|
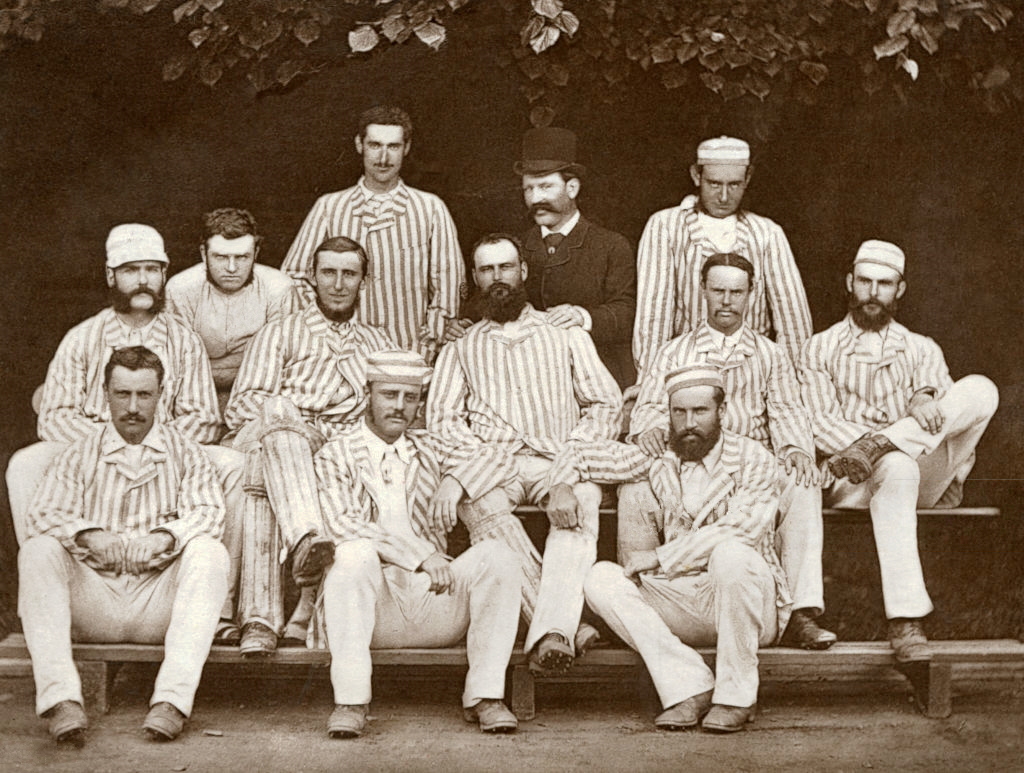
Reginald Shirley Brooks
Reginald Shirley Walkinshaw Brooks (October 1854 – 10 May 1888) was an English journalist whose spoof obituary of English cricket gave rise to the legend of The Ashes. Life and career Brooks was born in Pancras, London, the elder son of Shirley Brooks, the satirical writer and editor of '' Punch'', and Emily Walkinshaw Brooks. Brooks' father died in 1874; Reginald Shirley Brooks collated some of his father's satirical writing for ''Punch'' about a pompous middle-class couple called ''The Naggletons'' into book form and it was published the following year. A further volume of his father's epigrammatic verses was published under the title of ''Wit and Humour'' and reviewed in 1884. Brooks became a writer and journalist himself, joining '' The Sporting Times'' no later than 1876. He wrote under the pen-name "Peter Blobbs"; the newspaper, known as the "Pink Un", covered sports in general but particularly horse-racing, and also dealt in society gossip. In 1880 he was announced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia National Cricket Team
The Australia men's national cricket team represents Australia in international cricket. Along with England, it is the joint oldest team in Test cricket history, playing and winning the first ever Test match in 1877; the team also plays One-Day International and Twenty20 International cricket, participating in both the first ODI, against England in the 1970–71 season and the first T20I, against New Zealand in the 2004–05 season, winning both games. The team draws its players from teams playing in the Australian domestic competitions – the Sheffield Shield, the Australian domestic limited-overs cricket tournament and the Big Bash League. Australia are the current ICC Cricket World Cup champions. They are often regarded as the most successful national team in the history of cricket. The national team has played 875 Test matches, winning 419, losing 234, 219 drawn and with 2 tied , Australia is first in the ICC Test Rankings. Australia is the most successful team in T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
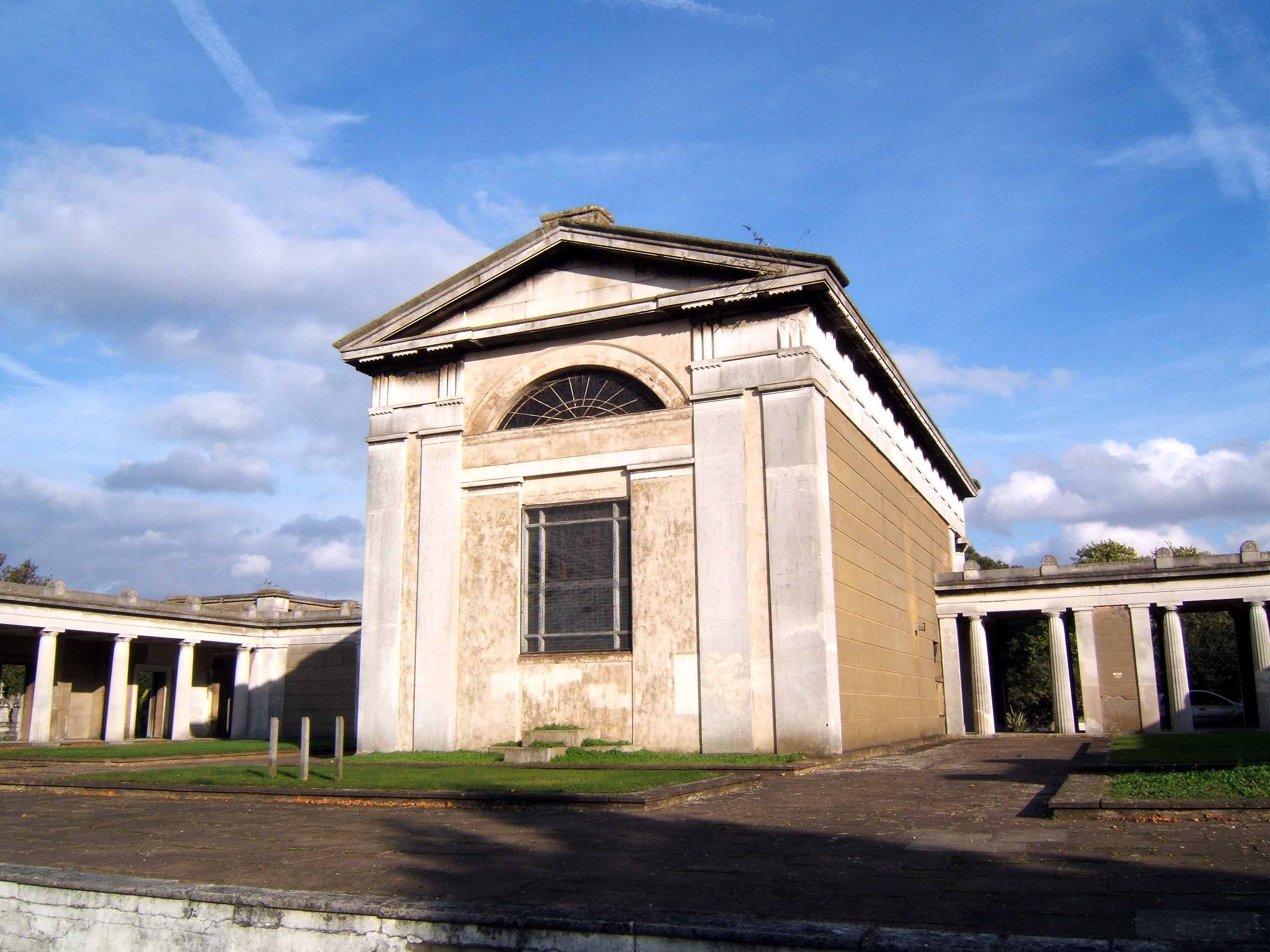
Kensal Green Cemetery
Kensal Green Cemetery is a cemetery in the Kensal Green area of North Kensington in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea and the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham in London, England. Inspired by Père Lachaise Cemetery in Paris, it was founded by the barrister George Frederick Carden.The Founding of Kensal Green Cemetery , Kensalgreen.co.uk, accessed 7 February 2014 The cemetery opened in 1833 and comprises of grounds, including two conservation areas, adjoining a canal. The cemetery is home to at least 33 species of bird and other wildlife. This distinctive cemetery has memorials ranging from large s housing the rich and famous to many distinctive smaller g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Spectator
''The Spectator'' is a weekly British political and cultural news magazine. It was first published in July 1828, making it the oldest surviving magazine in the world. ''The Spectator'' is politically conservative, and its principal subject areas are politics and culture. Alongside columns and features on current affairs, the magazine also contains arts pages on books, music, opera, film, and TV reviews. It had an average circulation of 107,812 as of December 2023, excluding Australia. Editorship of the magazine has often been a step on the ladder to high office in the Conservative Party in the United Kingdom. Past editors include Boris Johnson (1999–2005) and other former cabinet members Ian Gilmour (1954–1959), Iain Macleod (1963–1965), and Nigel Lawson (1966–1970). The former Conservative MP Michael Gove took over from Fraser Nelson as editor on 4 October 2024. Today, the magazine is a print-digital hybrid. In 2020, ''The Spectator'' became the longest-live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galahad Threepwood
The Honourable Galahad "Gally" Threepwood is a fictional character in the Blandings Castle stories by P. G. Wodehouse. Lord Emsworth's younger brother, a lifelong bachelor, Gally was, according to Beach, the Blandings butler, "somewhat wild as a young man". When he appears in the Blandings books, he is in his fifties, has thick grey hair and wears a black-rimmed monocle on a black ribbon. Life and character Galahad is the only one of the Threepwood siblings never to have married. He is the younger brother of Lord Emsworth and has ten sisters, all but one of them (Lady Diana Phipps) disapprove of his lifestyle. His true love was Dolly Henderson, with whom he was in love from 1896 to 1898 but who, as a music-hall singer who wore pink tights, was not an appropriate bride for a man of his social status. His father sent him to South Africa to prevent him from marrying, following which he spent most of his life drinking heavily and getting up to mischief. A member of the notorious P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summer Lightning
''Summer Lightning'' is a novel by P. G. Wodehouse, first published in the United States on 1 July 1929 by Doubleday (publisher), Doubleday, Doran, New York, under the title ''Fish Preferred'', and in the United Kingdom on 19 July 1929 by Herbert Jenkins Ltd, Herbert Jenkins, London.McIlvaine (1990), pp. 56–57, A41. It was serialised in ''The Pall Mall Magazine'' (UK) between March and August 1929 and in ''Collier's Weekly, Collier's'' (US) from 6 April to 22 June 1929. It forms part of the Blandings Castle saga, being the third full-length novel to be set there, after ''Something Fresh'' (1915) and ''Leave It to Psmith'' (1923). ''Heavy Weather (Wodehouse novel), Heavy Weather'' (1933) forms a semi-sequel to the story, with many of the same characters involved. Plot introduction Galahad Threepwood, Gally is down at Blandings and writing his memoirs, to the horror of all who knew him in their wild youths, particularly Lord Emsworth's neighbour and pig-fancying rival Sir Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covent Garden
Covent Garden is a district in London, on the eastern fringes of the West End, between St Martin's Lane and Drury Lane. It is associated with the former fruit-and-vegetable market in the central square, now a popular shopping and tourist site, and with the Royal Opera House, itself known as "Covent Garden". The district is divided by the main thoroughfare of Long Acre, north of which is given over to independent shops centred on Neal's Yard and Seven Dials, while the south contains the central square with its street performers and most of the historical buildings, theatres and entertainment facilities, including the London Transport Museum and the Theatre Royal, Drury Lane. The area was fields until briefly settled in the 7th century when it became the heart of the Anglo-Saxon trading town of Lundenwic, then abandoned at the end of the 9th century after which it returned to fields. By 1200 part of it had been walled off by the Abbot of Westminster Abbey for use as arabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Café Royal
A coffeehouse, coffee shop, or café (), is an establishment that serves various types of coffee, espresso, latte, americano and cappuccino, among other hot beverages. Many coffeehouses in West Asia offer ''shisha'' (actually called ''nargile'' in Levantine Arabic, Greek, and Turkish), flavored tobacco smoked through a hookah. An espresso bar is a type of coffeehouse that specializes in serving espresso and espresso-based drinks. Some coffeehouses may serve iced coffee among other cold beverages, such as iced tea, as well as other non-caffeinated beverages. A coffeehouse may also serve food, such as light snacks, sandwiches, muffins, cakes, breads, pastries or donuts. Many doughnut shops in Canada and the U.S. serve coffee as an accompaniment to doughnuts, so these can be also classified as coffee shops, although doughnut shop tends to be more casual and serve lower-end fare which also facilitates take-out and drive-through which is popular in those countries, compared to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire, Leicester Square
The Empire, Leicester Square is a cinema currently operated by Cineworld on the north side of Leicester Square, London, England. The Empire was originally built in 1884 as a variety theatre and was rebuilt for films in the 1920s. It is one of several cinemas in and adjoining Leicester Square which are regularly used for film premieres and first runs. Today, it has nine auditoria, including an IMAX, a Superscreen and a 4DX screen. History 1884: The Empire Theatre opens The Empire Theatre opened on 17 April 1884 under the ownership of Daniel Nicols as a West End variety theatre on Leicester Square, as well as a ballet venue, with a capacity of about 2,000 seats. The first performance was '' Chilpéric'', with music by Hervé, adapted by H. Hersee and H. B. Farnie and described as ''a Grand Musical Spectacular, in three acts and seven tableaux''. The corps de ballet for the performance was 50 strong. Edward Solomon and Sydney Grundy premièred their comic opera, ''Pocaho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hollingshead
John Hollingshead (9 September 1827 – 9 October 1904) was an English theatrical impresario, journalist and writer during the latter half of the 19th century. After a journalism career, Hollingshead managed the Alhambra Theatre and was later the first manager of the Gaiety Theatre, London. Hollingshead also wrote several books during his life. An innovative producer, Hollingshead brought Gilbert and Sullivan together in 1871 to produce their first joint work, a musical extravaganza called ''Thespis (opera), Thespis''. Among other theatrical works that he produced, he mounted a long series of popular Victorian burlesques at the Gaiety, engaging Meyer Lutz to compose original scores for them. He also produced operettas, plays and other works. These productions made stars of Nellie Farren and several others. At the Gaiety, in 1878, Hollingshead was the first theatre manager to light his auditorium with electric lights. Life and career Hollingshead was born in Hoxton, Greater Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truth (British Periodical)
''Truth'' was a British periodical publication founded by the diplomat and Liberal Party (UK), Liberal politician Henry Labouchère. The first issue was published on 4 January 1877. Labouchère founded the periodical after he left a virtual rival publication, ''The World''. ''Truth'' was known for its exposures of many kinds of frauds, and was at the centre of several civil lawsuits. Although Labouchère himself contributed to ''Truth'', it was for the most part controlled by Horace Voules in its early days. Later in its existence, ''Truth'' was close to the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party. In 1941, it was briefly the subject of political controversy following allegations made in Parliament of the United Kingdom, Parliament, but publication continued when the allegations were refuted. Later, ''Truth'' came under the direction of Collin Brooks. In its final years, it moved away from its right-wing editorial line back to the more liberal agenda of its early days. ''Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremation Society Of Great Britain
The Cremation Society of Great Britain (now known as The Cremation Society) was founded in 1874 to promote the use of cremation as an alternative means of dealing with the bodies of the dead instead of burial which until then was the only option. Today the society is a registered charity and is not conducted for profit. Early history In Europe, a movement to reintroduce cremation as a viable method for body disposal began in the early 1870s. This was made possible by the invention of new furnace technology and contact with Eastern cultures that practiced it. At the time, many proponents believed in the miasma theory, and that cremation would reduce the "bad air" that caused diseases. In 1869, the idea was presented to the Medical International Congress of Florence by Professors Coletti and Castiglioni "in the name of public health and civilization". In 1873 Professor Paolo Gorini of Lodi and Professor Ludovico Brunetti of Padua published reports of practical work they had conduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |