|
Rufinus (Byzantine Official)
Rufinus () was a Byzantine military officer and emissary of the 6th century, active during the reigns of emperors Anastasius I Dicorus (r. 491–518), Justin I (r. 518–527), and Justinian I (r. 527–565). Of Greek origin, he was the son and brother, respectively, of the officers Silvanus and Timostratus. He first appeared in 502, when he was sent by Anastasius to the court of the Sasanian shah Kavad I (r. 488–496; 499–531) with large amounts of money to prevent attacks on the Byzantine Empire. When Rufinus learned of the Persian attacks, he left the money in Caesarea and met in Amida Kavad I, who imprisoned him until January 503, when he was released and sent to the emperor. Rufinus reappears in 515, when he was appointed ''magister militum'' of Thrace by Anastasius to replace the rebel Vitalian, and then in 525/6 when the ''magister militum'' of the East and future emperor Justinian sent him to the court of Kavad I to discuss the terms of Justinian's adoption of Khosrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Monarchs Of The Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian monarchs were the rulers of Iran after their victory against their former suzerain, the Parthian Empire, at the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224. At its height, the Sasanian Empire spanned from Turkey and Rhodes in the west to Pakistan in the east, and also included territory in what is now the Caucasus, Yemen, UAE, Oman, Egypt, Palestine, Israel, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan and Central Asia. The Sasanian Empire was recognized as one of the main powers in the world alongside its neighboring arch rival, the Roman Empire for a period of more than 400 years.Norman A. Stillman ''The Jews of Arab Lands'' pp 22 Jewish Publication Society, 1979 International Congress of Byzantine Studies ''Proceedings of the 21st International Congress of Byzantine Studies, London, 21–26 August 2006, Volumes 1-3'' pp 29. Ashgate Pub Co, 30 sep. 2006 The Sasanian dynasty began with Ardashir I in 224, who was a Persian people, Persian from Istakhr, and ended with Yazdegerd III in 651. The period fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Consul
The consuls were the highest elected public officials of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC). Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum''an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspiredafter that of the Roman censor, censor, which was reserved for former consuls. Each year, the Centuriate Assembly elected two consuls to serve jointly for a one-year term. The consuls alternated each month holding ''fasces'' (taking turns leading) when both were in Rome. A consul's ''imperium'' (military power) extended over Rome and all its Roman provinces, provinces. Having two consuls created a check on the power of any one individual, in accordance with the republican belief that the powers of the former King of Rome, kings of Rome should be spread out into multiple offices. To that end, each consul could veto the actions of the other consul. After the establishment of the Roman Empire, Empire (27 BC), the consuls became mere symboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophanes The Confessor
Theophanes the Confessor (; 759 – 817 or 818) was a member of the Byzantine aristocracy who became a monk and chronicler. He served in the court of Emperor Leo IV the Khazar before taking up the religious life. Theophanes attended the Second Council of Nicaea in 787 and resisted the iconoclasm of Leo V the Armenian, for which he was imprisoned. He died shortly after his release. Theophanes the Confessor, venerated on 12 March in both the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Roman Catholic Church, should not be confused with Theophanes of Nicaea, whose feast is commemorated on 11 October. Biography Theophanes was born in Constantinople of wealthy and noble iconodule parents: Isaac, governor of the islands of the Aegean Sea, and Theodora, of whose family nothing is known. His father died when Theophanes was three years old, and the Byzantine Emperor Constantine V (740–775) subsequently saw to the boy's education and upbringing at the imperial court. Theophanes would hold several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solidus Justin I , a character in ''Metal Gear Solid 2: Sons of Liberty''
{{disambiguation ...
Solidus (Latin for "solid") may refer to: * Solidus (coin), a Roman coin of nearly solid gold * Solidus (punctuation), or slash, a punctuation mark * Solidus (chemistry), the line on a phase diagram below which a substance is completely solid * Solidus Snake The ''Metal Gear'' franchise, created by Hideo Kojima and featuring character and mecha designs by Yoji Shinkawa, features a large cast of characters, several of whom are soldiers with supernatural powers provided by scientific advancements. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpetual Peace (532)
The Perpetual Peace or the Treaty of Eternal Peace (), signed in 532 between the East Roman (Byzantine) Empire and Sassanid Persia, was a peace treaty of indefinite duration, which concluded the Iberian War (527–531) between the two powers. It heralded a period of relatively cordial relations, but lasted only until 540, when hostilities resumed over the control of Lazica. History The Iberian War, which had been provoked by the uprising of the Iberians against the Persians in 524/5, had been largely indecisive: the Persians swiftly crushed the revolt, but were unable to make any gains in Byzantine territory except for two forts, Scanda and Sarapanis, in Lazica. The Byzantines had recovered from some early reversals to inflict two major defeats on the Persians in 530 at Dara and Satala. In their aftermath, they gained the two border forts of Bolum and Pharangium in Persarmenia, but were in turn defeated at Callinicum in 531. Throughout these conflicts, periods of truce and ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorotheus (magister Militum)
Dorotheus was a Byzantine military commander. While being ''magister militum per Armeniam'' he won a battle against the Persians, in 530, as well as taking part in the Battle of Satala. At Satala he defended the city while his superior Sittas was hidden with some cavalry in the nearby area and attacked the Persians in the rear, routing their 30,000 with the Byzantine 15,000. He defeated the Persians again in 531 and later drove the Sabir Huns out through the Caucasus The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i .... He was sent to North Africa with Belisarius, but died on the way, which caused mourning throughout the army. References 533 deaths Generals of Justinian I People of the Roman–Sasanian Wars {{Byzantine-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dara
The Battle of Dara was fought between the Eastern Roman Empire and the Sasanians in 530 AD. It was one of the battles of the Iberian War. Procopius's account of this engagement is among the most detailed descriptions of a late Roman battle. Background The Byzantine Empire was at war with the Sasanians from 527, supposedly because Kavadh I had tried to force the Iberians to become Zoroastrians. The Iberian king fled from Kavadh, but Kavadh tried to make peace with the Byzantines, and attempted to have Justin I adopt his son Khosrau. Justin agreed, but on the terms that he would do so only in a rite reserved for barbarians. This failed to satisfy Kavadh, who attacked Byzantine allies, so Justin sent his generals Sittas and Belisarius into Persia, where they were initially defeated. In 529, the failed negotiations of Justin's successor Justinian prompted a Sasanian expedition of 40,000 men towards Dara. The next year, Belisarius was sent back to the region alongside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dara
Dara is a given name in several languages. Dara, Daraa, or DARA may also refer to: Geography Africa * Dar'a, region in northern Ethiopia * Dara (woreda), region in southern Ethiopia Asia * Dara (Mesopotamia), an archeological site in Mardin province, Turkey * Dara, Iran, a village in East Azerbaijan Province, Iran * Daraa Governorate, province of Syria * Daraa, capital city of the Daraa Governorate Europe * Dara, Greece, community in Arcadia, Greece * Dara, a village in Pietroasele Commune, Buzău County, Romania * Dara, a village in Dorolț Commune, Satu Mare County, Romania * Daranak, Armenia, also called ''Dara'' Film and entertainment * Dara (film), ''Dara'' (film), a 2007 Indonesian short film ** Macabre (2009 film), ''Macabre'' (film), a 2009 Indonesian film based on the short film ''Dara'' * Dara of Jasenovac a Serbian historical drama film * Dara (game) West African strategy game People * Dara clan, a clan of Jats in India * Sandara Park, South Korean singer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
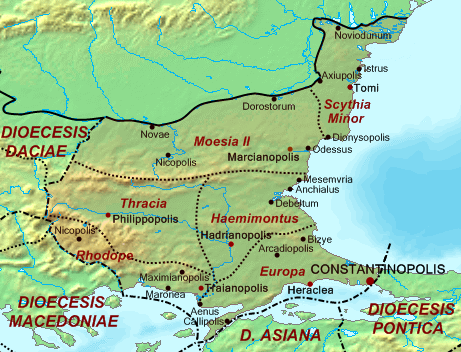
Vitalian (consul)
Vitalian (, ; died 520) was a general of the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire. A native of Moesia in the northern Balkans, and probably of mixed Roman and Goths, Gothic or Scythian barbarian descent, he followed his father into the imperial army, and by 513 had become a senior commander in Thrace. In that year he rebelled against Emperor Anastasius I (emperor), Anastasius I (r. 491–518), whose fiscal stringency and promotion of Miaphysitism were widely unpopular, and allowed Vitalian to quickly win over large parts of the army and the people of Thrace to his cause. After scoring a series of victories over loyalist armies, Vitalian came to threaten Constantinople itself, and forced Anastasius to officially recant his adoption of Miaphysitism in summer 515. Soon after, however, as Anastasius failed to honour some of the terms of the agreement, Vitalian marched on Constantinople, only to be decisively defeated by Anastasius' admiral, Marinus (praetorian prefect), Marinus. Vit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east, it comprises present-day southeastern Bulgaria (Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece (Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey (East Thrace). Lands also inhabited by ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into Macedonia (region), Macedonia. Etymology The word ''Thrace'', from ancient Greek ''Thrake'' (Θρᾴκη), referred originally to the Thracians (ancient Greek ''Thrakes'' Θρᾷκες), an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' (ancient Greek Εὐρώπη), also at first referred to this region, before that term expanded to include its Europe, modern sense. It has been suggested that the name ''Thrace'' derives from the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |