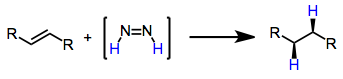|
Reductions With Diimide
Reductions with diimide are a chemical reactions that convert unsaturated organic compounds to reduced alkane products. In the process, diimide () is oxidized to dinitrogen. Introduction In 1929, the conversion of oleic acid to stearic acid in the presence of hydrazine was observed. The short-lived intermediate diimide was not implicated in this reductive process until the 1960s. Since that time, several methods of generating transient amounts of diimide have been developed. In the presence of unpolarized alkenes, alkynes or allenes, diimide is converted into dinitrogen with reduction (net addition of dihydrogen) of the unsaturated functionality. Diimide formation is the rate-limiting step of the process, and a concerted mechanism involving ''cis''-diimide has been proposed. This reduction represents a metal-free alternative to catalytic hydrogenation reductions, and does not lead to the cleavage of sensitive O–O and N–O bonds. Mechanism and stereochemistry Prevailing mechanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkane
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula . The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane (), where ''n'' = 1 (sometimes called the parent molecule), to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like hexacontane () or 4-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl) octane, an isomer of dodecane (). The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) defines alkanes as "acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having the general formula , and therefore consisting entirely of hydrogen atoms and saturated carbon atoms". However, some sources use the term to denote ''any'' saturated hydrocarbon, including those that are either monocyclic (i.e. the cycloalkanes) or polycycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |