|
Romanian Lei
The Romanian leu (, plural lei ; ISO code: RON; numeric code: 946) is the currency of Romania. It is subdivided into 100 (, singular: ), a word that also means "money" in the Romanian language. Etymology The name of the currency means "lion", and is derived from the Dutch thaler ( "lion thaler/dollar"). The Dutch ''leeuwendaalder'' was imitated in several German and Italian cities. These coins circulated in Romania, Moldova and Bulgaria and gave their name to their respective currencies: the ''Romanian leu'', the ''Moldovan leu'' and the ''Bulgarian lev''. History First leu: 1867–1947 In 1860, the Domnitor Alexandru Ioan Cuza attempted to create a national ''românul'' ("the Romanian") and the ''romanat''; however, the project was not approved by the Ottoman Empire. On 22 April 1867, a bimetallic currency was adopted, with the leu equal to 5 grams of 83.5% silver or 0.29032 grams of gold. The first leu coin was minted in Romania in 1870. Before 1878 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ten Bani
The ten-bani coin is a coin of the Romanian leu. It was reintroduced on 1 July 2005 and is the second-largest denomination coin in Romania. In addition to Romania, it has been minted in the United Kingdom (1867), Belgium (1900, 1905-1906), Germany (1906) and Russia (1952). History Principality of Romania The first ten-bani coin was struck in 1867 by two different mints in Birmingham, England: Birmingham Mint, Heaton and Watt & Co. The coin measured 30mm in diameter and weighed 10g. It was composed of 95% copper, 4% tin and 1% zinc. The obverse featured the name of the country and its coat of arms. The reverse featured the denomination within a laurel branch and oak branch. The denomination within the wreath read ''10 BANI'' and 1867. Each mint struck 12.5 million of the coin. Watt & Co. used the mintmark ''WATT & Co'' below the wreath while Heaton used one of ''HEATON''. The coins entered circulation on 1 January 1868. Kingdom of Romania A second ten-bani coin was struck only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thaler
A thaler or taler ( ; , previously spelled ) is one of the large silver coins minted in the states and territories of the Holy Roman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy during the Early Modern period. A ''thaler'' size silver coin has a diameter of about and a weight of about 25 to 30 grams (roughly 1 ounce). The word is shortened from , the original ''thaler'' coin minted in Joachimsthal, Bohemia, from 1520. While the first standard coin of the Holy Roman Empire was the of 1524, its longest-lived coin was the , which contained Cologne Mark of fine silver (or 25.984 g), and which was issued in various versions from 1566 to 1875. From the 17th century a lesser-valued '' North German thaler'' currency unit emerged, which by the 19th century became par with the . The ''thaler'' silver coin type continued to be minted until the 20th century in the form of the Mexican peso until 1914, the five Swiss franc coin until 1928, the US silver dollar until 1935, and the Austrian Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
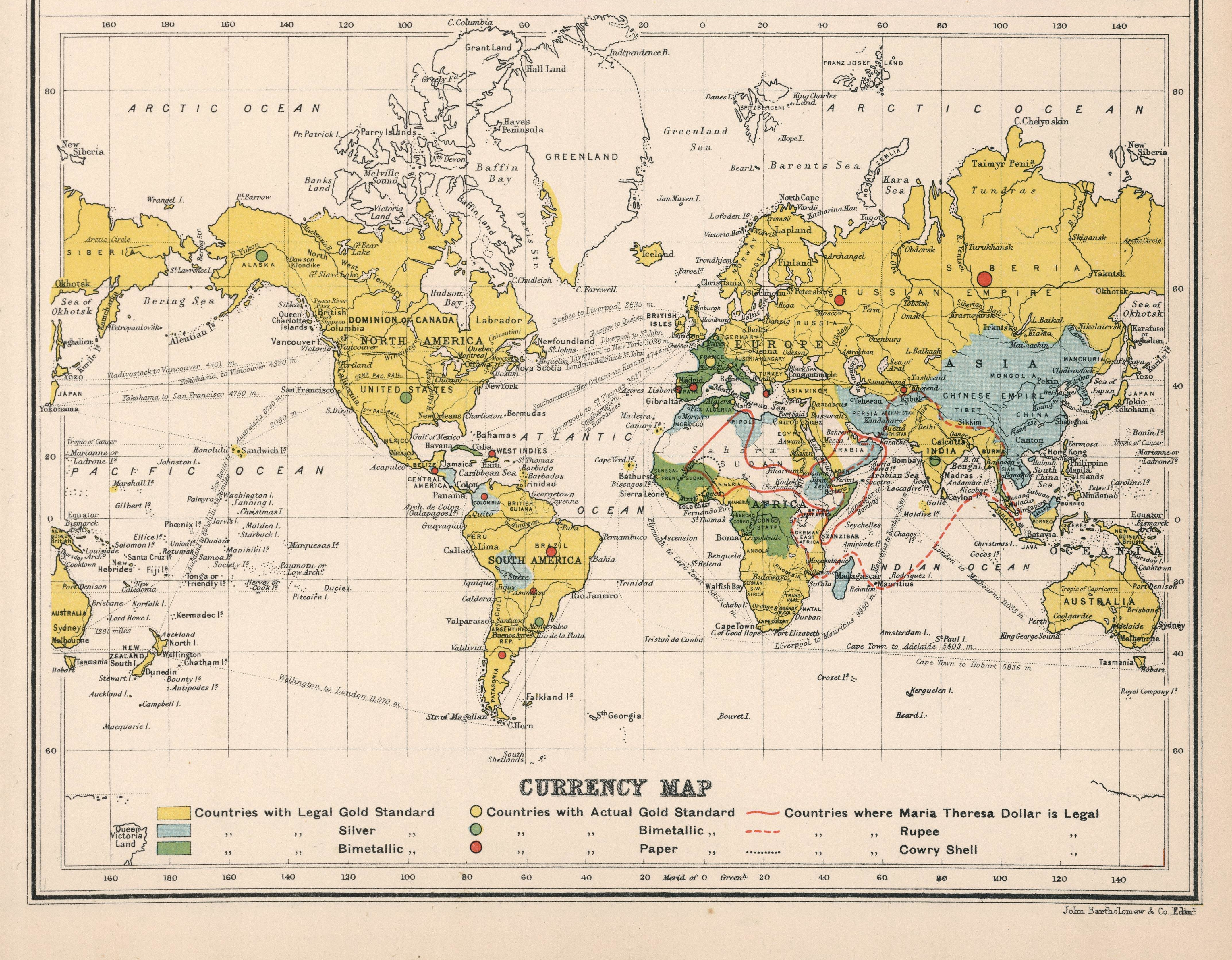
Gold Standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the late 1920s to 1932 as well as from 1944 until 1971 when the United States unilaterally terminated convertibility of the US dollar to gold, effectively ending the Bretton Woods system. Many states nonetheless hold substantial gold reserves. Historically, the silver standard and bimetallism have been more common than the gold standard. The shift to an international monetary system based on a gold standard reflected accident, network externalities, and path dependence. Great Britain accidentally adopted a ''de facto'' gold standard in 1717 when Isaac Newton, then-master of the Royal Mint, set the exchange rate of silver to gold too low, thus causing silver coins to go out of circulation. As Great Britain became the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Monetary Union
The Monetary Convention of 23 December 1865 was a unified system of coinage that provided a degree of monetary integration among several European countries, initially Belgium, France, Italy and Switzerland, at a time when the circulation of banknotes in these countries remained relatively marginal. In early 1866, it started being referred to in the British press as the Latin Monetary Union, with intent to make clear that the United Kingdom would not join, and has been generally referred to under that name () and the acronym LMU since then. A number of countries minted coins according to the LMU standard even though they did not formally join the LMU. The LMU has been viewed as a forerunner of late-20th-century European monetary union but cannot be directly compared with it, not least since the LMU did not rely on any common institutions. Unlike the Scandinavian Monetary Union established a few years later, the Latin Monetary Union remained limited to coinage and never extended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Ruble
The ruble or rouble (; Currency symbol, symbol: ₽; ISO 4217, ISO code: RUB) is the currency of the Russia, Russian Federation. Banknotes and coins are issued by the Central Bank of Russia, which is Russia's central bank, monetary authority independent of all other government bodies.wikisource:en:Constitution of Russia#Article 75, Article 75 - Constitution of the Russian Federation (English translation) The ruble is the second-oldest currency in continuous use and the first Decimalisation, decimal currency. The ruble was the currency of the Russian Empire, which was replaced by the Soviet ruble (code: SUR) during the Soviet Union, Soviet period. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, by 1992, the Soviet ruble was replaced in the Russian Federation by the Russian ruble (code: RUR) Par value, at par. The Russian ruble then further continued to be used in 11 post-Soviet states, forming a "ruble zone" until 1993. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimetallism
Bimetallism, also known as the bimetallic standard, is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed Exchange rate, rate of exchange between them. For scholarly purposes, "proper" bimetallism is sometimes distinguished as permitting that both gold and silver money are legal tender in unlimited amounts and that gold and silver may be taken to be coined by the Mint (facility), government mints in unlimited quantities. This distinguishes it from "limping standard" bimetallism, where both gold and silver are legal tender but only one is freely coined (e.g. the monies of France, Germany, and the United States after 1873), and from "trade" bimetallism, where both metals are freely coined but only one is legal tender and the other is used as "trade money" (e.g. most monies in western Europe from the 13th to 18th centuries). Economists also distinguish ''legal'' bimeta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandru Ioan Cuza
Alexandru Ioan Cuza (, or Alexandru Ioan I, also Anglicised as Alexander John Cuza; 20 March 1820 – 15 May 1873) was the first ''domnitor'' (prince) of the Romanian Principalities through his double election as List of monarchs of Moldavia#Post-Phanariote period, Prince of Moldavia on 5 January 1859 and List of princes of Wallachia#Post-Phanariote period, Prince of Wallachia on 24 January 1859, which resulted in Unification of Moldavia and Wallachia, the unification of the two states. He was a prominent figure of the Moldavian Revolution of 1848. Following his double election, he initiated a series of liberalism, liberal and progressivism, progressive reforms that contributed to the modernization of Romanian society and of state structures. As ruler of the Romanian Principalities, he supported a political and diplomatic activity for the recognition of the union of Moldavia and Wallachia by the suzerain Ottoman Empire and achieved constitutional and administrative unity betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domnitor
''Prince Domnitor'', in full ''Principe Domnitor'' (Romanian pl. ''Principi Domnitori'') was the official title of the ruler of Romania between 1862 and 1881. It was usually translated as "prince regnant" in English and most other languages, and less often as "grand duke". "Domnitor" is an adjective derived from the Romanian word "''domn''" (''lord'' or ''ruler'') and, in turn, from the Latin " Dominus". The title Domn had been in use since the Middle Ages and it is also the Romanian equivalent to the Slavic Hospodar. Moldavian and Wallachian rulers had used this term for their title of authority as the head of state, while " voievod" represented the military rank as the head of the army. The title acquired an officially recognized meaning after Moldavia and Wallachia united to form the Romanian United Principalities under Alexander John I, who had become the ruler of both states since 1859. Alexander John abdicated in 1866 and was succeeded by Carol I, who promulgated the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania 500 Lei Banknote Of 1936, King Carol II Of Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a mainly continental climate, and an area of with a population of 19 million people. Romania is the twelfth-largest country in Europe and the sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Europe's second-longest river, the Danube, empties into the Danube Delta in the southeast of the country. The Carpathian Mountains cross Romania from the north to the southwest and include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Bucharest is the country's largest urban area and financial centre. Other major urban areas include Cluj-Napoca, Timișoara, Iași, Constanța and Brașov. Settlement in the territory of modern Romania began in the Lower Paleolithic, later becoming the Dacian Kingdom before Roman conquest and Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1883 5lei Romania
Events January * January 4 – ''Life'' magazine is founded in Los Angeles, California, United States. * January 10 – A fire at the Newhall Hotel in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States, kills 73 people. * January 16 – The Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act, establishing the United States civil service, is passed. * January 19 – The first electric lighting system employing overhead wires begins service in Roselle, New Jersey, United States, installed by Thomas Edison. February * February 15 – Tokyo Electrical Lightning Grid, predecessor of Tokyo Electrical Power (TEPCO), one of the largest electrical grids in Asia and the world, is founded in Japan. * February 16 – The ''Ladies' Home Journal'' is published for the first time, in the United States. * February 23 – Alabama becomes the first U.S. state to enact an antitrust law. * February 28 – The first vaudeville theater is opened, in Boston, Massachusetts. * February &ndas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1870 20 Lei
Year 187 ( CLXXXVII) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Quintius and Aelianus (or, less frequently, year 940 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 187 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Septimius Severus marries Julia Domna (age 17), a Syrian princess, at Lugdunum (modern-day Lyon). She is the youngest daughter of high-priest Julius Bassianus – a descendant of the Royal House of Emesa. Her elder sister is Julia Maesa. * Clodius Albinus defeats the Chatti, a highly organized German tribe that controlled the area that includes the Black Forest. By topic Religion * Olympianus succeeds Pertinax as bishop of Byzantium (until 198). Births * Cao Pi, Chinese emperor of the Cao Wei state (d. 226) * Gu Shao, Chinese official and politici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |