|
Reid W. Barton
Reid William Barton (born May 6, 1983) is a mathematician and also one of the most successful performers in the International Science Olympiads.. Biography Barton is the son of two environmental engineers. Barton took part-time classes at Tufts University in chemistry (5th grade), physics (6th grade), and subsequently Swedish, Finnish, French, and Chinese. Since eighth grade he worked part-time with MIT computer scientist Charles E. Leiserson on CilkChess, a computer chess program. Subsequently, he worked at Akamai Technologies with computer scientist Ramesh Sitaraman to build one of the earliest video performance measurement systems that have since become a standard in industry.Ramesh Sitaraman and Reid W. Barton. After Akamai, Barton went to grad school at Harvard to pursue a Ph.D. in mathematics, which he completed in 2019 under the supervision of Michael J. Hopkins. Afterwards, he did research as a post-doctoral fellow at Pittsburgh and Carnegie Mellon University and wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arlington, Massachusetts
Arlington is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The town is six miles (10 km) northwest of Boston, Massachusetts, Boston, and its population was 46,308 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. History European colonists settled the Town of Arlington in 1635 as a village within the boundaries of Cambridge, Massachusetts, under the name Menotomy, an Algonquian languages, Algonquian word considered by some to mean "swift running water", though linguistic anthropologists dispute that translation. A larger area was incorporated on February 27, 1807, as West Cambridge, replacing Menotomy. This includes the town of Belmont, Massachusetts, Belmont, and outwards to the shore of the Mystic River, which had previously been part of Charlestown, Massachusetts, Charlestown. The town was renamed Arlington on April 30, 1867, in honor of those buried in Arlington National Cemetery. The Massachusett tribe lived around the Mystic Lakes, the Mystic River, and Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Language
Finnish (endonym: or ) is a Finnic languages, Finnic language of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland, alongside Swedish language, Swedish. In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. Kven language, Kven, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norway, Norwegian counties of Troms and Finnmark by a minority of Finnish descent. Finnish is morphological typology, typologically agglutinative language, agglutinative and uses almost exclusively Suffix, suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, Numeral (linguistics), numerals and verbs are inflection, inflected depending on their role in the Sentence (linguistics), sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel Carroll
Gabriel Drew Carroll (born December 24, 1982) is a professor of economics at the University of Toronto. He was born to tech industry worker parents in Oakland. He graduated from Harvard University with B.A. in mathematics and linguistics in 2005 and received his doctorate in economics from MIT in 2012. He was recognized as a child prodigy and received numerous awards in mathematics while a student. Carroll won two gold medals (1998, 2001) and a silver medal (1999) at the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO), earning a perfect score at the 2001 International Mathematical Olympiad held in Washington, D.C., shared only with American teammate Reid W. Barton and Chinese teammates Liang Xiao and Zhiqiang Zhang. Gabriel earned a place among the top five ranked competitors (who are themselves not ranked against each other) in the William Lowell Putnam Competition all four years that he was eligible (2000–2003), a feat matched by only seven others (Don Coppersmith (1968–1971 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lean (proof Assistant)
Lean is a proof assistant and a Functional programming, functional programming language. It is based on the calculus of constructions with inductive types. It is an open-source project hosted on GitHub. Development is currently supported by the Nonprofit organization, non-profit Lean Focused Research Organization, Focused Research Organization (FRO). History Lean was developed primarily by Leonardo de Moura while employed by Microsoft Research and now Amazon Web Services, and has had significant contributions from other coauthors and collaborators during its history. It was launched by Leonardo de Moura at Microsoft Research in 2013. The initial versions of the language, later known as Lean 1 and 2, were experimental and contained features such as support for homotopy type theory – based foundations that were later dropped. Lean 3 (first released Jan 20, 2017) was the first moderately stable version of Lean. It was implemented primarily in C++ with some features written in L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The institution was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools. In 1912, it became the Carnegie Institute of Technology and began granting four-year degrees. In 1967, it became Carnegie Mellon University through its merger with the Mellon Institute of Industrial Research, founded in 1913 by Andrew Mellon and Richard B. Mellon and formerly a part of the University of Pittsburgh. The university consists of seven colleges, including the College of Engineering, the School of Computer Science, and the Tepper School of Business. The university has its main campus located 5 miles (8 km) from downtown Pittsburgh. It also has over a dozen degree-granting locations in six continents, including campuses in Qatar, Silicon Valley, and Kigali, Rwanda ( Carnegie Mellon University Africa) and partnerships with universities nationally and glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Pittsburgh
The University of Pittsburgh (Pitt) is a Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The university is composed of seventeen undergraduate and graduate schools and colleges at its Urban university, urban Pittsburgh campus, home to the university's central administration and around 28,000 undergraduate and graduate students. The 132-acre Pittsburgh campus includes various historic buildings that are part of the Schenley Farms Historic District, most notably its 42-story Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic revival centerpiece, the Cathedral of Learning. Pitt is a member of the Association of American Universities and is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". Pitt traces its roots to the Pittsburgh Academy founded by Hugh Henry Brackenridge in 1787. While the city was still on the History of Pittsburgh#Gatewa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States. Its influence, wealth, and rankings have made it one of the most prestigious universities in the world. Harvard was founded and authorized by the Massachusetts General Court, the governing legislature of colonial-era Massachusetts Bay Colony. While never formally affiliated with any denomination, Harvard trained Congregational clergy until its curriculum and student body were gradually secularized in the 18th century. By the 19th century, Harvard emerged as the most prominent academic and cultural institution among the Boston elite. Following the American Civil War, under Harvard president Charles William Eliot's long tenure from 1869 to 1909, Harvard developed multiple professional schools, which transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesh Sitaraman
Ramesh Sitaraman is an Indian American computer scientist known for his work on distributed algorithms, content delivery networks, streaming video delivery, and application delivery networks. He helped build the Akamai content delivery network, one of the world's largest distributed computing platforms. He is currently in the computer science department at University of Massachusetts Amherst. Biography Ramesh Sitaraman received a B.Tech in electrical engineering from the Indian Institute of Technology, Madras and a Ph.D (1993) in computer science from Princeton University under Robert Tarjan. He helped build Akamai's high-performance network for delivering web and media content and is an Akamai Fellow. Currently, he is a distinguished professor in the computer science department at University of Massachusetts, Amherst. Research Sitaraman's early research centered on algorithms for building reliable parallel networks from unreliable components by emulating a virtual overlay ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
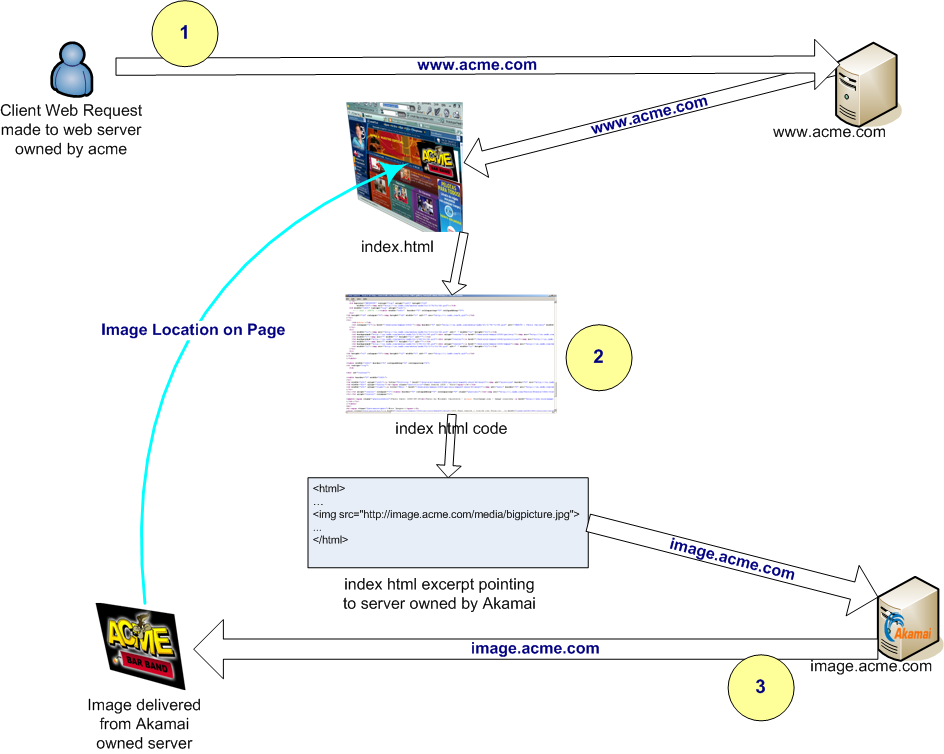
Akamai Technologies
Akamai Technologies, Inc. is an American company specialized in content delivery networkJ. Dilley, B. Maggs, J. Parikh, H. Prokop, R. Sitaraman, and B. Weihl. (CDN), cybersecurity, DDoS mitigation, and cloud services. It is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. History The company was named after '' akamai'', which means 'clever', or more colloquially, 'cool' in Hawaiian. Co-founder Daniel M. Lewin found the term in a Hawaiian–English dictionary after a colleague's suggestion. Akamai Technologies entered the 1998 MIT $50K competition with a business proposition based on their research on consistent hashing and was selected as one of the finalists. By August 1998, they had developed a working prototype, and with the help of Jonathan Seelig and Randall Kaplan, they took steps to incorporate the company. Akamai Technologies was incorporated on August 20, 1998. In late 1998 and early 1999, a group of business professionals and scientists joined the founding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Chess
Computer chess includes both hardware (dedicated computers) and software capable of playing chess. Computer chess provides opportunities for players to practice even in the absence of human opponents, and also provides opportunities for analysis, entertainment and training. Computer chess applications that play at the level of a Chess title, chess grandmaster or higher are available on hardware from supercomputers to Smartphone, smart phones. Standalone chess-playing machines are also available. Stockfish (chess), Stockfish, Leela Chess Zero, GNU Chess, Fruit (software), Fruit, and other free open source applications are available for various platforms. Computer chess applications, whether implemented in hardware or software, use different strategies than humans to choose their moves: they use Heuristic (computer science), heuristic methods to build, search and evaluate Tree (data structure), trees representing sequences of moves from the current position and attempt to execute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CilkChess
Cilk, Cilk++, Cilk Plus and OpenCilk are general-purpose programming languages designed for multithreaded parallel computing. They are based on the C and C++ programming languages, which they extend with constructs to express parallel loops and the fork–join idiom. Originally developed in the 1990s at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the group of Charles E. Leiserson, Cilk was later commercialized as Cilk++ by a spinoff company, Cilk Arts. That company was subsequently acquired by Intel, which increased compatibility with existing C and C++ code, calling the result Cilk Plus. After Intel stopped supporting Cilk Plus in 2017, MIT is again developing Cilk in the form of OpenCilk. History MIT Cilk The Cilk programming language grew out of three separate projects at the MIT Laboratory for Computer Science: * Theoretical work on scheduling multi-threaded applications. * StarTech – a parallel chess program built to run on the Thinking Machines Corporation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |