Akamai Technologies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Akamai Technologies, Inc. is an American company specialized in
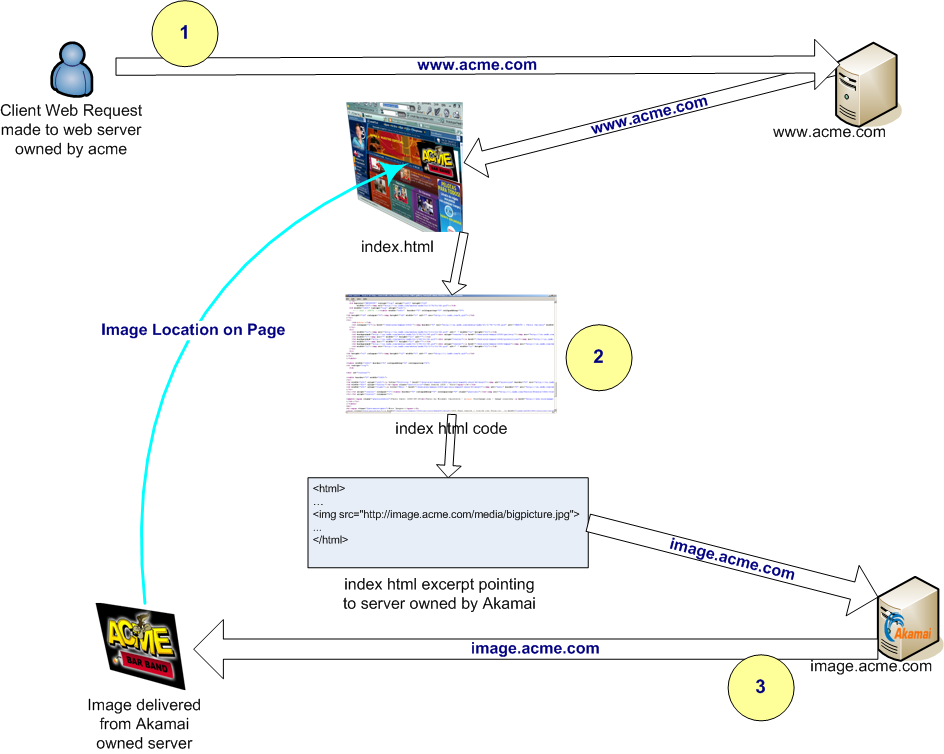 The content delivery process begins with a user submitting a request to a browser. When a user enters a URL, a DNS request is triggered to Akamai's authoritative DNS, and an
The content delivery process begins with a user submitting a request to a browser. When a user enters a URL, a DNS request is triggered to Akamai's authoritative DNS, and an
Karger, D., Lehman, E., Leighton, T., Panigrahy, R., Levine, M., Lewin, D. "Consistent Hashing and Random Trees: Distributed Caching Protocols for Relieving Hot Spots on the World Wide Web". ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, 1997, pp. 654–663.
J. Dilley, B. Maggs, J. Parikh, H. Prokop, R. Sitaraman, and B. Weihl. "Globally Distributed Content Delivery", ''IEEE Internet Computing'', September/October 2002, pp. 50–58.
Bruce Maggs and Ramesh Sitaraman. "Algorithmic nuggets in content delivery". ''ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review'', Volume=45, Issue=3, 2015.''
F. Chen, R. Sitaraman, and M. Torres. "End-User Mapping: Next Generation Request Routing for Content Delivery". ACM SIGCOMM conference, Aug 2015.
Kyle Schomp, Onkar Bhardwaj, Eymen Kurdoglu, Mashooq Muhaimen, and Ramesh K. Sitaraman. "Akamai DNS: Providing Authoritative Answers to the World's Queries", ACM SIGCOMM conference, Aug 2020.
D. Gillman, Y. Lin, B. Maggs and R. K. Sitaraman. "Protecting Websites from Attack with Secure Delivery Networks", ''IEEE Computer'', vol. 48, no. 4, pp. 26–34, Apr. 2015.
content delivery network
A content delivery network (CDN) or content distribution network is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and their data centers. The goal is to provide high availability and performance ("speed") by distributing the service spat ...
J. Dilley, B. Maggs, J. Parikh, H. Prokop, R. Sitaraman, and B. Weihl. (CDN), cybersecurity, DDoS mitigation, and cloud services. It is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. It is a suburb in the Greater Boston metropolitan area, located directly across the Charles River from Boston. The city's population as of the 2020 United States census, ...
.
History
The company was named after '' akamai'', which means 'clever', or more colloquially, 'cool' in Hawaiian. Co-founder Daniel M. Lewin found the term in a Hawaiian–English dictionary after a colleague's suggestion. Akamai Technologies entered the 1998 MIT $50K competition with a business proposition based on their research on consistent hashing and was selected as one of the finalists. By August 1998, they had developed a working prototype, and with the help of Jonathan Seelig and Randall Kaplan, they took steps to incorporate the company. Akamai Technologies was incorporated on August 20, 1998. In late 1998 and early 1999, a group of business professionals and scientists joined the founding team—most notably, Paul Sagan, former president of New Media for Time Inc., and George Conrades, former chairman and chief executive officer of BBN Corp. and senior vice president of US operations forIBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
. Conrades became chief executive officer of Akamai in April 1999. The company launched its commercial service in April 1999 and was listed on the NASDAQ Stock Market from October 29, 1999.
On July 1, 2001, Akamai was added to the Russell 3000 Index and Russell 2000 Index.
On September 11, 2001, co-founder Daniel M. Lewin died in the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
at the age of 31, when he was stabbed by one of the hijackers aboard American Airlines Flight 11, the first plane to crash into the World Trade Center. He was seated closest to the hijackers and may have tried to stop them.
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
news network Al Jazeera was an Akamai customer from March 28, 2003 to April 2, 2003, when Akamai decided to end the relationship, which the network's English-language managing editor claimed was due to "political pressure".
In 2005, Paul Sagan was named chief executive officer of Akamai, taking over from Conrades. Sagan worked to differentiate Akamai from its competitors by expanding its breadth of services. Under his leadership, it grew to $1.37 billion in revenue.
In July 2007, Akamai was added to the S&P 500
The Standard and Poor's 500, or simply the S&P 500, is a stock market index tracking the stock performance of 500 leading companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is one of the most commonly followed equity indices and in ...
index.
In 2013, co-founder Tom Leighton was elected chief executive officer, replacing Sagan.
In 2013, the Securities and Exchange Commission charged a former executive at Akamai Technologies for illegally tipping non-public information about the company's financial predicament as part of the insider trading scheme operated by now-imprisoned Galleon Management hedge fund founder Raj Rajaratnam. In 2014 it was reported that the National Security Agency and Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic Intelligence agency, intelligence and Security agency, security service of the United States and Federal law enforcement in the United States, its principal federal law enforcement ag ...
used Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
's Akamai CDN to collect information on Facebook users.
On February 9, 2021, Akamai announced that it would reorganize into two internal groups Security Technology and Edge Technology. It also re-established the role of chief technology officer and named Robert Blumofe to that role. Long-time chief security officer (CSO) Andy Ellis announced he would leave in March 2021.
Akamai's headquarters are in Kendall Square. It started in Technology Square and later expanded to multiple buildings in Cambridge Center. It consolidated its offices in a purpose-built building at 145 Broadway in December 2019.
In February 2025, Akamai was chosen as the strategic cloud computing provider by one of the world's largest technology companies, with a multi-year commitment to spend over $100 million on cloud infrastructure services. The company's cloud infrastructure services primarily consist of compute and storage solutions developed based on Linode, a cloud hosting provider acquired by Akamai for $900 million in 2022.
Akamai Intelligent Edge Platform
The Akamai Intelligent Platform is a distributed cloud computing platform that operates worldwide, a network of over approximately 365,000 servers in more than 135 countries. These servers reside on roughly 1,350 of the world's networks, gathering real-time information about traffic, congestion, and trouble spots. Each Akamai server is equipped with proprietary software that uses complex algorithms to process requests from nearby users.Content delivery process
 The content delivery process begins with a user submitting a request to a browser. When a user enters a URL, a DNS request is triggered to Akamai's authoritative DNS, and an
The content delivery process begins with a user submitting a request to a browser. When a user enters a URL, a DNS request is triggered to Akamai's authoritative DNS, and an IP address
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as that is assigned to a device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. IP addresses serve two main functions: network interface i ...
is retrieved. With the IP address, the browser can then directly contact the Akamai edge server for subsequent requests. In a content delivery network
A content delivery network (CDN) or content distribution network is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and their data centers. The goal is to provide high availability and performance ("speed") by distributing the service spat ...
(CDN) structure, the domain name
In the Internet, a domain name is a string that identifies a realm of administrative autonomy, authority, or control. Domain names are often used to identify services provided through the Internet, such as websites, email services, and more. ...
of the URL is translated by the mapping system into the IP address of an edge server to serve the content to the user.
Akamai delivers web content over its Intelligent Platform by transparently mirroring elements such as HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets ( ...
, CSS, software downloads, and media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Means of communication, tools and channels used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Interactive media, media that is inter ...
objects from customers' servers. The Akamai server is automatically chosen depending on the type of content and the user's network location. The servers are located in more than 200 countries and territories. Receiving content from a server nearer to the user allows for faster downloads and less vulnerability to network congestion. Akamai claims to provide better scalability by delivering the content over the last mile from servers close to end-users, avoiding the middle-mile bottleneck of the Internet. The Download Delivery product line includes HTTP downloads for large downloadable objects, a customizable application for consumers, and analytics tools with metrics that monitor and report on the download process.
Peer-to-peer networking
In addition to using its own servers, Akamai delivers certain content from other end-users' computers, in the form ofpeer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network, forming a peer-to-peer network of Node ...
networking.
OPEN Initiative
On October 9, 2013, Akamai announced its Open Initiative at the 2013 Akamai Edge Conference. OPEN allows customers and partners to develop and customize how they interact with the Akamai Intelligent Platform. Its key components include system and development operations integration, real-timebig data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with ...
integration, and a single-point user interface.
Acquisitions
* On February 10, 2000, Akamai acquired Network24 Communications for 621,000 shares of common stock and $12.5 million in cash. * On April 20, 2000, Akamai acquired InterVU Inc. for 10.0 million shares of common stock. * On July 25, 2000, Akamai acquired CallTheShots, Inc., for an aggregate purchase price of $3.7 million. * On June 10, 2005, Akamai acquired Speedera Networks, Inc. for 10.6 million shares of Akamai common stock and options to purchase 1.7 million shares of Akamai common stock. * On December 13, 2006, Akamai acquired Nine Systems, Inc., for an aggregate purchase price of $157.5 million. * On March 13, 2007, Akamai acquired Netli Inc. (Netli), for an aggregate purchase price of $154.4 million. * On April 12, 2007, Akamai acquired Red Swoosh Inc. for an aggregate purchase price of $18.7 million. * On November 3, 2008, Akamai acquired aCerno Inc., for an aggregate purchase price of $90.8 million. * On June 10, 2010, Akamai acquired Velocitude LLC, for an aggregate purchase price of $12 million. * On February 7, 2012, Akamai acquired Blaze Software, Inc., for an aggregate purchase price of $19.3 million. * On March 6, 2012, Akamai acquired Cotendo, Inc., for an aggregate purchase price of $278.9 million. * On September 13, 2012, Akamai acquired FastSoft, Inc., for an aggregate purchase price of $14.4 million. * On December 4, 2012, Akamai acquired Verivue, Inc., for an aggregate purchase price of $30.9 million. * On November 8, 2013, Akamai acquired Velocius Networks for an aggregate purchase price of $4.3 million. * In February 2014, Akamai acquiredcyber security
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and networks from thr ...
provider Prolexic Technologies for an aggregate purchase price of $390 million.
* In February 2015, Akamai acquired Xerocole Inc., a domain name system technology company.
* On April 6, 2015, Akamai acquired Octoshape, a cloud OTT IPTV service provider, for an undisclosed amount.
* On November 2, 2015, Akamai acquired Bloxx, a provider of Secure Web Gateway (SWG) technology, for an undisclosed amount.
* On September 28, 2016, Akamai acquired Concord Systems, a provider of technology for the high performance processing of data at scale, for an undisclosed amount.
* On October 4, 2016, Akamai acquired Soha Systems, an enterprise secure access delivered as a service provider, for an undisclosed amount.
* On December 19, 2016, Akamai acquired Cyberfend, a bot and automation detection solutions provider, for an undisclosed amount.
* On March 29, 2017, Akamai acquired SOASTA, a digital performance management company based in Mountain View, CA, for an undisclosed all-cash amount.
* On October 11, 2017, Akamai acquired Nominum, a carrier-grade DNS and DHCP provider and one of the major players in the creation of the modern DNS, for an undisclosed all-cash amount.
* On January 24, 2019, Akamai acquired CIAM provider Janrain.
* In October 2019, Akamai agreed to acquire security software provider ChameleonX for $20 million.
* On October 27, 2020, Akamai acquired IoT and mobile security provider Asavie.
* On February 1, 2021, Akamai acquired Inverse Inc. a Montreal Canadian based security company making an open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use and view the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open source model is a decentrali ...
network access controller (NAC) called PacketFence.
* On September 29, 2021, Akamai Technologies acquired Guardicore for $600 million.
* On February 15, 2022, Akamai acquired Linode for $900 million.
* On May 7, 2024, Akamai announced its intent to acquire API Security vendor Noname Security for $450 million. The deal was completed on June 25, 2024.
Key scientific publications
These papers in scientific conferences and journals describe Akamai's technology in greater detail:Karger, D., Lehman, E., Leighton, T., Panigrahy, R., Levine, M., Lewin, D. "Consistent Hashing and Random Trees: Distributed Caching Protocols for Relieving Hot Spots on the World Wide Web". ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, 1997, pp. 654–663.
J. Dilley, B. Maggs, J. Parikh, H. Prokop, R. Sitaraman, and B. Weihl. "Globally Distributed Content Delivery", ''IEEE Internet Computing'', September/October 2002, pp. 50–58.
Bruce Maggs and Ramesh Sitaraman. "Algorithmic nuggets in content delivery". ''ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review'', Volume=45, Issue=3, 2015.''
F. Chen, R. Sitaraman, and M. Torres. "End-User Mapping: Next Generation Request Routing for Content Delivery". ACM SIGCOMM conference, Aug 2015.
Kyle Schomp, Onkar Bhardwaj, Eymen Kurdoglu, Mashooq Muhaimen, and Ramesh K. Sitaraman. "Akamai DNS: Providing Authoritative Answers to the World's Queries", ACM SIGCOMM conference, Aug 2020.
D. Gillman, Y. Lin, B. Maggs and R. K. Sitaraman. "Protecting Websites from Attack with Secure Delivery Networks", ''IEEE Computer'', vol. 48, no. 4, pp. 26–34, Apr. 2015.
See also
* '' Akamai Techs., Inc. v. Limelight Networks, Inc.''References
External links
* {{Authority control 1998 establishments in Massachusetts 1999 initial public offerings American companies established in 1998 Apple Inc. partnerships Cloud computing providers Companies based in Cambridge, Massachusetts Companies listed on the Nasdaq Computer companies established in 1998 Content delivery networks Internet technology companies of the United States Peer-to-peer computing Technology companies based in the Boston area