|
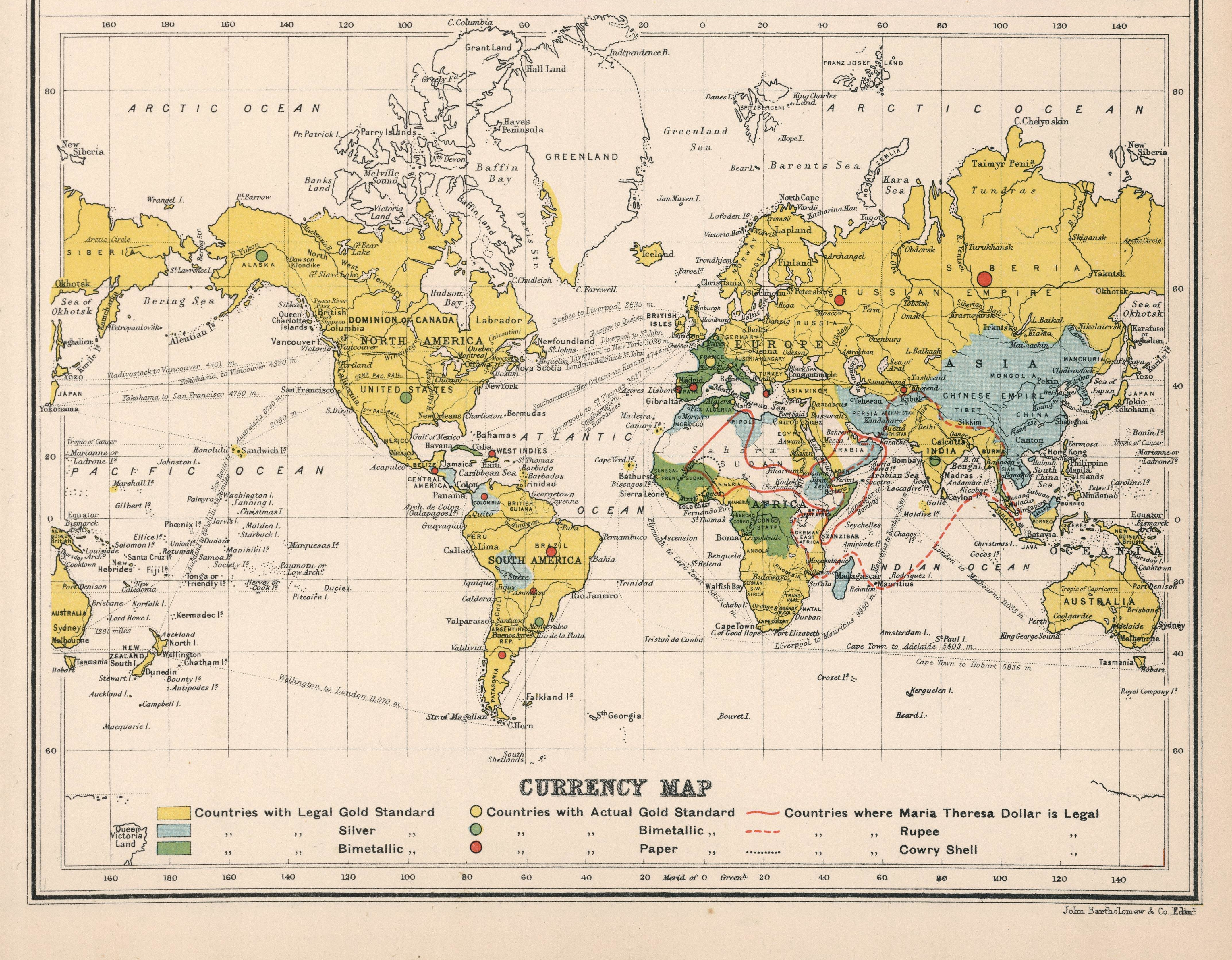
Bimetallism
Bimetallism, also known as the bimetallic standard, is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed Exchange rate, rate of exchange between them. For scholarly purposes, "proper" bimetallism is sometimes distinguished as permitting that both gold and silver money are legal tender in unlimited amounts and that gold and silver may be taken to be coined by the Mint (facility), government mints in unlimited quantities. This distinguishes it from "limping standard" bimetallism, where both gold and silver are legal tender but only one is freely coined (e.g. the monies of France, Germany, and the United States after 1873), and from "trade" bimetallism, where both metals are freely coined but only one is legal tender and the other is used as "trade money" (e.g. most monies in western Europe from the 13th to 18th centuries). Economists also distinguish ''legal'' bimeta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the late 1920s to 1932 as well as from 1944 until 1971 when the United States unilaterally terminated convertibility of the US dollar to gold, effectively ending the Bretton Woods system. Many states nonetheless hold substantial gold reserves. Historically, the silver standard and bimetallism have been more common than the gold standard. The shift to an international monetary system based on a gold standard reflected accident, network externalities, and path dependence. Great Britain accidentally adopted a ''de facto'' gold standard in 1717 when Isaac Newton, then-master of the Royal Mint, set the exchange rate of silver to gold too low, thus causing silver coins to go out of circulation. As Great Britain became the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
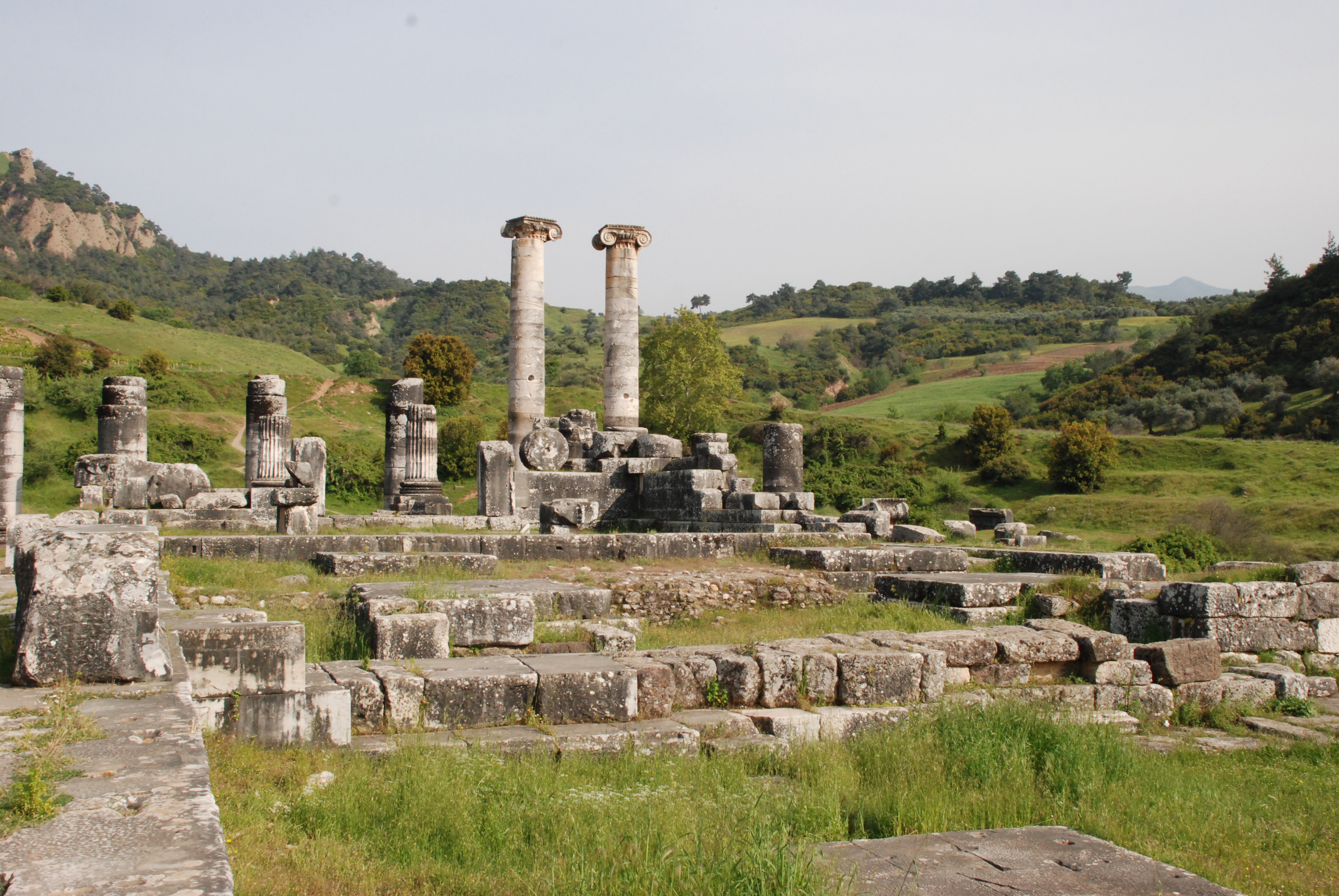
Croeseid
The Croeseid, anciently ''Kroiseioi stateres'', was a type of coin, either in gold or silver, which was minted in Sardis by the king of Lydia Croesus (561–546 Before Christ, BC) from around 550 BC. Croesus is credited with issuing the first true gold coins with a standardised purity for general circulation, and the world's first bimetallism, bimetallic monetary system. Precedents Before Croesus, his father Alyattes of Lydia, Alyattes had already started to mint various types of non-standardized coins. They were made in a naturally occurring material called electrum, a variable mix of gold and silver (with about 54% gold and 44% silver), and were in use in Lydia, its capital city Sardis and surrounding areas for about 80 years before Croesus' reign as King of Lydia. The unpredictability of electrum coins' composition implied that they had a variable value, which greatly hampered the development of standardised coinage. The royal symbol stamped on the coin, similar to a seal, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydia
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis. At some point before 800 BC, the Lydian people achieved some sort of political cohesion, and existed as an independent kingdom by the 600s BC. At its greatest extent, during the 7th century BC, it covered all of western Anatolia. In 546 BC, it became a Lydia (satrapy), satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire, known as ''Sparda'' in Old Persian. In 133 BC, it became part of the Roman Republic, Roman Asia (Roman province), province of Asia. Lydian coins, made of electrum, are among the oldest in existence, dated to around the 7th century BC. Geography Lydia is generally located east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provinces of Uşak Province, Uşak, Manisa Province, Manisa and inland İzmir Province, İzmir.Rhodes, P.J. ''A History of the Classical Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monometallism
Metallism is the economic principle that the Value (economics) , value of money derives from the purchasing power of the commodity upon which it is based. The currency in a metallist monetary system may be made from the commodity itself (commodity money) or it may use representative money, tokens (such as national banknotes) redeemable in that commodity. Georg Friedrich Knapp (1842–1926) coined the term "metallism" to describe monetary systems using coin minted in silver, gold or other metals. In metallist economic theory, the value of the currency derives from the market economy , market value of the commodity upon which it is based independent of its monetary role. Carl Menger (1840–1921) theorized that money came about when buyers and sellers in a market agreed on a common commodity as a medium of exchange in order to reduce the costs of barter. The intrinsic value of that commodity must be sufficient to make it highly "saleable", or readily accepted as payment. In this sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monetary Standard
A monetary system is a system where a government manages money in a country's economy. Modern monetary systems usually consist of the national treasury, the mint, the central banks and commercial banks. Commodity money system A commodity money system is a type of monetary system in which a commodity such as gold or seashells is made the unit of value and physically used as money. The money retains its value because of its physical properties. In some cases, a government may stamp a metal coin with a face, value or mark that indicates its weight or asserts its purity, but the value remains the same even if the coin is melted down. Commodity-backed money One step away from commodity money is "commodity-backed money", also known as "representative money". Many currencies have consisted of bank-issued notes which have no inherent physical value, but which may be exchanged for a precious metal, such as gold. This is known as the gold standard. A silver standard was widespread af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monetary Unit
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific environment over time, especially for people in a nation state. Under this definition, the British Pound sterling (£), euros (€), Japanese yen (¥), and U.S. dollars (US$) are examples of (government-issued) fiat currencies. Currencies may act as stores of value and be traded between nations in foreign exchange markets, which determine the relative values of the different currencies. Currencies in this sense are either chosen by users or decreed by governments, and each type has limited boundaries of acceptance; i.e., legal tender laws may require a particular unit of account for payments to government agencies. Other definitions of the term ''currency'' appear in the respective synonymous articles: banknote, coin, and money. This article use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Standard
The silver standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is a fixed weight of silver. Silver was far more widespread than gold as the monetary standard worldwide, from the Sumerians 3000 BC until 1873. Following the discovery in the 16th century of large deposits of silver at the Cerro Rico in Potosí, Bolivia, an international silver standard came into existence in conjunction with the Spanish pieces of eight. These silver dollar coins were an international trading currency for nearly four hundred years. The move away from the silver to the gold standard began in the 18th century when Great Britain set the gold guinea’s price in silver higher than international prices, on the recommendation of Sir Isaac Newton, thus attracting gold and putting Great Britain on a de facto gold standard. Great Britain formalised the gold standard in 1821 and introduced it to its colonies afterwards. Imperial Germany’s move to the gold standard in 1873 trigger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Kindleberger
Charles Poor Kindleberger (October 12, 1910 – July 7, 2003) was an American economic historian and author of over 30 books. His 1978 book ''Manias, Panics, and Crashes'', about speculative stock market bubbles, was reprinted in 2000 after the dot-com bubble. He is well known for his role in developing what would become hegemonic stability theory, arguing that a hegemonic power was needed to maintain a stable international monetary system. He has been referred to as "the master of the genre" on financial crisis by ''The Economist''. Life Background Kindleberger was born in New York City on October 12, 1910. He graduated from the Kent School in 1928, the University of Pennsylvania in 1932, and received a PhD from Columbia University in 1937. During the summer of 1931, he traveled to Europe and attended a seminar hosted by Salvador de Madariaga, but, when the latter was appointed Spanish Ambassador to the United States, Kindleberger attended lectures at the Graduate Institute o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allen & Unwin
George Allen & Unwin was a British publishing company formed in 1911 when Sir Stanley Unwin purchased a controlling interest in George Allen & Co. It became one of the leading publishers of the twentieth century and established an Australian subsidiary in 1976. In 1990 Allen & Unwin was sold to HarperCollins, and the Australian branch was the subject of a management buy-out. George Allen & Unwin in the UK George Allen & Sons was established in 1871 by George Allen, with the backing of John Ruskin, becoming George Allen & Co. Ltd. in 1911 when it merged with Swan Sonnenschein and then George Allen & Unwin on 4 August 1914 as a result of Stanley Unwin's purchase of a controlling interest. Frank Arthur Mumby and Frances Helena Swan Stallybrass, Unwin's son Rayner S. Unwin and his nephew Philip helped him to run the company, which published works by Bertrand Russell, Arthur Waley, Roald Dahl, Lancelot Hogben and Thor Heyerdahl. It became well known as J. R. R. Tolkien's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marc Flandreau
Marc or MARC may refer to: People * Marc (given name), people with the first name * Marc (surname), people with the family name Acronyms * MARC standards, a data format used for library cataloging, * MARC Train, a regional commuter rail system serving Maryland, Washington, D.C., and eastern West Virginia * MARC (archive), a computer-related mailing list archive * M/A/R/C Research, a marketing research and consulting firm * Massachusetts Animal Rights Coalition, a non-profit, volunteer organization * Matador Automatic Radar Control, a guidance system for the Martin MGM-1 Matador cruise missile * Mid-America Regional Council, the Council of Governments and the Metropolitan Planning Organization for the bistate Kansas City region * Midwest Association for Race Cars, a former American stock car racing organization * Revolutionary Agrarian Movement of the Bolivian Peasantry (''Movimiento Agrario Revolucionario del Campesinado Boliviano''), a defunct right-wing political moveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angela Redish
Angela Redish is a professor of economics at the Vancouver School of Economics at the University of British Columbia and the acting President of the Canadian Economics Association. From 2001 to 2006, Redish served as the Head of Department of Economics at the University of British Columbia and was awarded The President's Medal of Excellence by the University of British Columbia in 2018 for her contributions towards establishing the Vancouver School of Economics. Education and work Redish was born in United Kingdom and moved to Hamilton, Ontario, Canada with her family during her teen years. She graduated from Wilfrid Laurier University having earned a B.A. in economics. Following this, she took a two-year break to work at Cuso International as a volunteer in Papua New Guinea. Upon returning to Canada, she received a Ph.D. from the University of Western Ontario. Shortly after, she joined the University of British Columbia as an assistant professor of economics at the Vancouve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |