|
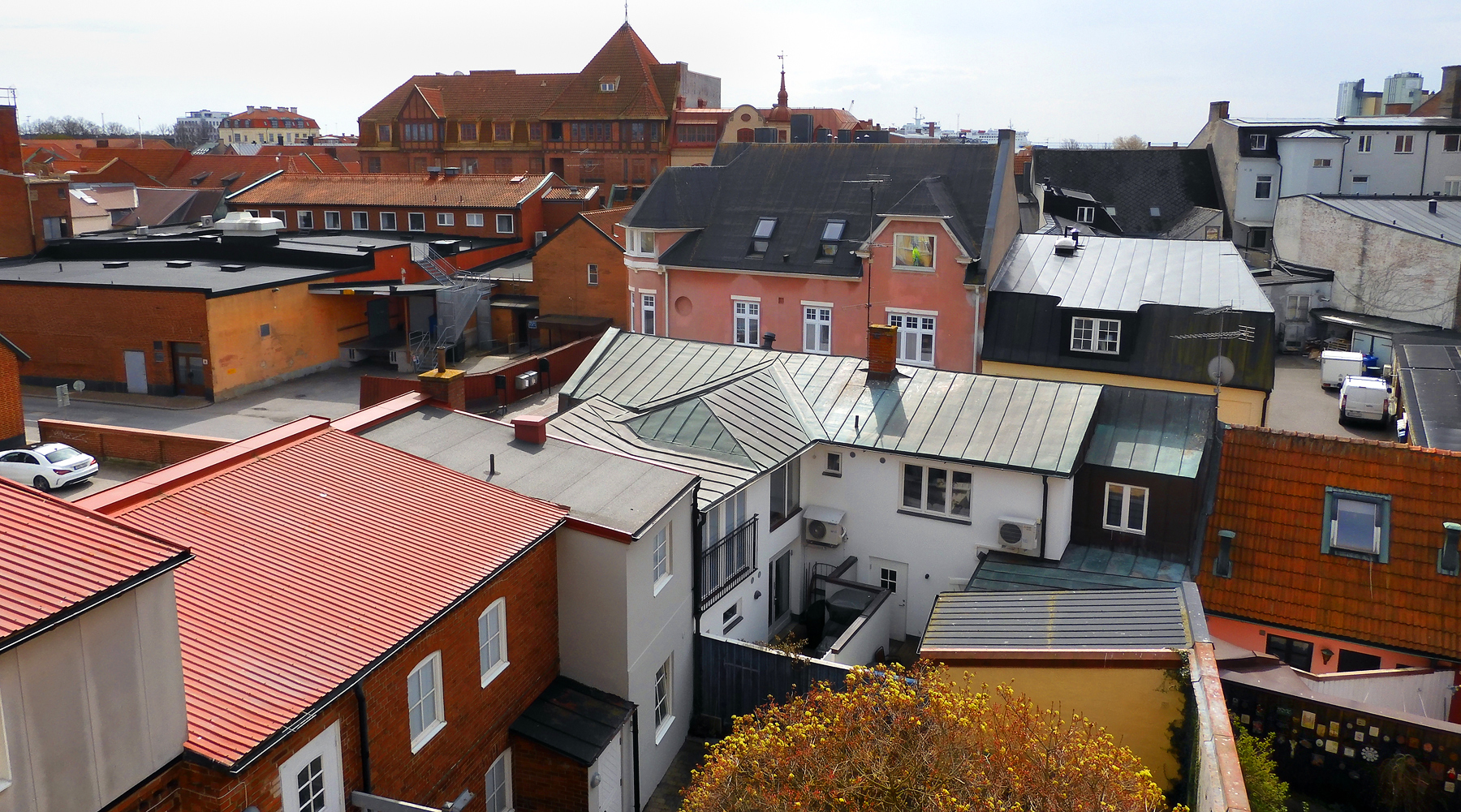
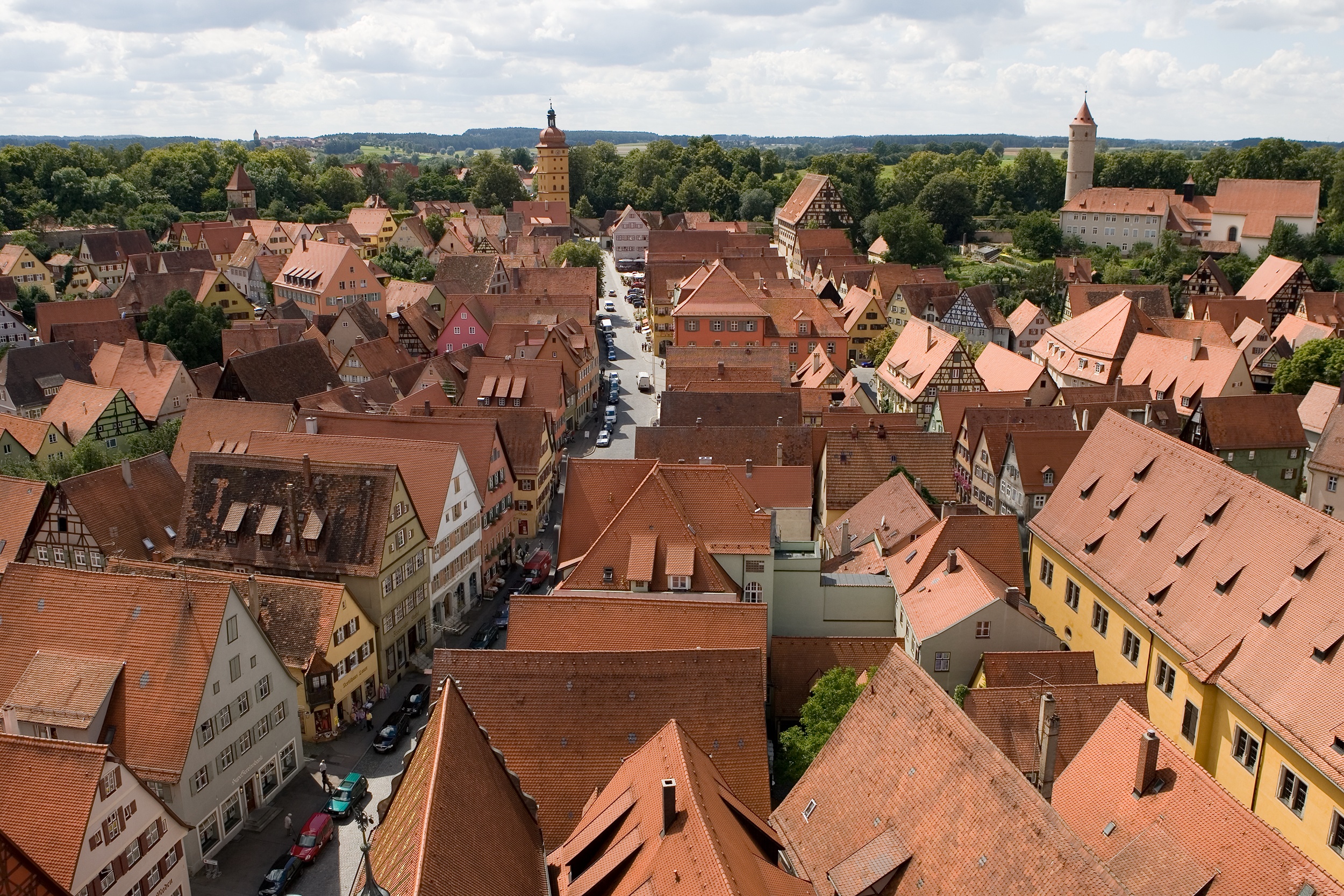
Roof
A roof (: roofs or rooves) is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of temperature, and wind. A roof is part of the building envelope. The characteristics of a roof are dependent upon the purpose of the building that it covers, the available roofing materials and the local traditions of construction and wider concepts of architectural design and practice, and may also be governed by local or national legislation. In most countries, a roof protects primarily against rain. A verandah may be roofed with material that protects against sunlight but admits the other elements. The roof of a Conservatory (greenhouse), garden conservatory protects plants from cold, wind, and rain, but admits light. A roof may also provide additional living space, for example, a roof garden. Etymology Old English 'roof, ceiling, top, summ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roof Tiles
Roof tiles are overlapping tiles designed mainly to keep out precipitation such as rain or snow, and are traditionally made from locally available materials such as clay or slate. Later tiles have been made from materials such as concrete, glass, and plastic. Roof tiles can be affixed by screws or nail (fastener), nails, but in some cases historic designs utilize interlocking systems that are self-supporting. Tiles typically cover an List of commercially available roofing materials, underlayment system, which seals the roof against water intrusion. Categories There are numerous profiles, or patterns, of roof tile, which can be separated into categories based on their installation and design. Shingle / flat tiles One of the simplest designs of roof tile, these are simple overlapping slabs installed in the same manner as traditional roof shingle, shingles, usually held in place by nails or screws at their top. All forms of slate tile fall into this category. When installed, mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper In Architecture
Copper has earned a respected place in the related fields of architecture, building construction, and interior design.Kireta Jr., Andy (2009). The copper advantage, ''Metal Architecture,'' June 2009; www.metalarchitecture.com From cathedrals to castles and from homes to offices, copper is used for a variety of architectural elements, including roofing material, roofs, flashing (weatherproofing), flashings, rain gutter, gutters, downspouts, domes, spires, vault (architecture), vaults, copper cladding, wall cladding, and building expansion joints. The history of copper in architecture can be linked to its durability, corrosion resistance, prestigious appearance, and ability to form complex shapes.Austin, Jim (2006). Copper: The peacock of metals, ''Metal Roofing,'' April–May 2006; www.metalroofingmag.com For centuries, craftsmen and designers utilized these attributes to build aesthetically pleasing and long-lasting building systems.Seale, Wayne (2007). The role of copper, br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domestic Roof Construction
Domestic roof construction is the framing and roof covering which is found on most detached houses in cold and temperate climates. Such roofs are built with mostly timber, take a number of different shapes, and are covered with a variety of materials. Overview Modern timber roofs are mostly framed with pairs of common rafters or prefabricated wooden trusses fastened together with truss connector plates. Timber framed and historic buildings may be framed with principal rafters or timber roof trusses. Roofs are also designated as ''warm'' or ''cold roof'' depending on the way they are designed and built with regard to thermal building insulation and ventilation. The steepness or roof pitch of a sloped roof is determined primarily by the roof covering material and aesthetic design. Flat roofs actually slope up to approximately ten degrees to shed water. Flat roofs on houses are primarily found in arid regions. In high-wind areas, such as where a cyclone or hurricane may make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roof Garden
A roof garden is a garden on the roof of a building. Besides the decorative benefit, roof plantings may provide food, temperature control, hydrological benefits, architectural enhancement, habitats or corridors for wildlife, recreational opportunities, and in large scale it may even have ecological benefits. The practice of cultivating food on the rooftop of buildings is sometimes referred to as rooftop farming. Rooftop farming is usually done using green roof, hydroponics, aeroponics or air-dynaponics systems or container gardens. History Humans have grown plants atop structures since the ziggurats of ancient Mesopotamia (4th millennium BC–600 BC) had plantings of trees and shrubs on aboveground terraces. An example in Roman Empire, Roman times was the Villa of the Mysteries in Pompeii, which had an elevated terrace where plants were grown. A roof garden has also been discovered around an audience hall in Roman-Byzantine Caesarea Maritima, Caesarea. The History of Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitumen
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscosity, viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American English, the material is commonly referred to as asphalt or tar. Whether found in natural deposits or refined from petroleum, the substance is classed as a pitch (resin), pitch. Prior to the 20th century, the term asphaltum was in general use. The word derives from the Ancient Greek word (), which referred to natural bitumen or pitch. The largest natural deposit of bitumen in the world is the Pitch Lake of southwest Trinidad, which is estimated to contain 10 million tons. About 70% of annual bitumen production is destined for road surface, road construction, its primary use. In this application, bitumen is used to bind construction aggregate, aggregate particles like gravel and forms a substance referred to as asphalt concrete, which is collo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow
Snow consists of individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes. It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout its life cycle, starting when, under suitable conditions, the ice crystals form in the atmosphere, increase to millimeter size, precipitate and accumulate on surfaces, then metamorphose in place, and ultimately melt, slide, or Sublimation (phase transition), sublimate away. Snowstorms organize and develop by feeding on sources of atmospheric moisture and cold air. Snowflakes Nucleation, nucleate around particles in the atmosphere by attracting supercooling, supercooled water droplets, which Freezing, freeze in hexagonal-shaped crystals. Snowflakes take on a variety of shapes, basic among these are platelets, needles, columns, and Hard rime, rime. As snow accumulates into a snowpack, it may blow into drifts. Over time, accumulated snow m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Envelope
A building envelope or building enclosure is the physical separator between the conditioned and unconditioned environment of a building, including the resistance to air, water, heat, light, and noiseSyed, Asif. ''Advanced building technologies for sustainability''. Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2012. 115. Print. transfer. Discussion The building envelope or enclosure is all of the elements of the outer shell that maintain a dry, heated, or cooled indoor environment and facilitate its climate control. Building envelope design is a specialized area of architectural and engineering practice that draws from all areas of building science and indoor climate control. The many functions of the building envelope can be separated into three categories:Straube, J.F., Burnett, E.F.P. ''Building Science for Building Enclosures''. Building Science Press, Westford, 2005. * Support (to resist and transfer structural and dynamic loads) * Control (the flow of matter and energy of all typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EPDM Rubber
EPDM rubber (ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber) is a type of synthetic rubber that is used in many applications. EPDM is an M-Class rubber under ASTM standard D-1418; the ''M'' class comprises elastomers with a saturated polyethylene chain (the M deriving from the more correct term polymethylene). EPDM is made from ethylene, propylene, and a diene comonomer that enables crosslinking via sulfur vulcanization. Typically used dienes in the manufacture of EPDM rubbers are ethylidene norbornene (ENB), dicyclopentadiene (DCPD), and vinyl norbornene (VNB). Varying diene contents are reported in commercial products, which are generally in the range from 2 to 12%. The earlier relative of EPDM is EPR, ethylene propylene rubber (useful for high-voltage electrical cables), which is not derived from any diene precursors and can be crosslinked only using radical methods such as peroxides. As with most rubbers, EPDM as used is always compounded with fillers such as carbon black and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
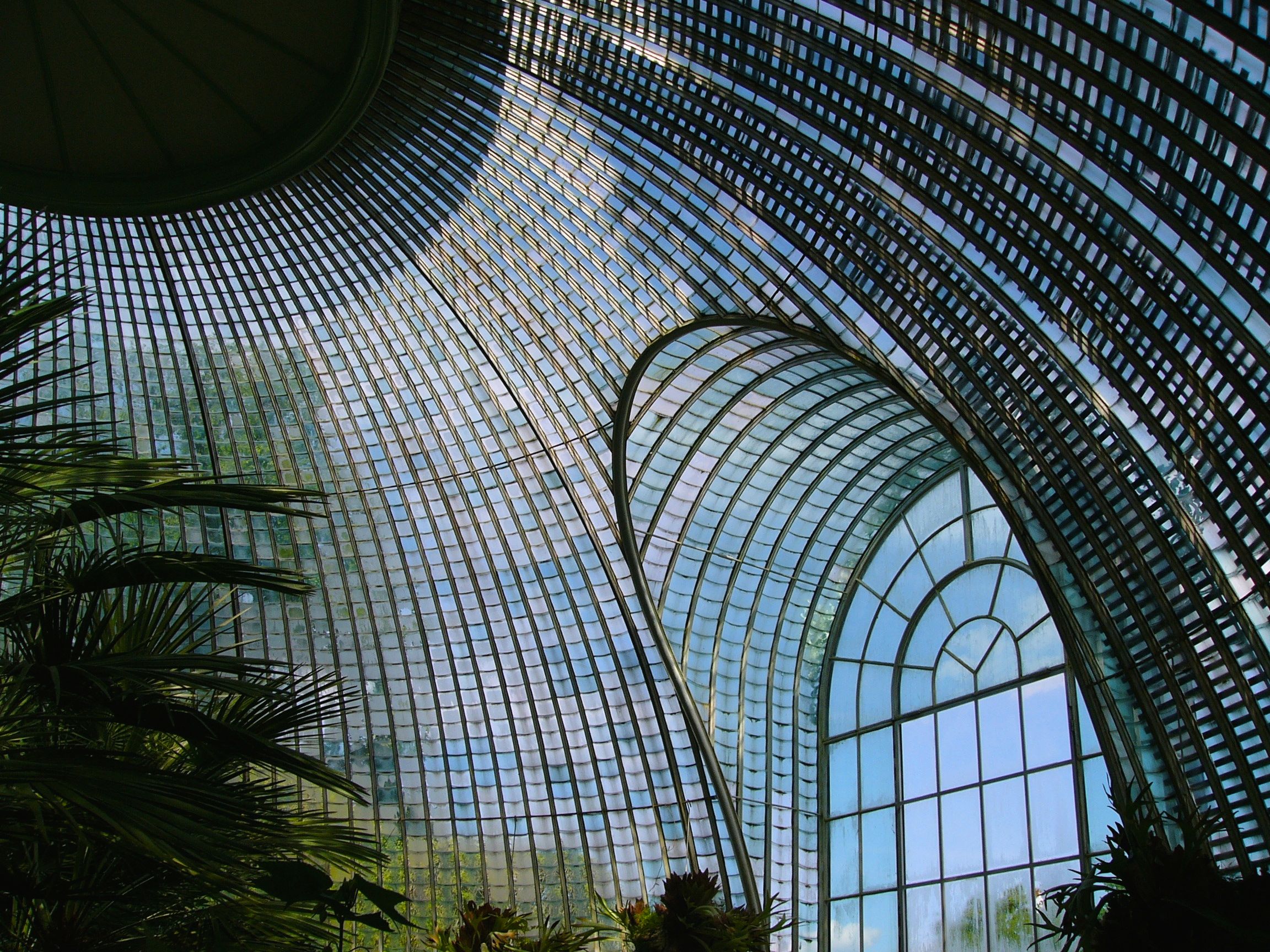
Conservatory (greenhouse)
A conservatory is a building or room having glass or other transparent roofing and walls, used as a greenhouse or a sunroom. Usually it refers to a space attached to a conventional building such as a house, especially in the United Kingdom. Elsewhere, especially in America, it can often refer to a large freestanding glass-walled building in a botanic garden or park, sometimes also called a palm house if tall enough for trees. Municipal conservatories became popular in the early 19th century. Description Many cities, especially those in cold climates and with large European populations, have built municipal conservatories to display tropical plants and hold flower displays. This type of conservatory was popular in the early nineteenth century, and by the end of the century people were also giving them a social use (e.g., tea parties). Conservatory architecture varies from typical Victorian glasshouses to modern styles, such as geodesic domes. Many were large and impressive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceiling
A ceiling is an overhead interior roof that covers the upper limits of a room. It is not generally considered a structural element, but a finished surface concealing the underside of the roof structure or the floor of a story above. Ceilings can be decorated to taste, and there are many examples of frescoes and artwork on ceilings, especially within religious buildings. A ceiling can also be the upper limit of a tunnel. The most common type of ceiling is the dropped ceiling, which is suspended from structural elements above. Panels of drywall are fastened either directly to the ceiling joists or to a few layers of moisture-proof plywood which are then attached to the joists. Pipework or ducts can be run in the gap above the ceiling, and insulation and fireproofing material can be placed here. Alternatively, ceilings may be spray painted instead, leaving the pipework and ducts exposed but painted, and using spray foam. A subset of the dropped ceiling is the suspended ceiling, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building
A building or edifice is an enclosed Structure#Load-bearing, structure with a roof, walls and window, windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, monument, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the :Human habitats, human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much architecture, artistic expression. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |