|
Roman Jackiw
Roman Wladimir Jackiw (; ; November 8, 1939 – June 14, 2023) was a Polish-born American theoretical physicist and Dirac Medallist. Biography Born in Lubliniec, Poland in 1939 to a Ukrainian family, the family later moved to Austria and Germany before settling in New York City when Jackiw was about 10. Jackiw earned his undergraduate degree from Swarthmore College and his PhD from Cornell University in 1966 under Hans Bethe and Kenneth Wilson. He was a professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Center for Theoretical Physics from 1969 until his retirement. He retained his affiliation in emeritus status in 2019. Jackiw co-discovered the chiral anomaly, which is also known as the Adler–Bell–Jackiw anomaly. In 1969, he and John Stewart Bell published their explanation, which was later expanded and clarified by Stephen L. Adler, of the observed decay of a neutral pion into two photons. This decay is forbidden by a symmetry of classical electrodynamics, but Bell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubliniec
Lubliniec (, ; Silesian language, Silesian: ''Lublini'c'') is a town in southern Poland with 23,784 inhabitants (2019). It is the capital of Lubliniec County, part of Silesian Voivodeship. Geography Lubliniec is situated in the north of the historic Upper Silesia region at the rim of the Upper Silesian Industrial Region, about northwest of Katowice. It is an important rail hub, with two major lines crossing there – east-west (from Częstochowa to Opole) and south–north (from Katowice to Poznań) – and a site of Light industry, light and chemical industry. The surrounding area is characterized by extended forests (''Lasy Lublinieckie''), including the Upper Liswarta Forests Landscape Park north of the town. History Lubliniec was established about 1270 by the Silesian Piasts, Piast duke Władysław Opolski, Władysław of Opole on the road leading from his residence Opole to Kraków. It was part of the Duchy of Opole within fragmented Piast-ruled Kingdom of Poland (1025� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Vacuum
In quantum field theory, the theta vacuum is the semi-classical vacuum state of non- abelian Yang–Mills theories specified by the vacuum angle ''θ'' that arises when the state is written as a superposition of an infinite set of topologically distinct vacuum states. The dynamical effects of the vacuum are captured in the Lagrangian formalism through the presence of a ''θ''-term which in quantum chromodynamics leads to the fine tuning problem known as the strong CP problem. It was discovered in 1976 by Curtis Callan, Roger Dashen, and David Gross, and independently by Roman Jackiw and Claudio Rebbi. Yang–Mills vacuum Topological vacua The semi-classical vacuum structure of non-abelian Yang–Mills theories is often investigated in Euclidean spacetime in some fixed gauge such as the temporal gauge A_0 = 0. Classical ground states of this theory have a vanishing field strength tensor which corresponds to pure gauge configurations A_i = i\Omega \nabla_i \Omega^, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Field Theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines Field theory (physics), field theory and the principle of relativity with ideas behind quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct physical models of subatomic particles and in condensed matter physics to construct models of quasiparticles. The current standard model of particle physics is based on QFT. History Quantum field theory emerged from the work of generations of theoretical physicists spanning much of the 20th century. Its development began in the 1920s with the description of interactions between light and electrons, culminating in the first quantum field theory—quantum electrodynamics. A major theoretical obstacle soon followed with the appearance and persistence of various infinities in perturbative calculations, a problem only resolved in the 1950s with the invention of the renormalization procedure. A second major barrier came with QFT's apparent inabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Electrodynamics
Classical electromagnetism or classical electrodynamics is a branch of physics focused on the study of interactions between electric charges and currents using an extension of the classical Newtonian model. It is, therefore, a classical field theory. The theory provides a description of electromagnetic phenomena whenever the relevant length scales and field strengths are large enough that quantum mechanical effects are negligible. For small distances and low field strengths, such interactions are better described by quantum electrodynamics which is a quantum field theory. History The physical phenomena that electromagnetism describes have been studied as separate fields since antiquity. For example, there were many advances in the field of optics centuries before light was understood to be an electromagnetic wave. However, the theory of electromagnetism, as it is currently understood, grew out of Michael Faraday's experiments suggesting the existence of an electromagnetic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can move no faster than the speed of light measured in vacuum. The photon belongs to the class of boson particles. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While Planck was trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, he proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pion
In particle physics, a pion (, ) or pi meson, denoted with the Greek alphabet, Greek letter pi (letter), pi (), is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more generally, the lightest hadrons. They are unstable, with the charged pions and decaying after a mean lifetime of 26.033 nanoseconds ( seconds), and the neutral pion decaying after a much shorter lifetime of 85 attoseconds ( seconds). Charged pions most often particle decay, decay into muons and muon neutrinos, while neutral pions generally decay into gamma rays. The exchange of virtual particle, virtual pions, along with vector meson, vector, rho meson, rho and omega mesons, provides an explanation for the nuclear force, residual strong force between nucleons. Pions are not produced in radioactive decay, but commonly are in high-energy collisions between hadrons. Pions also result from some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen L
Stephen or Steven is an English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or " protomartyr") of the Christian Church. The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ( ); related names that have found some currency or significance in English include Stefan (pronounced or in English), Esteban (often pronounced ), and the Shakespearean Stephano ( ). Origins The name "Stephen" (and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Stewart Bell
John Stewart Bell (28 July 1928 – 1 October 1990) was a physicist from Northern Ireland and the originator of Bell's theorem, an important theorem in quantum mechanics, quantum physics regarding hidden-variable theory, hidden-variable theories. In 2022, the Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Alain Aspect, John Clauser, and Anton Zeilinger for work on Bell test, Bell inequalities and the Aspect's experiment, experimental validation of Bell's theorem. Biography Early life and work Bell was born in Belfast, Northern Ireland to a working class family. Due to financial hardship, neither parent and none of his three older siblings completed high school, typically dropping out of school by age 14 to work. When he was 11 years old, he decided to be a scientist, and encouraged by his mother, at 16 he graduated from Belfast Technical High School. Then in an exceptionally rare occurrence for someone of his background, Bell attended the Queen's University of Belfast, where, in 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
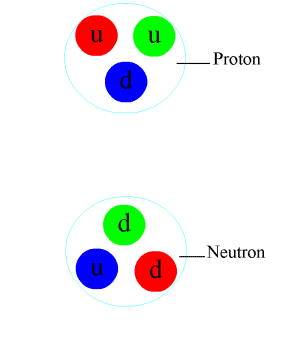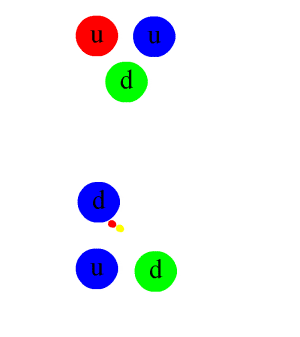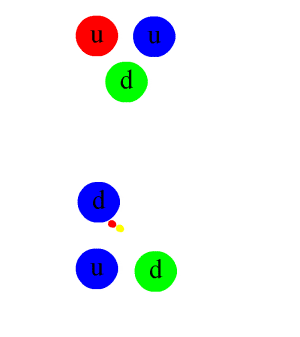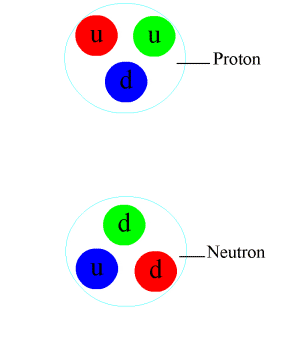
Chiral Anomaly
In theoretical physics, a chiral anomaly is the anomalous nonconservation of a chiral current. In everyday terms, it is analogous to a sealed box that contained equal numbers of left and right-handed bolts, but when opened was found to have more left than right, or vice versa. Such events are expected to be prohibited according to classical conservation laws, but it is known there must be ways they can be broken, because we have evidence of charge–parity non-conservation ("CP violation"). It is possible that other imbalances have been caused by breaking of a ''chiral law'' of this kind. Many physicists suspect that the fact that the observable universe contains more matter than antimatter is caused by a chiral anomaly. Research into chiral symmetry breaking laws is a major endeavor in particle physics research at this time. Informal introduction The chiral anomaly originally referred to the anomalous decay rate of the neutral pion, as computed in the current algebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emeritus
''Emeritus/Emerita'' () is an honorary title granted to someone who retires from a position of distinction, most commonly an academic faculty position, but is allowed to continue using the previous title, as in "professor emeritus". In some cases, the term is conferred automatically upon all persons who retire at a given rank, but in others, it remains a mark of distinguished performance (usually in the area of research) awarded selectively on retirement. It is also used when a person of distinction in a profession retires or hands over the position, enabling their former rank to be retained in their title. The term ''emeritus'' does not necessarily signify that a person has relinquished all the duties of their former position, and they may continue to exercise some of them. In descriptions of deceased professors emeriti listed at U.S. universities, the title ''emeritus'' is replaced by an indication of the years of their appointments, except in obituaries, where it may be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT Center For Theoretical Physics
The MIT Center for Theoretical Physics (CTP) is the hub of theoretical nuclear physics, particle physics, and quantum information research at MIT. It is a subdivision of MIT Laboratory for Nuclear Science and Department of Physics. Research CTP activities range from string theory and cosmology at the highest energies down through unification and beyond-the-standard-model physics, through the standard model, to QCD, hadrons, quark matter, and nuclei at the low energy scale. Members of the CTP are also currently working on quantum computation and on energy policy. The breadth and depth of research in nuclear, particle, string, and gravitational physics at the CTP makes it a unique environment for researchers in these fields. Members In addition to the 15 MIT faculty members working in the CTP, at any one time there are roughly a dozen postdoctoral fellows, and as many, or more, long-term visitors working at the postdoctoral or faculty level. The CTP supports 25-35 MIT graduate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Institute Of Physics
The American Institute of Physics (AIP) promotes science and the profession of physics, publishes physics journals, and produces publications for scientific and engineering societies. The AIP is made up of various member societies. Its corporate headquarters are at the American Center for Physics in College Park, Maryland, but the institute also has offices in Melville, New York, and Beijing. Historical overview The AIP was founded in 1931 as a response to lack of funding for the sciences during the Great Depression. /www.aip.org/aip/history "History of AIP" American Institute of Physics. July 2010. The AIP was founded in 1931 at a joint meeting between four physics societies: the American Physical Society, the Optical Society of America, the Acoustical Society of America, and the Society of Rheology. These were soon joined by the American Association of Physics Teachers, for a total of five societies. It formally incorporated in 1932 consisting of five original "member so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |