|
Resminostat
Resminostat (4SC-201 or RAS2410) is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of histone deacetylases (HDACs), of which inhibitors are antineoplastic agents. In 2011, the German drug maker 4SC was granted orphan drug designation for resminostat by the US FDA for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In 2016, the FDA granted IND for clinical tests in combination with sorafenib for HCC. 4SC say "In several phase I and phase II trials, resminostat has already demonstrated very good safety and tolerability, alongside promising indications of efficacy." Clinical trials Resminostat has undergone a phase I/II clinical trial for K-ras mutated advanced colorectal carcinoma. It has undergone a phase II clinical trial for relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. Mechanism Resminostat restrains the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and p70S6k, indicating a disturbance with Akt signalling pathway. The treatment of resminostat leads to a drop of Bim and Bax protein level and Bcl-xL level. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Deacetylase
Histone deacetylases (, HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups (O=C-CH3) from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on both histone and non-histone proteins. HDACs allow histones to wrap the DNA more tightly. This is important because DNA is wrapped around histones, and DNA expression is regulated by acetylation and de-acetylation. HDAC's action is opposite to that of histone acetyltransferase. HDAC proteins are now also called lysine deacetylases (KDAC), to describe their function rather than their target, which also includes non-histone proteins. In general, they suppress gene expression. HDAC super family Together with the acetylpolyamine amidohydrolases and the acetoin utilization proteins, the histone deacetylases form an ancient protein superfamily known as the histone deacetylase superfamily. Classes of HDACs in higher eukaryotes HDACs, are classified in four classes depending on sequence homology to the yeast original enzymes and domain organization: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bcl-xL
B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL), encoded by the BCL2-like 1 gene, is a transmembrane molecule in the mitochondria. It is a member of the Bcl-2 family of proteins, and acts as an anti-apoptotic protein by preventing the release of mitochondrial contents such as cytochrome c, which leads to caspase activation and ultimately, programmed cell death. Function It is a well-established concept in the field of apoptosis that relative amounts of pro- and anti-survival Bcl-2 family of proteins determine whether the cell will undergo cell death; if more Bcl-xL is present, then pores are non-permeable to pro-apoptotic molecules and the cell survives. However, if Bax and Bak become activated, and Bcl-xL is sequestered away by gatekeeper BH3-only factors (e.g. Bim) causing a pore to form, cytochrome c is released leading to initiation of caspase cascade and apoptotic events. While the exact signaling pathway of Bcl-xL is still not known, it is believed that Bcl-xL differs highly fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxamic Acids
In organic chemistry, hydroxamic acids are a class of organic compounds having a general formula bearing the functional group , where R and R' are typically organyl groups (e.g., alkyl or aryl) or hydrogen. They are amides () wherein the nitrogen atom has a hydroxyl () substituent. They are often used as metal chelation, chelators. Common example of hydroxamic acid is aceto-''N''-methylhydroxamic acid (). Some uncommon examples of hydroxamic acids are formo-''N''-chlorohydroxamic acid () and chloroformo-''N''-methylhydroxamic acid (). Synthesis and reactions Hydroxamic acids are usually prepared from either esters or acid chlorides by a reaction with hydroxylamine salts. For the synthesis of benzohydroxamic acid ( or , where Ph is phenyl group), the overall equation is: : Hydroxamic acids can also be synthesized from aldehydes and ''N''-sulfonylhydroxylamine via the Angeli-Rimini reaction. Alternatively, molybdenum oxide diperoxide oxidizes trimethylsilyl, trimethylsilated ami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
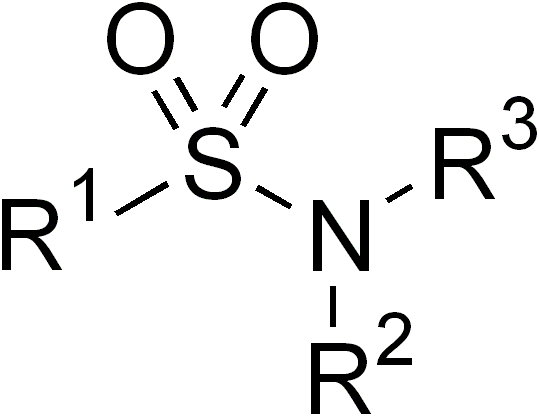
Sulfonamides
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the Chemical structure, structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for Sulfonamide (m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei and in most Archaeal phyla. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn are wrapped into 30-nanometer fibers that form tightly packed chromatin. Histones prevent DNA from becoming tangled and protect it from DNA damage. In addition, histones play important roles in gene regulation and DNA replication. Without histones, unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long. For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA if completely stretched out; however, when wound about histones, this length is reduced to about 9 micrometers (0.09 mm) of 30 nm diameter chromatin fibers. There are five families of histones, which are designated H1/H5 (linker histones), H2, H3, and H4 (core histones). The nucleosome core is formed of two H2A-H2B dimers and a H3-H4 tetramer. The tight wrapp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo a form of apoptosis that is genetically determined. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |