (IoT). Cybersecurity has emerged as one of the most significant new challenges facing the contemporary world, due to both the complexity of information systems and the societi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk-based Authentication
In authentication Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an Logical assertion, assertion, such as the Digital identity, identity of a computer system user. In contrast with iden ..., risk-based authentication is a non-static authentication system which takes into account the profile (IP address, User-Agent HTTP header, time of access, and so on) of the agent requesting access to the system to determine the risk profile associated with that transaction. The risk profile is then used to determine the complexity of the challenge. Higher risk profiles leads to stronger challenges, whereas a static username/password may suffice for lower-risk profiles. Risk-based implementation allows the application to challenge the user for additional credentials only when the risk level is appropriate. The point is that user validation accuracy is improved without inconveniencing a user, and risk-based authenticat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capability-based Security
Capability-based security is a concept in the design of secure computing systems, one of the existing security models. A capability (known in some systems as a key) is a communicable, unforgeable token of authority. It refers to a value that references an object along with an associated set of access rights. A user program on a capability-based operating system must use a capability to access an object. Capability-based security refers to the principle of designing user programs such that they directly share capabilities with each other according to the principle of least privilege, and to the operating system infrastructure necessary to make such transactions efficient and secure. Capability-based security is to be contrasted with an approach that uses traditional UNIX permissions and access control lists. Although most operating systems implement a facility which resembles capabilities, they typically do not provide enough support to allow for the exchange of capabilitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organisation-based Access Control
In computer security, organization-based access control (OrBAC) is an access control model first presented in 2003. The current approaches of the access control In physical security and information security, access control (AC) is the action of deciding whether a subject should be granted or denied access to an object (for example, a place or a resource). The act of ''accessing'' may mean consuming ... rest on the three entities (''subject'', ''action'', ''object'') to control the access the policy specifies that some subject has the permission to realize some action on some object. OrBAC allows the policy designer to define a security policy independently of the implementation. The chosen method to fulfill this goal is the introduction of an abstract level. * Subjects are abstracted into roles. A role is a set of subjects to which the same security rule apply. * Similarly, an activity is a set of actions to which the same security rule apply. * And, a view is a set of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice-based Access Control
In computer security, lattice-based access control (LBAC) is a complex access control model based on the interaction between any combination of objects (such as resources, computers, and applications) and subjects (such as individuals, groups or organizations). In this type of label-based mandatory access control model, a lattice (order), lattice is used to define the levels of security that an object may have and that a subject may have access to. The subject is only allowed to access an object if the security level of the subject is greater than or equal to that of the object. Mathematically, the security level access may also be expressed in terms of the lattice (a partial order set) where each object and subject have a greatest lower bound (meet) and least upper bound (join) of access rights. For example, if two subjects ''A'' and ''B'' need access to an object, the security level is defined as the meet of the levels of ''A'' and ''B''. In another example, if two object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
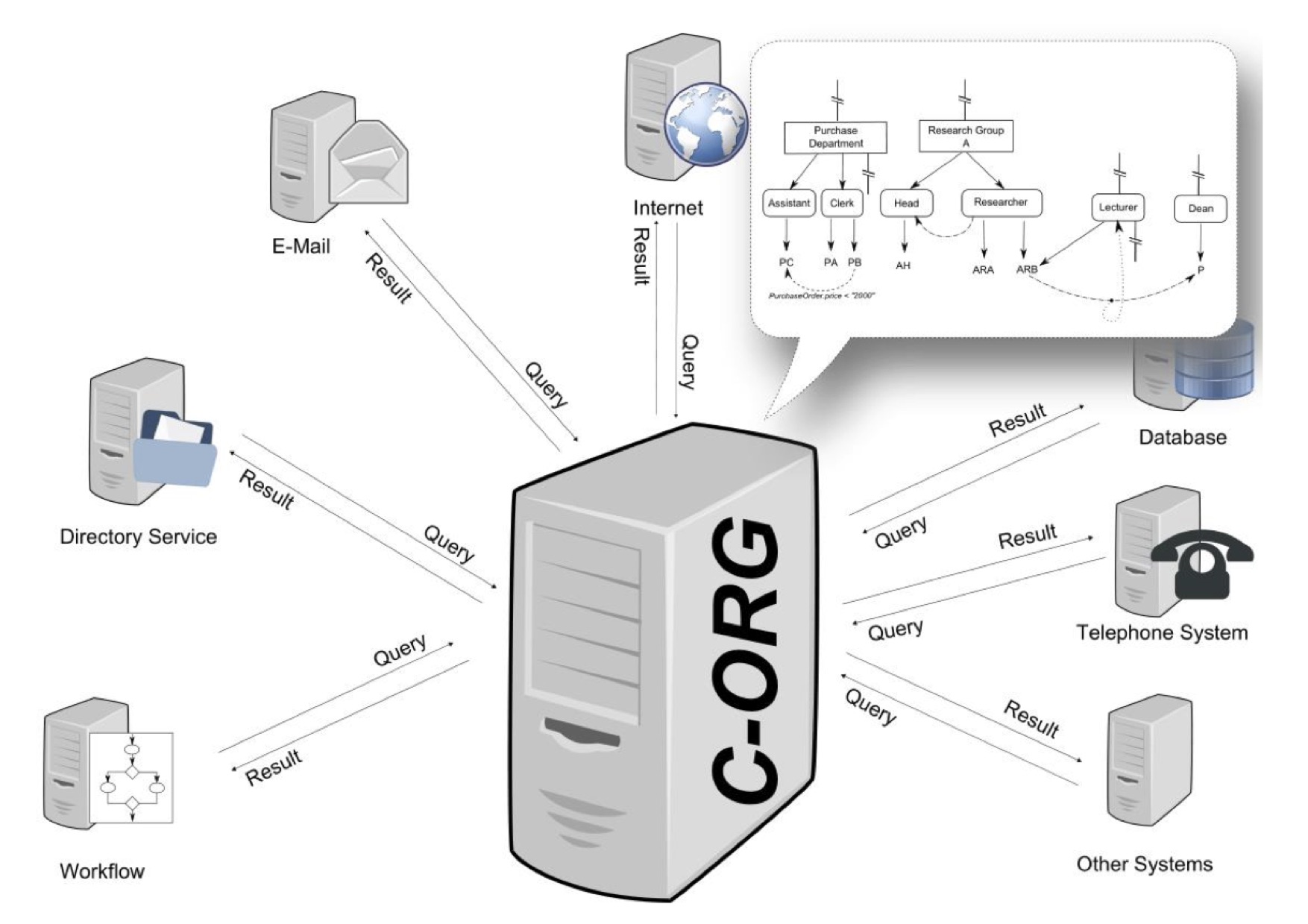
Graph-based Access Control
Graph-based access control (GBAC) is a declarative way to define access rights, task assignments, recipients and content in information systems. Access rights are granted to objects like files or documents, but also business objects such as an account. GBAC can also be used for the assignment of agents to tasks in workflow environments. Organizations are modeled as a specific kind of semantic graph comprising the organizational units, the roles and functions as well as the human and automatic agents (i.a. persons, machines). The main difference with other approaches such as role-based access control or attribute-based access control is that in GBAC access rights are defined using an organizational query language instead of total enumeration. History The foundations of GBAC go back to a research project named CoCoSOrg (Configurable Cooperation System) ">ref name="DISS">(in English language please see) at Bamberg University. In CoCoSOrg an organization is represented as a semant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discretionary Access Control
In computer security, discretionary access control (DAC) is a type of access control defined by the Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria (TCSEC) as a means of restricting access to objects based on the identity of subjects and/or groups to which they belong. The controls are discretionary in the sense that a subject with a certain access permission is capable of passing that permission (perhaps indirectly) on to any other subject (unless restrained by mandatory access control). Discretionary access control is commonly discussed in contrast to mandatory access control (MAC). Occasionally, a system as a whole is said to have "discretionary" or "purely discretionary" access control when that system lacks mandatory access control. On the other hand, systems can implement both MAC and DAC simultaneously, where DAC refers to one category of access controls that subjects can transfer among each other, and MAC refers to a second category of access controls that imposes constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Context-based Access Control
Context-based access control (CBAC) is a feature of firewall software, which intelligently filters TCP and UDP packets based on application layer protocol session information. It can be used for intranets, extranets and internets. CBAC can be configured to permit specified TCP and UDP traffic through a firewall only when the connection is initiated from within the network needing protection. (In other words, CBAC can inspect traffic for sessions that originate from the external network.) However, while this example discusses inspecting traffic for sessions that originate from the external network, CBAC can inspect traffic for sessions that originate from either side of the firewall. This is the basic function of a stateful inspection firewall. Without CBAC, traffic filtering is limited to access list implementations that examine packets at the network layer, or at most, the transport layer. However, CBAC examines not only network layer and transport layer information but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |