|
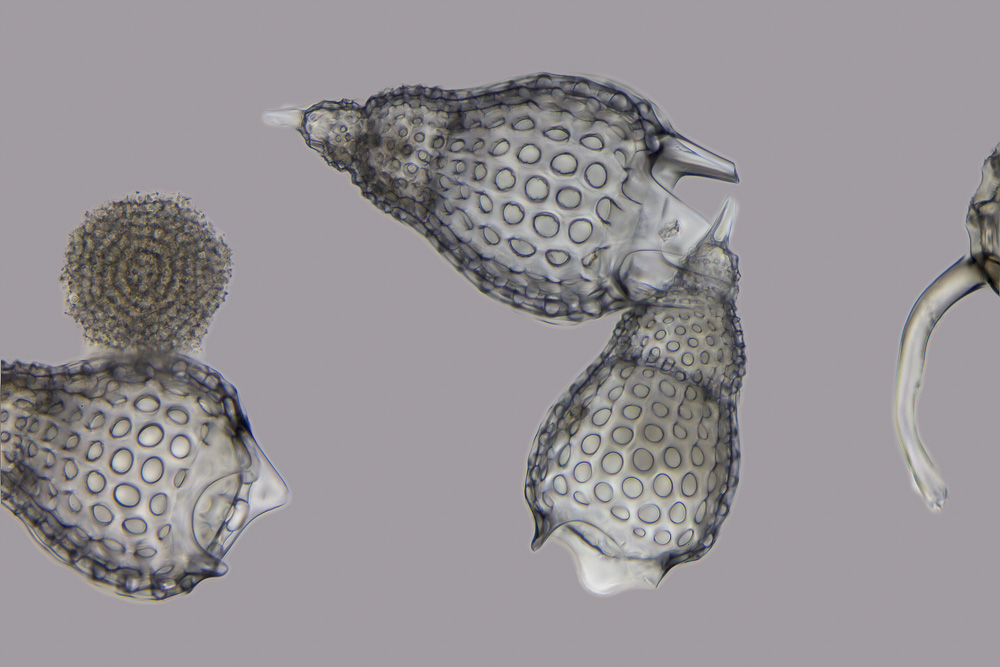
Radiolarians
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are unicellular eukaryotes of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elaborate mineral skeleton is usually made of silica. They are found as zooplankton throughout the global ocean. As zooplankton, radiolarians are primarily heterotrophic, but many have photosynthetic endosymbionts and are, therefore, considered mixotrophs. The skeletal remains of some types of radiolarians make up a large part of the cover of the ocean floor as siliceous ooze. Due to their rapid change as species and intricate skeletons, radiolarians represent an important diagnostic fossil found from the Cambrian onwards. Description Radiolarians have many needle-like pseudopods supported by bundles of microtubules, which aid in the radiolarian's buoyancy. The cell nucleus and most other organelles are in the endoplasm, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siliceous Ooze
Siliceous ooze is a type of biogenic pelagic sediment located on the Abyssal, deep ocean floor. Siliceous oozes are the least common of the deep sea sediments, and make up approximately 15% of the ocean floor. Oozes are defined as sediments which contain at least 30% skeletal remains of pelagic microorganisms. Siliceous oozes are largely composed of the silica based skeletons of microscopic marine organisms such as diatoms and radiolarians. Other components of siliceous oozes near continental margins may include terrestrially derived silica particles and sponge spicules. Siliceous oozes are composed of skeletons made from opal silica SiO2, SiO2·''n''H2O, as opposed to calcareous oozes, which are made from skeletons of calcium carbonate (CaCO3, CaCO3SiO2, ·''n''H2O) organisms (i.e. coccolithophores). Silicon (Si) is a bioessential element and is efficiently recycled in the marine environment through the silica cycle. Distance from land masses, water depth and ocean fertility are al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequently, they drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton (cyanobacteria and microalgae), which are the plant-like component of the plankton community (the " phyto-" prefix comes from , although taxonomically ''not'' plants). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding), often generating biological energy and macromolecules through chlorophyllic carbon fixation using sunlightin other words, zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food, while phytoplankton can. As a result, zooplankton must acquire nutrients by feeding on other organisms such as phytoplankton, which are generally smaller t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nassellaria
Nassellaria is an order of Rhizaria belonging to the class Radiolaria. The organisms of this order are characterized by a skeleton cross link with a cone or ring. Introduction Nassellaria is an order of Radiolaria under the class Polycystina. These organisms are unicellular eukaryotic heterotrophic plankton typically with a siliceous cone-shaped skeleton. The most common group of radiolarians are the polycystine radiolarians, which are divided into two subgroups: the spumellarians and the nassellarians. Both spumellarians and nassellarians are common chert-forming microfossils and are important in stratigraphical dating, as the oldest radiolarians are Precambrian in age. The nassellarians appear in the fossil record much later than their other polycystine relatives, the spumellarians. spumellarians can be seen as far back as the Precambrian, whereas nassellarians do not begin to appear until the Carboniferous. Nassellarians are believed to have been increasing in species diver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collodaria
Collodaria is a unicellular order (organisms within the order are called Collodarians) under the phylum Radiozoa (or Radiolaria) and the infrakingdom Rhizaria. Like most of the Radiolaria taxonomy, Collodaria was first described by Ernst Haeckel, a German scholar who published three volumes of manuscript describing the extensive samples of Radiolaria collected by the voyage of HMS ''Challenger''. Recent molecular phylogenetic studies concluded that there are Collodaria contains three families, Sphaerozodae, Collosphaeridae, and Collophidilidae. Story and origin Ernst Haeckel is the main contributor to species description in the phylum Radiolaria, which contains the order Collodaria. Members of Collodaria were first described in 1862. In 1881, ''Collodaria'' was defined by Haeckel in 1881 as “ Spumellaria without latticed shell.” The story behind this order involved the historic voyage of HMS ''Challenger''. As recorded in the manuscript of "Report on the Scientific Resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sticholonche
''Sticholonche'' is a genus of radiolarians with a single species, ''Sticholonche zanclea'', found in open oceans at depths of 99–510 metres. It is generally considered a heliozoan, placed in its own order, called the Taxopodida. However it has also been classified as an unusual radiolarian, and this has gained support from genetic studies, which place it near the Acantharea The Acantharia are a group of radiolarian protozoa, distinguished mainly by their strontium sulfate skeletons. Acantharians are heterotrophic marine Plankton, microplankton that range in size from about 200 microns in diameter up to several milli .... ''Sticholonche'' are usually around 200 μm, though this varies considerably, and have a bilaterally symmetric shape, somewhat flattened and widened at the front. The axopods are arranged into distinct rows, six of which lie in a dorsal groove and are rigid, and the rest of which are mobile. These are used primarily for buoyancy, rather than feeding. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeodaria
Phaeodarea or Phaeodaria is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They are distinguished by the structure of their central capsule and by the presence of a phaeodium, an aggregate of waste particles within the cell. The term "Radiozoa" has been used to refer to radiolaria when Phaeodarea is explicitly excluded. Phaeodarea produce hollow skeletons composed of amorphous silica and organic material, which rarely fossilize. The endoplasm is divided by a cape with three openings, of which one gives rise to feeding pseudopods, and the others let through bundles of microtubules that support the axopods. Unlike true radiolarians, there are no cross-bridges between them. They also lack symbiotic algae, generally living below the photic zone, and do not produce any Celestine (mineral), strontium sulfate. Character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acantharea
The Acantharia are a group of radiolarian protozoa, distinguished mainly by their strontium sulfate skeletons. Acantharians are heterotrophic marine Plankton, microplankton that range in size from about 200 microns in diameter up to several millimeters. Some acantharians have photosynthetic endosymbionts and hence are considered mixotrophs. Morphology Acantharian skeletons are composed of strontium sulfate, SrSO4, in the form of mineral Celestine (mineral), celestine crystal. Celestine is named for the delicate blue colour of its crystals, and is the heaviest mineral in the ocean. The denseness of their celestite ensures acantharian shells function as Ballast minerals, mineral ballast, resulting in fast sedimentation to bathypelagic, bathypelagic depths. High settling flux, fluxes of acantharian cysts have been observed at times in the Iceland Basin and the Southern Ocean, as much as half of the total gravitational organic carbon flux. Material was copied from this source, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spumellaria
Spumellaria is an order of radiolarians in the class Polycystinea. They are ameboid protists appearing in abundance in the world's oceans, possessing a radially-symmetrical silica (opal) skeleton that has ensured their preservation in fossil records. They belong among the oldest Polycystine organisms, dating back to the lower Cambrian (ca. 515 million years). Historically, many concentric radiolarians have been included in the Spumellaria order based on the absence of the initial spicular system, an early-develop structure that, by its lacking, sets them apart from Entactinaria despite their similar morphology. Mendez Sandin. Diversity and Evolution of Nassellaria and Spumellaria (Radiolaria). Protistology. Sorbonne Université, 2019. English. Accessed at: https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-03137926/file/MENDEZ_SA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycystine
The polycystines are a group of radiolarians. They include the vast majority of the fossil radiolaria, as their skeletons are abundant in marine sediments, making them one of the most common groups of microfossils. These skeletons are composed of opaline silica. In some it takes the form of relatively simple spicules, but in others it forms more elaborate lattices, such as concentric spheres with radial spines or sequences of conical chambers. Two of the orders belonging to this group are the radially-symmetrical Spumellaria, dating back to the late Cambrian period, and the bilaterally-symmetrical Nasselaria, whose origin is placed within the lower Devonian The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per .... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixotroph
A mixotroph is an organism that uses a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode, on the continuum from complete autotrophy to complete heterotrophy. It is estimated that mixotrophs comprise more than half of all microscopic plankton. There are two types of eukaryotic mixotrophs. There are those with their own chloroplasts – including those with endosymbionts providing the chloroplasts. And there are those that acquire them through kleptoplasty, or through symbiotic associations with prey, or through 'enslavement' of the prey's organelles.Leles S G et al, (2017). Oceanic protists with different forms of acquired phototrophy display contrasting biogeographies and abundance, ''Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences''. Possible combinations are photo- and chemotrophy, litho- and organotrophy ( osmotrophy, phagotrophy and myzocytosis), auto- and heterotrophy or other combinations of these. Mixotrophs can be either eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids are broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/ unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |