|
Rhachiosteus
''Rhachiosteus'' is an extinct monospecific genus of arthrodire placoderm from the Middle to Late Devonian of Germany. It is known only from a single specimen, which may be a larval or juvenile form, as the skull of said specimen is only 19 millimetres long. Phylogeny ''Rhachiosteus'' is a basal member of the clade Pachyosteomorphi, the sister taxon to Coccosteomorphi, which together are the two main sub-clades of Eubrachythoraci. The cladogram below shows the phylogeny A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spe ... of ''Rhachiosteus'': References Arthrodires Placoderms of Europe Arthrodire genera {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachyosteomorphi
Pachyosteomorphi is an extinct clade of arthrodire placoderms within the Eubrachythoraci (of the suborder Brachythoraci), armored fish most diverse during the Devonian. Most are considered to be pelagic (open ocean) long-distance swimmers, leading to their widespread distribution beginning from at least the Middle Devonian period. Phylogeny Pachyosteomorphi is the sister taxon to Coccosteomorphi, which together are the two main sub-clades of Eubrachythoraci. Pachyosteomorphi can be further sub-divided into Aspinothoracidi and Dunkleosteoidea, as shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... below: References Arthrodires {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janiosteus Timanicus
''Janiosteus'' is an extinct monospecific genus of placoderm arthrodire from the Middle Devonian: Late Givetian stage found in Timan, Russia. Phylogeny ''Janiosteus'' is a member of Panxiosteidae. In the 2010 Carr & Hlavin phylogenetic study, Panxiosteidae was recognized as the sister taxon to the family Dunkleosteidae, which together comprised the superfamily Dunkleosteoidea (one of the three major clades of Eubrachythoraci). The phylogeny of ''Janiosteus'' within Panxiosteidae is shown in the cladogram below from the 2013 Zhu & Zhu study: However, the subsequent 2016 Zhu ''et al.'' study using a larger morphological dataset recovered Panxiosteidae well outside of Dunkleosteoidea, instead within Coccosteomorphi and then Coccosteoidea as the sister group of Coccosteidae Coccosteidae is a family of arthrodire placoderms from the Early to Late Devonian. Fossils appear in various strata in Europe, North America and China. Phylogeny Coccosteidae belongs to the larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panxiosteus Ocullus
''Panxiosteus'' is an extinct monospecific genus of placoderm arthrodire from the Middle Devonian: Givetian stage of Yunnan province, China. Phylogeny ''Panxiosteus'' is a member of Panxiosteidae. In the 2010 Carr & Hlavin phylogenetic study, Panxiosteidae was recognized as the sister taxon to the family Dunkleosteidae, which together comprised the superfamily Dunkleosteoidea (one of the three major clades of Eubrachythoraci). The phylogeny of ''Panxiosteus'' within Panxiosteidae is shown in the cladogram below from the 2013 Zhu & Zhu study: However, the subsequent 2016 Zhu ''et al.'' study using a larger morphological dataset recovered Panxiosteidae well outside of Dunkleosteoidea, instead within Coccosteomorphi and then Coccosteoidea as the sister group of Coccosteidae Coccosteidae is a family of arthrodire placoderms from the Early to Late Devonian. Fossils appear in various strata in Europe, North America and China. Phylogeny Coccosteidae belongs to the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plourdosteus Canadensis
''Plourdosteus'' is an extinct genus of placoderm arthrodire which was relatively widespread in Euramerica during the Givetian to Frasnian ages of the Devonian. Etymology The name ''Plourdosteus'' commemorates the Plourde family at Miguasha National Park. Taxonomy ''Plourdosteus'' was previously assigned to the family Plourdosteidae within the Coccosteomorphi. However, subsequent studies found the family Plourdosteidae to be polyphyletic and should be dismissed. ''Plourdosteus'' was then proposed to be a member of Panxiosteidae. In the 2010 Carr & Hlavin phylogenetic study, Panxiosteidae was recognized as the sister taxon to the family Dunkleosteidae, which together comprised the superfamily Dunkleosteoidea (one of the three major clades of Eubrachythoraci). The phylogeny of ''Plourdosteus'' within Panxiosteidae is shown in the cladogram below from the 2013 Zhu & Zhu study: However, the subsequent 2016 Zhu ''et al.'' study using a larger morphological dataset recover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panxiosteidae
Panxiosteidae is an extinct family of arthrodire placoderms that lived during the Devonian period. Phylogeny The family Panxiosteidae was erected by Wang in 1979. Members of the family are noted for showing morphologically intermediate traits between coccosteids and dunkleosteids. In the 2010 Carr & Hlavin phylogenetic study, Panxiosteidae was recognized as the sister taxon to the family Dunkleosteidae, which together comprised the superfamily Dunkleosteoidea (one of the three major clades of Eubrachythoraci). The phylogeny of Panxiosteidae from the 2013 Zhu & Zhu study is shown in the cladogram below: However, the subsequent 2016 Zhu ''et al.'' study using a larger morphological dataset recovered Panxiosteidae well outside of Dunkleosteoidea, instead within Coccosteomorphi and then Coccosteoidea as the sister group of Coccosteidae Coccosteidae is a family of arthrodire placoderms from the Early to Late Devonian. Fossils appear in various strata in Europe, North Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccosteidae
Coccosteidae is a family of arthrodire placoderms from the Early to Late Devonian. Fossils appear in various strata in Europe, North America and China. Phylogeny Coccosteidae belongs to the larger clade Coccosteomorphi, which together with its sister clade Pachyosteomorphi forms the group Eubrachythoraci. The phylogeny of Coccosteidae can be shown in the cladogram below: Genera '' Belgiosteus'' A genus of very large coccosteids. Species are found in Middle Devonian Belgium and China. '' Clarkosteus'' ''Coccosteus'' The type genus of the family. Numerous species are found in Middle to Upper Devonian strata throughout Europe and parts of North America. '' Dickosteus'' '' Jiuchengia'' The earliest known coccosteid from Late Emsian Yunnan province, China. It is distinguished from other coccosteids by having an elongated occipital. '' Livosteus'' A genus of very large coccosteids known from Middle to Late Devonian strata of Eastern Europe. '' Millerosteus'' A genus of ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccosteoidea
Coccosteoidea is an extinct superfamily of arthrodire placoderms that lived during the Devonian period. Phylogeny Eubrachythoraci is divided into the sister clades Pachyosteomorphi and Coccosteomorphi, the latter of which can be further sub-divided into the two sister superfamilies Coccosteoidea and Incisoscutoidea, as shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... below: References {{Taxonbar, from=Q30971248 Arthrodires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eubrachythoraci
Eubrachythoraci is an extinct clade of arthrodire placoderms within the suborder Brachythoraci, armored fish most diverse during the Devonian. Most are considered to be pelagic (open ocean) long-distance swimmers, leading to their widespread distribution beginning from at least the Middle Devonian period. Phylogeny Brachythoraci is divided into the large derived clade Eubrachythoraci and several basal groups: Buchanosteoidea, Homosteidae, and Holonematidae. (Although Holonematidae's membership in Brachythoraci is disputed.) Eubrachythoraci is then further divided into the sub-clades Coccosteomorphi and Pachyosteomorphi, the latter of which can be further sub-divided into Aspinothoracidi and Dunkleosteoidea, as shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccosteomorphi
Coccosteomorphi is an extinct clade of arthrodire placoderms within the Eubrachythoraci (of the suborder Brachythoraci), armored fish most diverse during the Devonian. Most are considered to be pelagic (open ocean) long-distance swimmers, leading to their widespread distribution beginning from at least the Middle Devonian period. Phylogeny Coccosteomorphi is the sister taxon to Pachyosteomorphi, which together are the two main sub-clades of Eubrachythoraci. Coccosteomorphi can be further sub-divided into Coccosteoidea and Incisoscutoidea, as shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... below: References Arthrodires {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
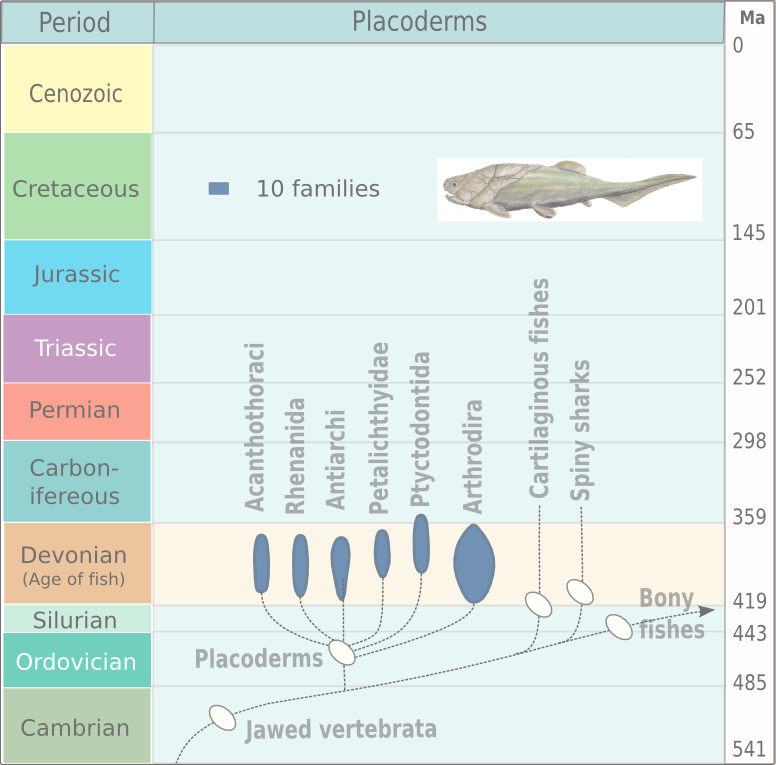
Arthrodire
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of Placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are protected by a bony ring, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus '' Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, '' Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed '' Rolfosteus'' measur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds ( taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frasnian
The Frasnian is one of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian Period. It lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Givetian Stage and followed by the Famennian Stage. Major reef-building was under way during the Frasnian Stage, particularly in western Canada and Australia. On land, the first forests were taking shape. In North America, the Antler orogeny peaked, which were contemporary with the Bretonic phase of the Variscan orogeny in Europe Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti .... The Frasnian coincides with the second half of the "charcoal gap" in the fossil record, a time when atmospheric oxygen levels were below 13 percent, the minimum necessary to sustain wildfires. North American subdivisions of the Frasnian include * Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)