|
Richard Vicars Boyle
Richard Vicars Boyle (1822–1908) was an Irish civil engineer, noted for his part in the Siege of Arrah in 1857, and as a railway pioneer in Japan. Life Born in Dublin on 14 March 1822, he was from a Scots-Irish background, the third son of Vicars Armstrong Boyle; his mother was Sophia, eldest daughter of David Courtney of Dublin. After education at a private school and two years' service on the trigonometrical survey of Ireland he became a pupil to Charles Blacker Vignoles. When he had finished his articles, he was engaged on railway construction in Ireland, at first as assistant to William Dargan, who employed him on the Belfast and Armagh and the Dublin and Drogheda Railways. In 1845, under Sir John Benjamin Macneill, he surveyed and laid out part of the Great Southern and Western Railway, and in 1846–7 was chief engineer for the Longford and Sligo Railway. In the autumn of 1852, he laid out railways and waterworks in Spain as chief assistant to George Willoughby Hemans, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Vicars Boyle 1
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", "Dick", "Dickon", " Dickie", "Rich", "Rick", "Rico", "Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English, German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Catalan "Ricard" and the Italian "Riccardo", among others (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * Richard Anderson (other) * Richard Cartwright (other) * Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vincent Eyre
Major-General Sir Vincent Eyre (22 January 1811 – 22 September 1881) was an officer in the Indian Army, who saw active service in India and Afghanistan. Early life Born in Portsdown, Portsmouth on 22 January 1811, Eyre was the third son of Captain Henry Eyre and was educated at Norwich School. Military career In 1827, he entered the Addiscombe Military Seminary and the service of the East India Company. He joined the Bengal Artillery in 1828, and in 1829 arrived in Calcutta. In 1837 he was appointed to the horse artillery and promoted Lieutenant. Two years later, he was appointed Commissary of Ordnance to the Cabul field force. In January 1842, During the First Anglo-Afghan War, Eyre and his family were captured by Akbar Khan. During nearly nine months in captivity, Eyre kept a diary describing his experiences, illustrated by the sketches of other officers and ladies. The manuscript was smuggled out to a friend in British India and was then published in England as ''Military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institution Of Civil Engineers
The Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) is an independent professional association for civil engineers and a charitable body in the United Kingdom. Based in London, ICE has over 92,000 members, of whom three-quarters are located in the UK, while the rest are located in more than 150 other countries. The ICE aims to support the civil engineering profession by offering professional qualification, promoting education, maintaining professional ethics, and liaising with industry, academia and government. Under its commercial arm, it delivers training, recruitment, publishing and contract services. As a professional body, ICE aims to support and promote professional learning (both to students and existing practitioners), managing professional ethics and safeguarding the status of engineers, and representing the interests of the profession in dealings with government, etc. It sets standards for membership of the body; works with industry and academia to progress engineering standards a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kensal Green Cemetery
Kensal Green Cemetery is a cemetery in the Kensal Green area of Queens Park in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea in London, England. Inspired by Père Lachaise Cemetery in Paris, it was founded by the barrister George Frederick Carden.The Founding of Kensal Green Cemetery Accessed 7 February 2014 The cemetery opened in 1833 and comprises of grounds, including two conservation areas, adjoining a canal. The cemetery is home to at least 33 species of bird and other wildlife. This distinctive cemetery has memorials ranging from large mausoleums housing the rich and famous to many distinctive smaller graves and includes special areas dedicated to the very young. It has three chapels and serves all faiths. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
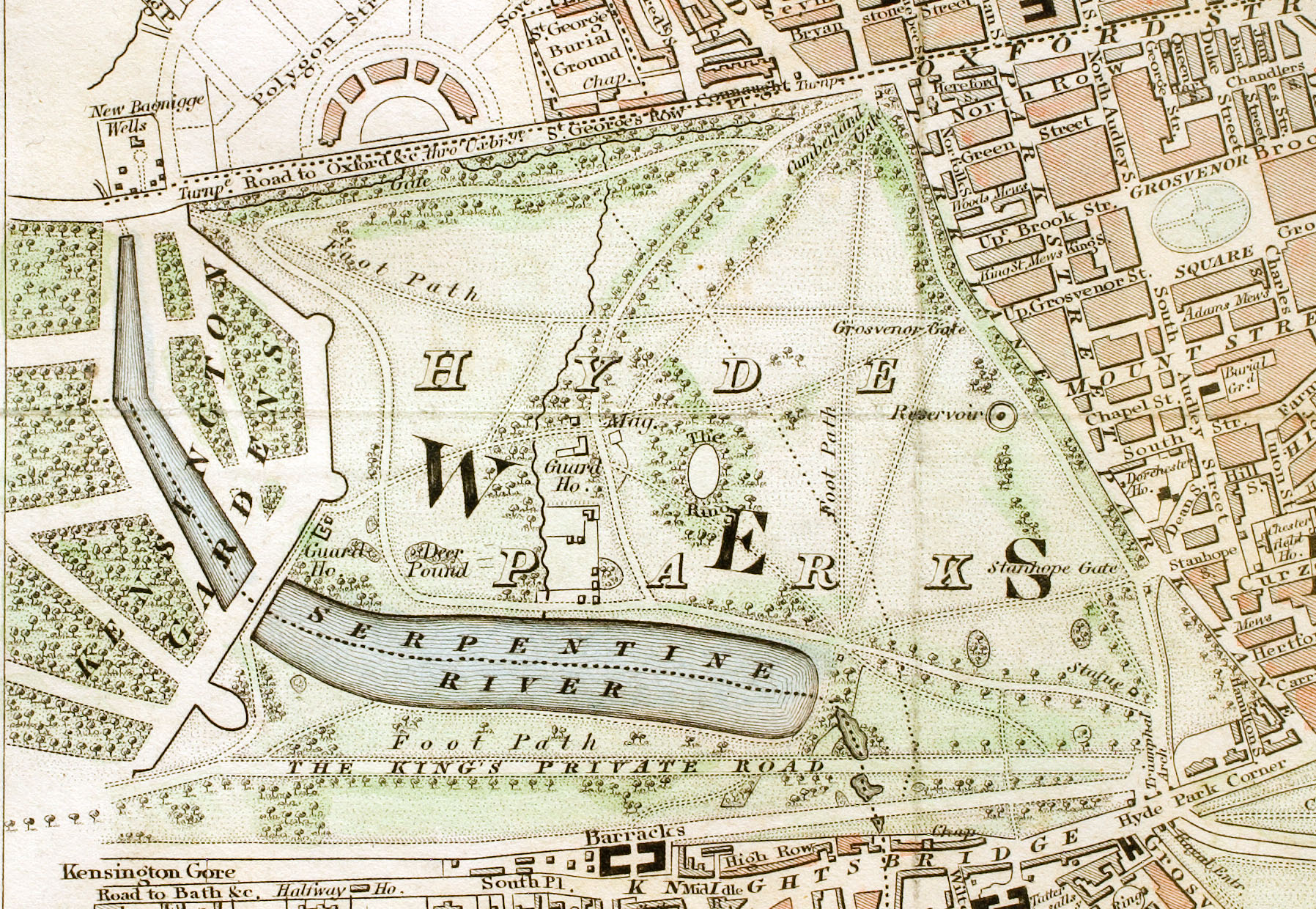
Hyde Park, London
Hyde Park is a Grade I-listed major park in Westminster, Greater London, the largest of the four Royal Parks that form a chain from the entrance to Kensington Palace through Kensington Gardens and Hyde Park, via Hyde Park Corner and Green Park past the main entrance to Buckingham Palace. The park is divided by the Serpentine and the Long Water lakes. The park was established by Henry VIII in 1536 when he took the land from Westminster Abbey and used it as a hunting ground. It opened to the public in 1637 and quickly became popular, particularly for May Day parades. Major improvements occurred in the early 18th century under the direction of Queen Caroline. Several duels took place in Hyde Park during this time, often involving members of the nobility. The Great Exhibition of 1851 was held in the park, for which The Crystal Palace, designed by Joseph Paxton, was erected. Free speech and demonstrations have been a key feature of Hyde Park since the 19th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institution Of Electrical Engineers
The Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) was a British professional organisation of electronics, electrical, manufacturing, and Information Technology professionals, especially electrical engineers. It began in 1871 as the Society of Telegraph Engineers. In 2006, it changed its name to the Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET). Notable past presidents have included Lord Kelvin (1889), Sir Joseph Swan (1898) and Sebastian de Ferranti (1910–11). Notable chairmen include John M. M. Munro (1910–11). History The IEE was founded in 1871 as the Society of Telegraph Engineers, changed its name in 1880 to the Society of Telegraph Engineers and Electricians and changed to the Institution of Electrical Engineers in 1888. It was Incorporated by a Royal Charter in 1921. In 1988 the Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) merged with the Institution of Electronic and Radio Engineers (IERE), originally the British Institution of Radio Engineers (Brit IRE) foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Morel (railway Engineer)
Edmund Morel (17 November 1840 – 5 November 1871) was a British civil engineer who was engaged in railway construction in many countries, including New Zealand, Australia, and Japan. He was the first foreign Engineer-in-Chief appointed by the Japanese government, for guiding and supervising railway construction. Biography Morel was born in London on 17 November 1840 (recorded as 1841 on his gravestone). He studied civil engineering at King's College London. In 1863 Morel was in Melbourne, Australia (see his letters) and between 1862 and 1863, Morel was involved in railway construction in New Zealand followed by a period in Australia between 1864 and 1865. In 1867, Morel was active in British North Borneo for the Labuan Coal Company, building railways and sinking mining shafts, living at Labuan island, when he was invited to Japan by British envoy Sir Harry Parkes. During his short assignment he made significant proposals to the Japanese government regarding engineerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Government Railways
The Japanese Government Railways (JGR) was the national railway system directly operated by the Japanese Ministry of Railways ( ja, 鉄道省, Tetsudō-shō, ) until 1949. It was a predecessor of Japanese National Railways and the later Japan Railways Group. Name The English name "Japanese Government Railways" was what the Ministry of Railways (established in 1920) used to call its own and sometimes the ministry itself as a railway operator. Other English names for the government railways include Imperial Japanese Government Railways and Imperial Government Railways, which were mainly used prior to the establishment of the ministry. This article covers the railways operated by the central government of Japan from 1872 to 1949 notwithstanding the official English name of the system of each era. Network By the end of World War II in 1945, the Japanese Government Railways operated on the main Japanese islands of Honshū, Hokkaidō, Kyūshū, Shikoku and Karafuto. The railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Companion Of The Order Of The Star Of India
The Most Exalted Order of the Star of India is an order of chivalry founded by Queen Victoria in 1861. The Order includes members of three classes: # Knight Grand Commander ( GCSI) # Knight Commander ( KCSI) # Companion ( CSI) No appointments have been made since the 1948 New Year Honours, shortly after the Partition of India in 1947. With the death in 2009 of the last surviving knight, the Maharaja of Alwar, the order became dormant. The motto of the order was "Heaven's Light Our Guide". The Star of India emblem, the insignia of order and the informal emblem of British India, was also used as the basis of a series of flags to represent the Indian Empire. The order was the fifth most senior British order of chivalry, following the Order of the Garter, Order of the Thistle, Order of St Patrick and Order of the Bath. It is the senior order of chivalry associated with the British Raj; junior to it is the Most Eminent Order of the Indian Empire, and there is also, for women ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Mutiny Medal
__NOTOC__ The Indian Mutiny Medal was a campaign medal approved in August 1858, for officers and men of British and Indian units who served in operations in suppression of the Indian Mutiny. The medal was initially sanctioned for award to troops who had been engaged in action against the mutineers. However, in 1868 the award was extended to all those who had borne arms or who had been under fire, including such people as members of the Indian judiciary and the Indian civil service, who were caught up in the fighting.John Sly. "Battle Stars". ''Ancestors'', issue 57, May 2007, pp36–43. Some 290,000 medals were awarded.British Battles and Medals, p136 The obverse depicts the diademed head of a young Queen Victoria with the legend VICTORIA REGINA, designed by William Wyon.British Battles and Medals, p136The reverse shows a helmeted Britannia holding a wreath in her right hand and a union shield on her left arm. She is standing in front of a lion. Above is the word INDIA, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bordering the Strait of Malacca to the west, the Singapore Strait to the south, the South China Sea to the east, and the Straits of Johor to the north. The country's territory is composed of one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet; the combined area of these has increased by 25% since the country's independence as a result of extensive land reclamation projects. It has the third highest population density in the world. With a multicultural population and recognising the need to respect cultural identities of the major ethnic groups within the nation, Singapore has four official languages: English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil. English is the lingua franca and numerous public services are available only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penang
Penang ( ms, Pulau Pinang, is a Malaysian state located on the northwest coast of Peninsular Malaysia, by the Malacca Strait. It has two parts: Penang Island, where the capital city, George Town, is located, and Seberang Perai on the Malay Peninsula. They are connected by Malaysia's two longest road bridges, the Penang Bridge and the Sultan Abdul Halim Muadzam Shah Bridge; the latter is also the second longest oversea bridge in Southeast Asia. The second smallest Malaysian state by land mass, Penang is bordered by Kedah to the north and the east, and Perak to the south. Penang is the 8th most populated state in Malaysia. Its population stood at nearly 1.767 million , while its population density was as high as . It has among the nation's highest population densities and is one of the country's most urbanised states. Seberang Perai is Malaysia's second-largest city by population. Its heterogeneous population is highly diverse in ethnicity, culture, language and religi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)