|
ROG Ally
The Asus ROG Ally is a handheld gaming computer developed and manufactured by Asus as part of their Republic of Gamers (ROG) brand. Released on June 13, 2023, the device competes with Valve's Steam Deck. The ROG Ally runs the Windows 11 operating system and uses an AMD Zen 4 processor called the AMD Ryzen Z1 and Z1 Extreme. In addition to handheld use, the ROG Ally can be connected to a TV or monitor through a docking station or a dongle and be used like a desktop computer or home video game console. History Asus began developing a handheld gaming computer in 2018 to compete with handheld computers such as the GPD Win 2. Development slowed down over the next few years but was accelerated after Valve's 2021 announcement of the Steam Deck, which quickly led to a renewed public interest in handheld gaming computers. The device was announced on April 1, 2023, leading many to believe it was an April Fools' Day prank, with Asus clarifying its legitimacy three days later. Asus reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows 11
Windows 11 is a version of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system, released on October 5, 2021, as the successor to Windows 10 (2015). It is available as a free upgrade for devices running Windows 10 that meet the #System requirements, Windows 11 system requirements. A Windows Server counterpart, Windows Server 2022, Server 2022 was also released in 2021 and was updated to Windows Server 2025, Server 2025 in 2024. Windows 11 is the first major version of Windows without a corresponding mobile edition, following the discontinuation of Windows 10 Mobile. Windows 11 introduced a redesigned Windows shell influenced by elements of the canceled Windows 10X project, including a centered Start menu, a separate "Widgets" panel replacing live tiles, and new window management features. It also incorporates gaming technologies from the Xbox Series X and Series S, such as Auto high-dynamic-range video, HDR and DirectStorage on supported hardware. The Chromium (web browser), Chromium-base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
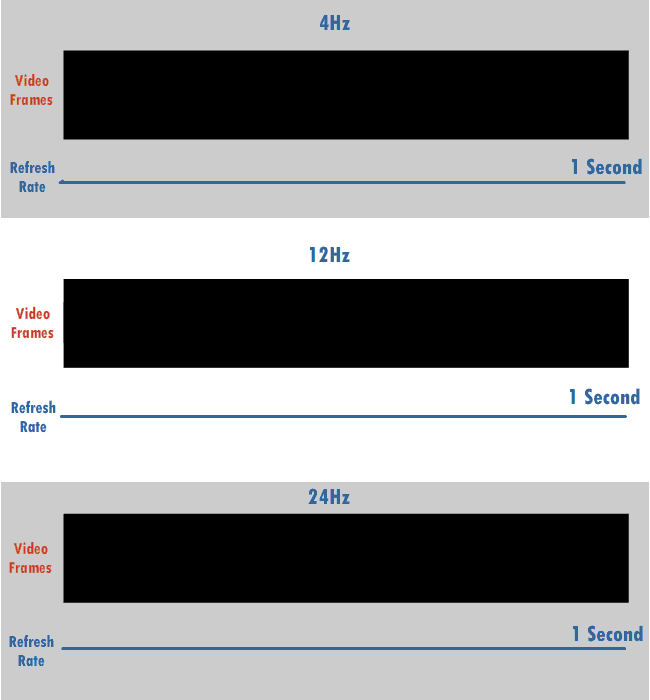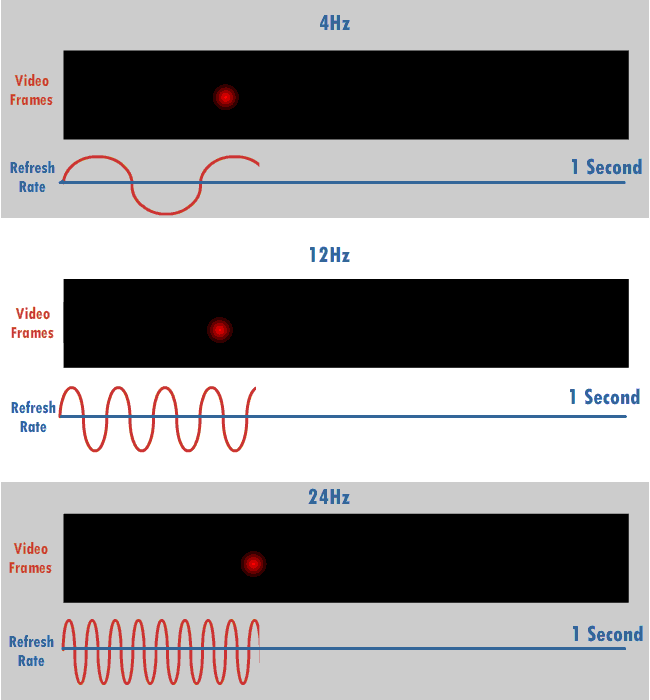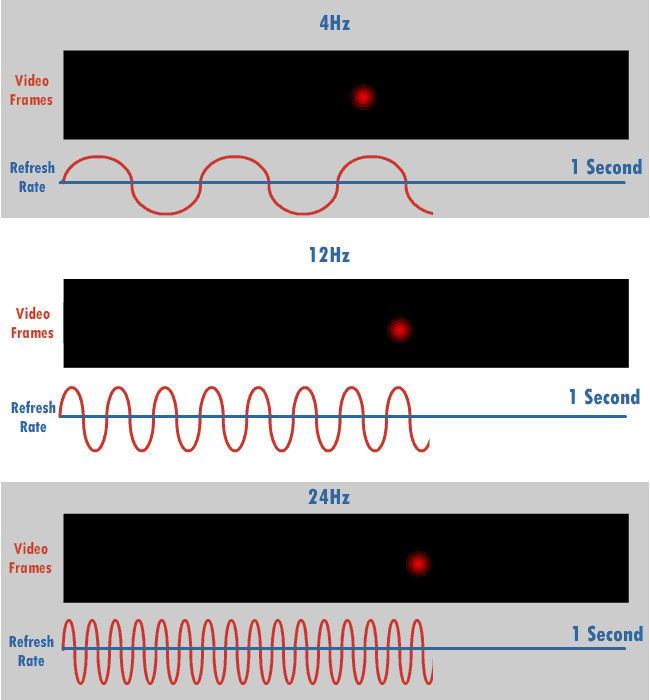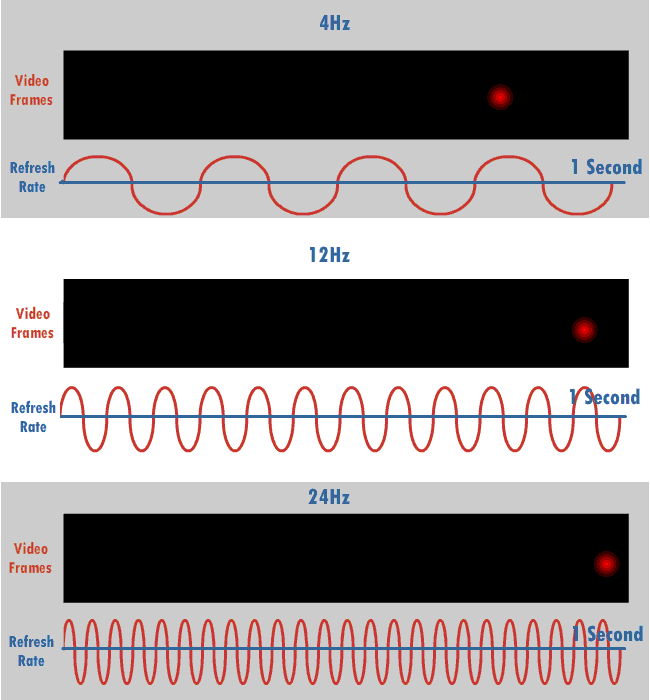
Refresh Rate
The refresh rate, also known as vertical refresh rate, vertical scan rate or vertical frequency in reference to terminology originating with the cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), is the number of times per second that a raster-based display device displays a new image. This is independent from frame rate, which describes how many images are stored or generated every second by the device driving the display. On CRT displays, higher refresh rates produce less flickering, thereby reducing eye strain. In other technologies such as liquid-crystal displays, the refresh rate affects only how often the image can potentially be updated. Non-raster displays may not have a characteristic refresh rate. Vector displays, for instance, do not trace the entire screen, only the actual lines comprising the displayed image, so refresh speed may differ by the size and complexity of the image data. For computer programs or telemetry, the term is sometimes applied to how frequently a datum is updated with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
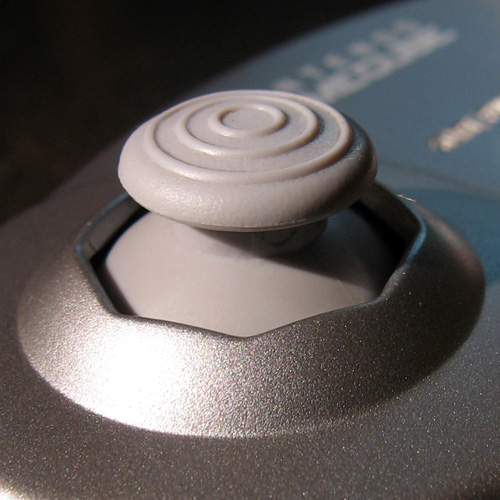
Analog Stick
An analog stick (analogue stick in British English), also known as a control stick, thumbstick or joystick, is an input method designed for video games that translates thumb movement into directional control. It consists of a protruding stick mounted on a pivot, with movement registered through continuous electrical signals rather than discrete switches, allowing for greater nuance than traditional digital inputs. Unlike D-pads, which rely on fixed electrical contacts, analog sticks use potentiometers to measure their position across a full range of motion. Many models allow the stick to be pressed down like a button, allowing users to execute commands without removing their thumb from the stick. Since its introduction, the analog stick has largely replaced the D-pad as the primary directional input in modern game controllers. Usage in video games The initial prevalence of analog sticks was as peripherals for flight simulator games, to better reflect the subtleties of control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolby Atmos
Dolby Atmos is a surround sound technology developed by Dolby Laboratories. It expands on existing surround sound systems by adding height channels as well as free-moving sound objects, interpreted as three-dimensional objects with neither horizontal nor vertical limitations. Following the release of Atmos for the cinema market, a variety of consumer technologies have been released under the Atmos brand. The initial cinema Atmos systems used in-ceiling loudspeaker, speakers, then upward-firing speakers (e.g. for soundbars) were introduced as an alternative for consumer products. Atmos is also used on some devices that do not have a height channel, such as headphones, televisions, mobile phones, and Tablet computer, tablets. History The first Dolby Atmos installation was in the El Capitan Theatre in Los Angeles, for the premiere of Brave (2012 film), ''Brave'' in June 2012. Throughout 2012, it saw a limited release of about 25 installations worldwide, with an increase to more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereo Speakers
Stereophonic sound, commonly shortened to stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that recreates a multi-directional, 3-dimensional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two independent audio channels through a configuration of two loudspeakers (or stereo headphones) in such a way as to create the impression of sound heard from various directions, as in natural hearing. Because the multi-dimensional perspective is the crucial aspect, the term ''stereophonic'' also applies to systems with more than two channels or speakers such as quadraphonic and surround sound. Binaural recording, Binaural sound systems are also ''stereophonic''. Stereo sound has been in common use since the 1970s in entertainment media such as broadcast radio, recorded music, television, video cameras, cinema, computer audio, and the Internet. Etymology The word ''stereophonic'' derives from the Greek language, Greek (''stereós'', "firm, solid") + (''phōnḗ'', "sound, tone, voice" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ada Lovelace (microarchitecture)
Ada Lovelace, also referred to simply as Lovelace, is a graphics processing unit (GPU) microarchitecture developed by Nvidia as the successor to the Ampere architecture, officially announced on September 20, 2022. It is named after the 19th century English mathematician Ada Lovelace, one of the first computer programmers. Nvidia announced the architecture along with the GeForce RTX 40 series consumer GPUs and the RTX 6000 Ada Generation workstation graphics card. The Lovelace architecture is fabricated on TSMC's custom 4N process which offers increased efficiency over the previous Samsung 8 nm and TSMC N7 processes used by Nvidia for its previous-generation Ampere architecture. Background The Ada Lovelace architecture follows on from the Ampere architecture that was released in 2020. The Ada Lovelace architecture was announced by Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang during a GTC 2022 keynote on September 20, 2022 with the architecture powering Nvidia's GPUs for gaming, workstations an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDNA 2
RDNA 2 is a GPU microarchitecture designed by AMD, released with the Radeon RX 6000 series on November 18, 2020. Alongside powering the RX 6000 series, RDNA 2 is also featured in the SoCs designed by AMD for the PlayStation 5, Xbox Series X/S, and Steam Deck consoles. Background On July 7, 2019, AMD released the first iteration of the RDNA microarchitecture, a new graphics architecture designed specifically for gaming that replaced the aging Graphics Core Next (GCN) microarchitecture. With RDNA, AMD sought to reduce latency and improve power efficiency over their previous Vega series based on GCN 5th gen and Nvidia's competing Turing microarchitecture. RDNA 2 was first publicly announced in January 2020 with AMD initially calling RDNA 2 a "refresh" of the original RDNA architecture from the previous year. At AMD's Financial Analysts Day held on March 5, 2020, AMD showed a client GPU roadmap that gave details on RDNA's successor, RDNA 2, that it would again be built using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampere (microarchitecture)
Ampere is the codename for a graphics processing unit (GPU) microarchitecture developed by Nvidia as the successor to both the Volta and Turing architectures. It was officially announced on May 14, 2020, and is named after French mathematician and physicist André-Marie Ampère. Nvidia announced the Ampere architecture GeForce 30 series consumer GPUs at a GeForce Special Event on September 1, 2020. Nvidia announced the A100 80 GB GPU at SC20 on November 16, 2020. Mobile RTX graphics cards and the RTX 3060 based on the Ampere architecture were revealed on January 12, 2021. Nvidia announced Ampere's successor, Hopper, at GTC 2022, and "Ampere Next Next" ( Blackwell) for a 2024 release at GPU Technology Conference 2021. Details Architectural improvements of the Ampere architecture include the following: * CUDA Compute Capability 8.0 for A100 and 8.6 for the GeForce 30 series * TSMC's 7 nm FinFET process for A100 * Custom version of Samsung's 8 nm pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nvidia
Nvidia Corporation ( ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and incorporated in Delaware. Founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang (president and CEO), Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Priem, it designs and supplies graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interfaces (APIs) for data science and high-performance computing, and system on a chip units (SoCs) for mobile computing and the automotive market. Nvidia is also a leading supplier of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware and software. Nvidia outsources the manufacturing of the hardware it designs. Nvidia's professional line of GPUs are used for edge-to-cloud computing and in supercomputers and workstations for applications in fields such as architecture, engineering and construction, media and entertainment, automotive, scientific research, and manufacturing design. Its GeForce line of GPUs are aimed at the consumer market and are used in ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superscalar Processor
A superscalar processor (or multiple-issue processor) is a CPU that implements a form of parallelism called instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. In contrast to a scalar processor, which can execute at most one single instruction per clock cycle, a superscalar processor can execute or start executing more than one instruction during a clock cycle by simultaneously dispatching multiple instructions to different execution units on the processor. It therefore allows more throughput (the number of instructions that can be executed in a unit of time which can even be less than 1) than would otherwise be possible at a given clock rate. Each execution unit is not a separate processor (or a core if the processor is a multi-core processor), but an execution resource within a single CPU such as an arithmetic logic unit. While a superscalar CPU is typically also pipelined, superscalar and pipelining execution are considered different performance enhancement techniq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teraflops
Floating point operations per second (FLOPS, flops or flop/s) is a measure of computer performance in computing, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations. For such cases, it is a more accurate measure than measuring instructions per second. Floating-point arithmetic Floating-point arithmetic is needed for very large or very small real numbers, or computations that require a large dynamic range. Floating-point representation is similar to scientific notation, except computers use base two (with rare exceptions), rather than base ten. The encoding scheme stores the sign, the exponent (in base two for Cray and VAX, base two or ten for IEEE floating point formats, and base 16 for IBM Floating Point Architecture) and the significand (number after the radix point). While several similar formats are in use, the most common is ANSI/IEEE Std. 754-1985. This standard defines the format for 32-bit numbers called ''single precision'', a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDNA 3
RDNA 3 is a GPU microarchitecture designed by AMD, released with the Radeon RX 7000 series on December 13, 2022. Alongside powering the RX 7000 series, RDNA 3 is also featured in the SoCs designed by AMD for the Asus ROG Ally, Lenovo Legion Go, and the PlayStation 5 Pro consoles. Background On June 9, 2022, AMD held their Financial Analyst Day where they presented a client GPU roadmap which contained mention of RDNA 3 coming in 2022 and RDNA 4 coming in 2024. AMD announced to investors their intention to achieve a performance-per-watt uplift of over 50% with RDNA 3 and that the upcoming architecture would be built using chiplet packaging on a 5 nm process. A sneak preview for RDNA 3 was included towards the end of AMD's Ryzen 7000 unveiling event on August 29, 2022. The preview included RDNA 3 running gameplay of '' Lies of P'', AMD CEO Lisa Su confirming that a chiplet design would be used, and a partial look at AMD's reference design for an RDNA 3 GPU. Full deta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |