|
Rozellid
Cryptomycota ('hidden fungi'), Rozellida, or Rozellomycota are a clade of micro-organisms that are either fungi or a sister group to fungi. They differ from classical fungi in that they lack chitinous cell walls at any Food web, trophic stage in their lifecycle, as reported by Jones and colleagues in 2011. Despite their unconventional phagocytic feeding habits (typical fungi are osmotrophic), chitin has been observed in the inner layer of resting spores, and in immature resting spores for some species of ''Rozella'', as indicated with Calcofluor-white, calcofluor-white stain as well as the presence of a fungal-specific chitin synthase gene. History Formation of the Rozelida concept Rozellida were first detected as DNA sequences retrieved from a freshwater laboratory enclosure. Phylogenetic analysis of these sequences formed a unique terminal clade of then unknown affiliation provisionally called after the first clone in the clade: LKM11. The term "Rozellida" was coined in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rozella
''Rozella'' is a fungal genus of obligate endoparasites of a variety of hosts, including Oomycota, Chytridiomycota, and Blastocladiomycota. ''Rozella'' was circumscribed by French mycologist Marie Maxime Cornu in 1872. Considered one of the earliest diverging lineages of fungi, the widespread genus contains 27 species, with the most well studied being ''Rozella allomycis''. ''Rozella'' is a member of a large clade of fungi referred to as the Cryptomycota/Rozellomycota. While some can be maintained in dual culture with the host, most have not been cultured, but they have been detected, using molecular techniques, in soil samples, and in freshwater and marine ecosystems. Zoospores have been observed, along with cysts, and the cells of some species are attached to diatoms. Morphology ''Rozella'' species grow inside their hosts. At first, the thallus is unwalled and indistinguishable from the host. As growth continues, the thallus will either form a zoosporangium using the wall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequence
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases within the nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. This succession is denoted by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of the nucleotides. By convention, sequences are usually presented from the 5' end to the 3' end. For DNA, with its double helix, there are two possible directions for the notated sequence; of these two, the sense strand is used. Because nucleic acids are normally linear (unbranched) polymers, specifying the sequence is equivalent to defining the covalent structure of the entire molecule. For this reason, the nucleic acid sequence is also termed the primary structure. The sequence represents genetic information. Biological deoxyribonucleic acid represents the information which directs the functions of an organism. Nucleic acids also have a secondary structure and tertiary structure. Primary structure is sometimes mistakenly referred to as "prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitin Synthase
In enzymology, a chitin synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine + ,4-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl) \rightleftharpoons UDP + ,4-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)+1 Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and ,4-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl), whereas its two products are UDP and ,4-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)+1. This enzyme belongs to the family of glycosyltransferases, specifically the hexosyltransferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:chitin 4-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyl-transferase. Other names in common use include chitin-UDP N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase, chitin-uridine diphosphate acetylglucosaminyltransferase, chitin synthetase, and trans-N-acetylglucosaminosylase. This enzyme participates in aminosugars metabolism. Production Chitin Synthase is manufactured in the rough endoplasmic reticulum of fungi as the inactive form, zymogen. The zym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
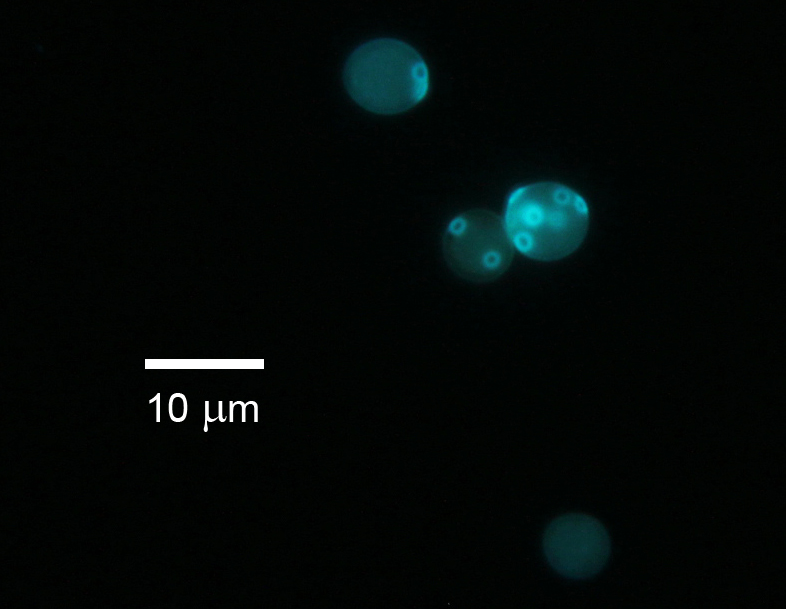
Calcofluor-white
Calcofluor-white or CFW is a fluorescent blue dye used in biology and textiles. It binds to 1–3 beta and 1–4 beta polysaccharides of chitin and cellulose that are present in cell walls on fungi, plants, and algae. In plant cell biology research, it is used for the staining of cell walls of both algae and higher plants. It is also useful in medicine and animal biology as a sensitive tool for the visualization and identification of fungi in the tissue. Usage Medicine CFW can be used in both clinical mycology and parasitology. Free-living amoebae in ocular species can have cysts that can be vividly seen with the stain. CFW can be used with the Papanicolaou stain to help strengthen the response of yeasts in Pap smears. Research In research, calcofluor-white is also used to stain bud scars of yeast cells because the bud scars have a higher content of chitin, which stains them more than the rest of the cell membrane. Due to this stain, it is possible to count the bud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resting Spore
A resting spore is a resistant cell, adapted to survive adverse environmental conditions. Resting spore is a term commonly applied to both diatoms and fungi. In fungi and oomycetes A resting spore can be a spore created by fungi which is thickly encysted (has a thick cell wall) in order to survive through stressful times, such as drought. It protects the spore from biotic (microbial, fungal viral), as well as abiotic (wind, heat, xeric conditions) factors. Resting spores of a particular oomycete species are important in causing late potato blight. They can lie dormant within the soil of a field for decades until the right conditions occur for viability (plant host present, rain, fire etc.). In diatoms A similar resting spore life stage is also present in diatoms, and in such case, is also often referred to as the hypnospore. Importantly, the resting spore of marine diatoms is not an obligate stage of the life cycle, except in the minority of studied taxa, where spore produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Web
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Position in the food web, or trophic level, is used in ecology to broadly classify organisms as autotrophs or heterotrophs. This is a non-binary classification; some organisms (such as carnivorous plants) occupy the role of mixotrophs, or autotrophs that additionally obtain organic matter from non-atmospheric sources. The linkages in a food web illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other heterotrophs. The food web is a simplified illustration of the various methods of feeding that link an ecosystem into a unified system of exchange. There are different kinds of consumer–resource interactions that can be roughly divided into herbivory, carnivory, scavenging, and parasitism. Some of the organic matter eaten by heterotrophs, such as sugars, provides energy. Autotrophs and hetero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitin
Chitin (carbon, C8hydrogen, H13oxygen, O5nitrogen, N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chitin are produced each year in the biosphere. It is a primary component of cell walls in fungi (especially filamentous and mushroom-forming fungi), the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans and insects, the radulae, cephalopod beaks and Gladius (cephalopod), gladii of molluscs and in some nematodes and diatoms. It is also synthesised by at least some fish and lissamphibians. Commercially, chitin is extracted from the shells of crabs, shrimps, shellfish and lobsters, which are major by-products of the seafood industry. The structure of chitin is comparable to cellulose, forming crystalline nanofibrils or whiskers. It is functionally comparable to the protein keratin. Chitin has proved useful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and taxon B are sister groups to each other. Taxa A and B, together with any other extant or extinct descendants of their most recent common ancestor (MRCA), form a monophyletic group, the clade AB. Clade AB and taxon C are also sister groups. Taxa A, B, and C, together with all other descendants of their MRCA form the clade ABC. The whole clade ABC is itself a subtree of a larger tree which offers yet more sister group relationships, both among the leaves and among larger, more deeply rooted clades. The tree structure shown connects through its root to the rest of the universal tree of life. In cladistic standards, taxa A, B, and C may represent specimens, species, genera, or any other taxonomic units. If A and B are at the same taxono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |