|
Retrophyllum Vitiense
''Retrophyllum vitiense'' is a species of conifer in the family Podocarpaceae. It is a large evergreen rainforest emergent tree native to Fiji, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and Solomon Islands. Description ''Retrophyllum vitiense'' is a large evergreen tree. The trunk is usually erect, straight and terete. Large trees frequently feature a bole clear of branches for the first 20 meters and a buttressed trunk base. The crown of a young plant is often pyramidal while older trees generally have rounded or spreading crowns. Branches are ascending or spreading in the upper parts of the crown, but pendulous in the shaded parts. The initially brown and smooth bark weathers gray and develops vertical fissures with age, flaking in strips. The leaves are mostly flat with a decurrent base and a spreading blade connected by a short twisting petiole, but leading and cone-bearing shoots also have smaller scale-like leaves. The phyllotaxis is spiral though the leaves of the lateral shoots ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conifer
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant conifers are perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The great majority are trees, though a few are shrubs. Examples include cedars, Douglas-firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews.Campbell, Reece, "Phylum Coniferophyta". Biology. 7th. 2005. Print. P. 595 As of 1998, the division Pinophyta was estimated to contain eight families, 68 genera, and 629 living species. Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are ecologically important. They are the dominant plants over large areas of land, most notably the taiga of the Northern Hemisphere, but also in similar cool climates in mountains further south. Boreal conifers have many wintertime ada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring haploid male genetic material from the anther of a single flower to the stigma of another in cross-pollination. In a case of self-pollination, this process takes place from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agathis
''Agathis'', commonly known as kauri or dammara, is a genus of 22 species of evergreen tree. The genus is part of the ancient conifer family Araucariaceae, a group once widespread during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, but now largely restricted to the Southern Hemisphere except for a number of extant Malesian ''Agathis''.de Laubenfels, David J. 1988. Coniferales. P. 337–453 in Flora Malesiana, Series I, Vol. 10. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic. Description Mature kauri trees have characteristically large trunks, with little or no branching below the crown. In contrast, young trees are normally conical in shape, forming a more rounded or irregularly shaped crown as they achieve maturity.Whitmore, T.C. 1977. ''A first look at Agathis''. Tropical Forestry Papers No. 11. University of Oxford Commonwealth Forestry Institute. The bark is smooth and light grey to grey-brown, usually peeling into irregular flakes that become thicker on more mature trees. The branch struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacrydium
''Dacrydium'' is a genus of conifers belonging to the podocarp family Podocarpaceae. Sixteen species of evergreen dioecious trees and shrubs are presently recognized. The genus was first described by Solander in 1786, and formerly included many more species, which were divided into sections A, B, and C by Florin in 1931. The revisions of de Laubenfels and Quinn (see references), reclassified the former section A as the new genus ''Falcatifolium'', divided Section C into new genera '' Lepidothamnus, Lagarostrobos'' and ''Halocarpus'', and retained Section B as genus ''Dacrydium''. Species Distribution The natural range of ''Dacrydium'' extends from New Zealand, New Caledonia, Fiji and the Solomon Islands through Malesia (New Guinea, Indonesia, Malaysia and the Philippines), to Thailand Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacrycarpus
''Dacrycarpus'' is a genus of conifers belonging to the family Podocarpaceae.Christopher N. Page. 1990. "Podocarpaceae" pages 332-346. In: Klaus Kubitzki (general editor); Karl U. Kramer and Peter S. Green (volume editors) ''The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants'' volume I. Springer-Verlag: Berlin;Heidelberg, Germany. The genus includes nine species of dioecious evergreen trees and shrubs to in height.James E. Eckenwalder. 2009. ''Conifers of the World''. Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA. . Species The species of ''Dacrycarpus'' range from New Zealand and Fiji, across New Caledonia, New Guinea, Indonesia, Malaysia and the Philippines to northern Myanmar Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ... and southern China. The greatest diversity (five species) exists in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podocarpus
''Podocarpus'' () is a genus of conifers, the most numerous and widely distributed of the podocarp family, the Podocarpaceae. The name comes from Greek πούς (poús, “foot”) + καρπός (karpós, “fruit”). ''Podocarpus'' species are evergreen shrubs or trees, usually from tall, known to reach at times. The cones have two to five fused cone scales, which form a fleshy, berry-like, brightly coloured receptacle at maturity. The fleshy cones attract birds, which then eat the cones and disperse the seeds in their droppings. About 97 to 107 species are placed in the genus depending on the circumscription of the species.Earle, Chris J.''Podocarpus''.The Gymnosperm Database. 2013. Species are cultivated as ornamental plants for parks and large gardens. The cultivar 'County Park Fire' has won the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit. Names and etymology Common names for various species include "yellowwood" and "pine", as in the plum pine ('' Podoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canopy (biology)
In biology, the canopy is the aboveground portion of a plant community, plant cropping or crop, formed by the collection of individual Crown (botany), plant crowns. In forest ecology, canopy also refers to the upper layer or habitat zone, formed by mature tree crowns and including other biological organisms (epiphytes, lianas, Arboreal, arboreal animals, etc.). The communities that inhabit the canopy layer are thought to be involved in maintaining forest diversity, resilience, and functioning. Sometimes the term canopy is used to refer to the extent of the outer layer of leaves of an individual tree or group of trees. Shade trees normally have a dense canopy that blocks light from lower growing plants. Observation Early observations of canopies were made from the ground using binoculars or by examining fallen material. Researchers would sometimes erroneously rely on extrapolation by using more reachable samples taken from the understory. In some cases, they would use unc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainforest, but other types have been described. Estimates vary from 40% to 75% of all biotic species being indigenous to the rainforests. There may be many millions of species of plants, insects and microorganisms still undiscovered in tropical rainforests. Tropical rainforests have been called the "jewels of the Earth" and the " world's largest pharmacy", because over one quarter of natural medicines have been discovered there. Rainforests as well as endemic rainforest species are rapidly disappearing due to deforestation, the resulting habitat loss and pollution of the atmosphere. Definition Rainforest are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, high humidity, the presence of moisture-dependent vegetation, a moist layer of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Cruz Islands
The Santa Cruz Islands are a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean, part of Temotu Province of the nation of Solomon Islands discovered by the Spaniards. They lie approximately 250 miles (400 km) to the southeast of the Solomon Islands archipelago. The Santa Cruz Islands lie just north of the archipelago of Vanuatu, and are considered part of the Vanuatu rain forests ecoregion. Geography The term Santa Cruz Islands is sometimes used to encompass all of the islands of the present-day Solomon Islands province of Temotu. The largest island is Nendö, which is also known as Santa Cruz Island proper (505.5 km2, highest point , population over 5000). Lata, located on Nendö, is the largest town, and the capital of Temotu province. Other islands belonging to the Santa Cruz group are Vanikoro (173.2 km2, population 800, which is actually two islands, Banie and its small neighbor Teanu) and Utupua (69.0 km2, highest point , population 848). The Santa Cru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
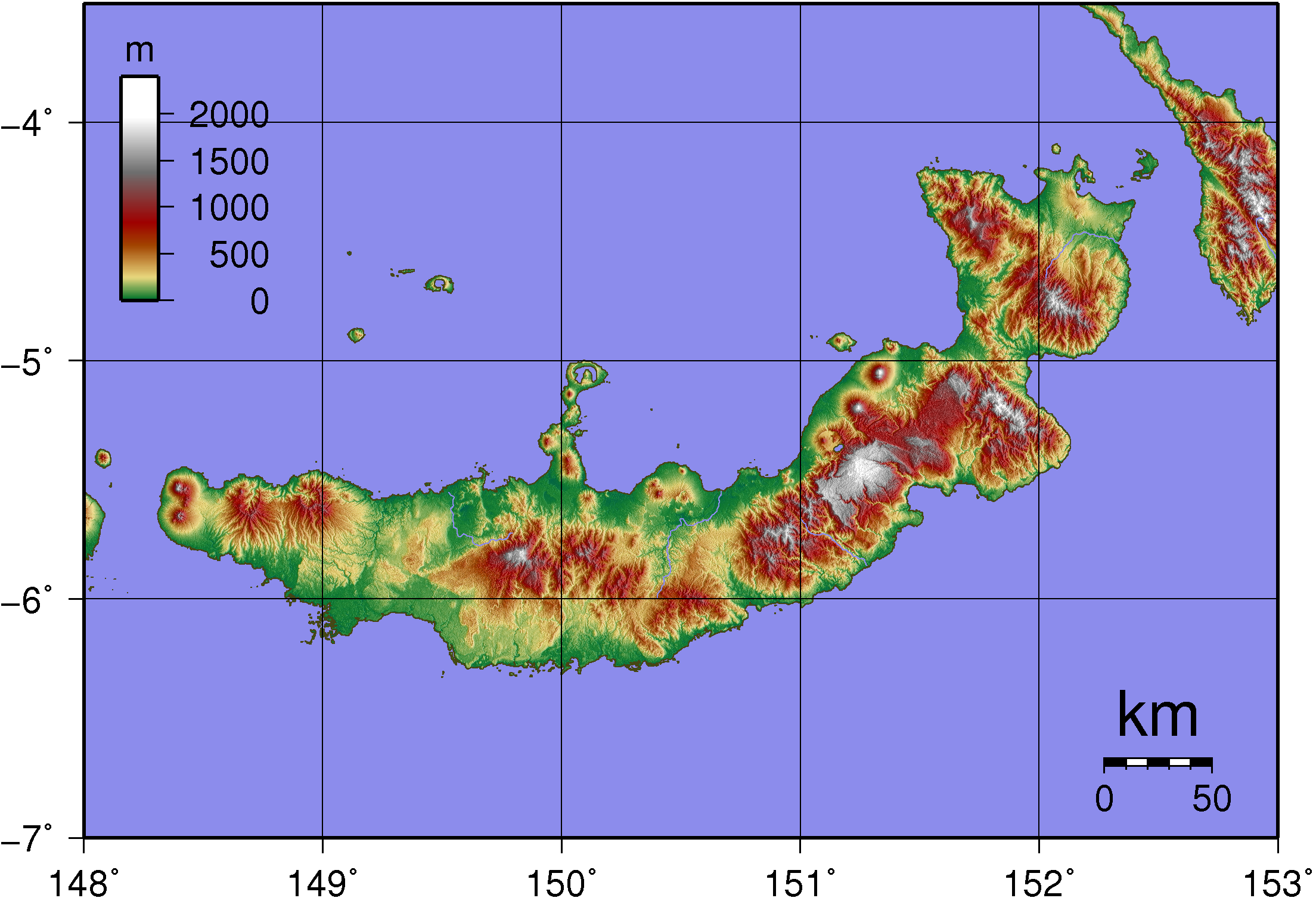
New Britain
New Britain ( tpi, Niu Briten) is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi the Dampier and Vitiaz Straits) and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel. The main towns of New Britain are Rabaul/ Kokopo and Kimbe. The island is roughly the size of Taiwan. While the island was part of German New Guinea, it was named Neupommern ("New Pomerania"). In common with most of the Bismarcks it was largely formed by volcanic processes, and has active volcanoes including Ulawun (highest volcano nationally), Langila, the Garbuna Group, the Sulu Range, and the volcanoes Tavurvur and Vulcan of the Rabaul caldera. A major eruption of Tavurvur in 1994 destroyed the East New Britain provincial capital of Rabaul. Most of the town still lies under metres of ash, and the capital has been moved to nearby Kokopo. Geography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua. The largest cities on the island are Jayapura (capital of Papua, Indonesia) and Port Moresby (capital of Papua New Guinea). Names The island has been known by various names: The name ''Papua'' was used to refer to parts of the island before contact with the West. Its etymology is unclear; one theory states that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands (; Indonesian: ''Kepulauan Maluku'') or the Moluccas () are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located east of Sulawesi, west of New Guinea, and north and east of Timor. Lying within Wallacea (mostly east of the biogeographical Weber Line), the Maluku Islands have been considered as a geographical and cultural intersection of Asia and Oceania. The islands were known as the Spice Islands because of the nutmeg, mace and cloves that were exclusively found there, the presence of which sparked colonial interest from Europe in the sixteenth century. The Maluku Islands formed a single province from Indonesian independence until 1999, when it was split into two provinces. A new province, North Maluku, incorporates the area between Morotai and Sula, with the arc of islands from Buru and Seram to Wetar remaining within the existing Maluk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)