|
Raoul Bricard
Raoul Bricard (23 March 1870 – 26 November 1943) was a French engineer and a mathematician. He is best known for his work in geometry, especially descriptive geometry and scissors congruence, and kinematics, especially mechanical linkages. Biography Bricard taught geometry at Ecole Centrale des Arts et Manufactures. In 1908 he became a professor of applied geometry at the National Conservatory of Arts and Crafts in Paris. In 1932 he received the Poncelet Prize in mathematics from the Paris Academy of Sciences for his work in geometry. Work In 1896 Bricard published a paper on Hilbert's third problem, even before the problem was stated by Hilbert. In it he proved that mirror symmetric polytopes are scissors congruent, and proved a weak version of Dehn's criterion. In 1897 Bricard published an important investigation on flexible polyhedra. In it he classified all flexible octahedra, now known as Bricard octahedra. This work was the subject of Henri Lebesgue's l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Hilbert
David Hilbert (; ; 23 January 1862 – 14 February 1943) was a German mathematician, one of the most influential mathematicians of the 19th and early 20th centuries. Hilbert discovered and developed a broad range of fundamental ideas in many areas, including invariant theory, the calculus of variations, commutative algebra, algebraic number theory, the foundations of geometry, spectral theory of operators and its application to integral equations, mathematical physics, and the foundations of mathematics (particularly proof theory). Hilbert adopted and defended Georg Cantor's set theory and transfinite numbers. In 1900, he presented a collection of problems that set the course for much of the mathematical research of the 20th century. Hilbert and his students contributed significantly to establishing rigor and developed important tools used in modern mathematical physics. Hilbert is known as one of the founders of proof theory and mathematical logic. Life Early li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alain Connes
Alain Connes (; born 1 April 1947) is a French mathematician, and a theoretical physicist, known for his contributions to the study of operator algebras and noncommutative geometry. He is a professor at the , , Ohio State University and Vanderbilt University. He was awarded the Fields Medal in 1982. Career Source: Academic career timeline: (1966–1970) – Bachelor's degree from the École Normale Supérieure (now part of Paris Sciences et Lettres University). (1973) – doctorate from Pierre and Marie Curie University, Paris, France (1970–1974) – appointment at the French National Centre for Scientific Research, Paris (1975) – Queen's University at Kingston, Ontario, Canada (1976–1980) – the University of Paris VI (1979 – present) – the Institute of Advanced Scientific Studies, Bures-sur-Yvette, France (1981–1984) – the French National Centre for Scientific Research, Paris (1984–2017) – the , Paris (2003–2011) – Vanderbilt University, Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Mathematical Monthly
''The American Mathematical Monthly'' is a mathematical journal founded by Benjamin Finkel in 1894. It is published ten times each year by Taylor & Francis for the Mathematical Association of America. The ''American Mathematical Monthly'' is an expository journal intended for a wide audience of mathematicians, from undergraduate students to research professionals. Articles are chosen on the basis of their broad interest and reviewed and edited for quality of exposition as well as content. In this the ''American Mathematical Monthly'' fulfills a different role from that of typical mathematical research journals. The ''American Mathematical Monthly'' is the most widely read mathematics journal in the world according to records on JSTOR. Tables of contents with article abstracts from 1997–2010 are availablonline The MAA gives the Lester R. Ford Awards annually to "authors of articles of expository excellence" published in the ''American Mathematical Monthly''. Editors *2022� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morley's Trisector Theorem
In plane geometry, Morley's trisector theorem states that in any triangle, the three points of intersection of the adjacent angle trisectors form an equilateral triangle, called the first Morley triangle or simply the Morley triangle. The theorem was discovered in 1899 by Anglo-American mathematician Frank Morley. It has various generalizations; in particular, if all of the trisectors are intersected, one obtains four other equilateral triangles. Proofs There are many proofs of Morley's theorem, some of which are very technical. Several early proofs were based on delicate trigonometric calculations. Recent proofs include an algebraic proof by extending the theorem to general fields other than characteristic three, and John Conway's elementary geometry proof. The latter starts with an equilateral triangle and shows that a triangle may be built around it which will be similar to any selected triangle. Morley's theorem does not hold in spherical and hyperbolic geometry. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Lebesgue
Henri Léon Lebesgue (; June 28, 1875 – July 26, 1941) was a French mathematician known for his theory of integration, which was a generalization of the 17th-century concept of integration—summing the area between an axis and the curve of a function defined for that axis. His theory was published originally in his dissertation ''Intégrale, longueur, aire'' ("Integral, length, area") at the University of Nancy during 1902. Personal life Henri Lebesgue was born on 28 June 1875 in Beauvais, Oise. Lebesgue's father was a typesetter and his mother was a school teacher. His parents assembled at home a library that the young Henri was able to use. His father died of tuberculosis when Lebesgue was still very young and his mother had to support him by herself. As he showed a remarkable talent for mathematics in primary school, one of his instructors arranged for community support to continue his education at the Collège de Beauvais and then at Lycée Saint-Louis and Lycée L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also publishes Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
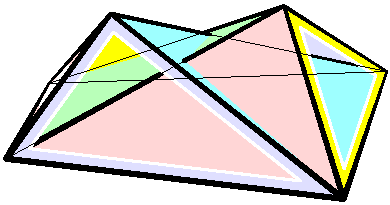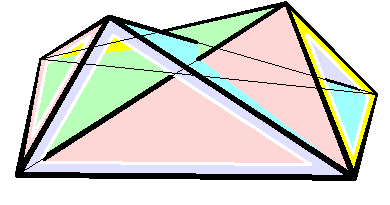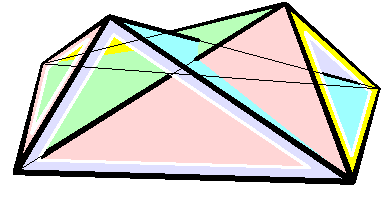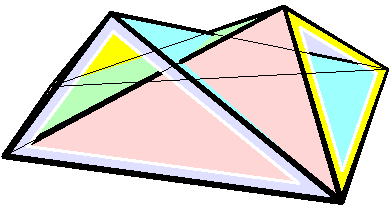
Bricard Octahedron
In geometry, a Bricard octahedron is a member of a family of flexible polyhedra constructed by Raoul Bricard in 1897. The overall shape of one of these polyhedron may change in a continuous motion, without any changes to the lengths of its edges nor to the shapes of its faces. These octahedra were the first flexible polyhedra to be discovered.. The Bricard octahedra have six vertices, twelve edges, and eight triangular faces, connected in the same way as a regular octahedron. Unlike the regular octahedron, the Bricard octahedra are all non-convex self-crossing polyhedra. By Cauchy's rigidity theorem, a flexible polyhedron must be non-convex, but there exist other flexible polyhedra without self-crossings. Avoiding self-crossings requires more vertices (at least nine) than the six vertices of the Bricard octahedra.. In his publication describing these octahedra, Bricard completely classified the flexible octahedra. His work in this area was later the subject of lectures by Henr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. A regular octahedron is the dual polyhedron of a cube. It is a rectified tetrahedron. It is a square bipyramid in any of three orthogonal orientations. It is also a triangular antiprism in any of four orientations. An octahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a cross polytope. A regular octahedron is a 3-ball in the Manhattan () metric. Regular octahedron Dimensions If the edge length of a regular octahedron is ''a'', the radius of a circumscribed sphere (one that touches the octahedron at all vertices) is :r_u = \frac a \approx 0.707 \cdot a and the radius of an inscribed sphere (tangent to each of the octahedron's faces) is :r_i = \frac a \approx 0.408\cdot a while the midradius, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexible Polyhedra
In geometry, a flexible polyhedron is a polyhedral surface without any boundary edges, whose shape can be continuously changed while keeping the shapes of all of its faces unchanged. The Cauchy rigidity theorem shows that in dimension 3 such a polyhedron cannot be convex (this is also true in higher dimensions). The first examples of flexible polyhedra, now called Bricard octahedra, were discovered by . They are self-intersecting surfaces isometric to an octahedron. The first example of a flexible non-self-intersecting surface in \mathbb^3, the Connelly sphere, was discovered by . Steffen's polyhedron is another non-self-intersecting flexible polyhedron derived from Bricard's octahedra. Bellows conjecture In the late 1970s Connelly and D. Sullivan formulated the bellows conjecture stating that the volume of a flexible polyhedron is invariant under flexing. This conjecture was proved for polyhedra homeomorphic to a sphere by using elimination theory, and then prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Dehn
Max Wilhelm Dehn (November 13, 1878 – June 27, 1952) was a German mathematician most famous for his work in geometry, topology and geometric group theory. Born to a Jewish family in Germany, Dehn's early life and career took place in Germany. However, he was forced to retire in 1935 and eventually fled Germany in 1939 and emigrated to the United States. Dehn was a student of David Hilbert, and in his habilitation in 1900 Dehn resolved Hilbert's third problem, making him the first to resolve one of Hilbert's well-known 23 problems. Dehn's students include Ott-Heinrich Keller, Ruth Moufang, Wilhelm Magnus, and the artists Dorothea Rockburne and Ruth Asawa. Biography Dehn was born to a family of Jewish origin in Hamburg, Imperial Germany. He studied the foundations of geometry with Hilbert at Göttingen in 1899, and obtained a proof of the Jordan curve theorem for polygons. In 1900 he wrote his dissertation on the role of the Legendre angle sum theorem in axiomatic geome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |