|
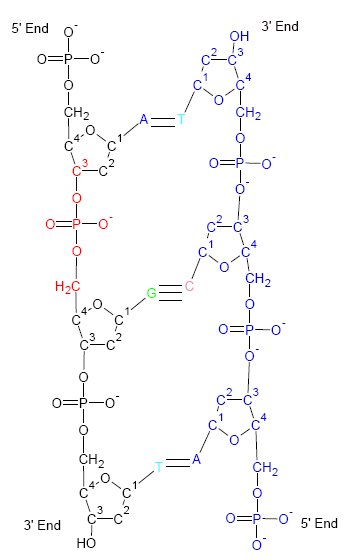
RNA Replicator
The RNA world is a hypothetical stage in the evolutionary history of life on Earth in which self-replicating RNA molecules proliferated before the evolution of DNA and proteins. The term also refers to the hypothesis that posits the existence of this stage. Alexander Rich first proposed the concept of the RNA world in 1962, and Walter Gilbert coined the term in 1986. Among the characteristics of RNA that suggest its original prominence are that: * Like DNA, RNA can store and replicate genetic information. Although RNA is considerably more fragile than DNA, some ancient RNAs may have evolved the ability to methylate other RNAs to protect them. The concurrent formation of all four RNA building blocks further strengthens the hypothesis. * Enzymes made of RNA (ribozymes) can catalyze (start or accelerate) chemical reactions that are critical for life, so it is conceivable that in an RNA world, ribozymes might have preceded enzymes made of protein. * Many coenzymes that have fundame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Difference DNA RNA-EN
Difference commonly refers to: * Difference (philosophy), the set of properties by which items are distinguished * Difference (mathematics), the result of a subtraction Difference, The Difference, Differences or Differently may also refer to: Music * Difference (album), ''Difference'' (album), by Dreamtale, 2005 * The Difference (album), ''The Difference'' (album), Pendleton, 2008 * The Difference (The Wallflowers song), "The Difference" (The Wallflowers song), 1997 * Differences (song), "Differences" (song), by Ginuwine, 2001 * Differently (album), ''Differently'' (album), by Cassie Davis, 2009 ** Differently (song), "Differently" (song), by Cassie Davis, 2009 * "Difference", a song by Benjamin Clementine from the 2022 album ''And I Have Been'' * "The Difference", a song by Matchbox Twenty from the 2002 album ''More Than You Think You Are'' * "The Difference", a song by Westlife from the 2009 album ''Where We Are'' * "The Difference", a song by Nick Jonas from the 2016 album ''L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins (). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) chain. Ribosomes bind to the messenger RNA molecules and use the RNA's sequence of nucleotides to determine the sequence of amino acids needed to generate a protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the riboso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Woese
Carl Richard Woese ( ; July 15, 1928 – December 30, 2012) was an American microbiologist and biophysicist. Woese is famous for defining the Archaea (a new domain of life) in 1977 through a pioneering phylogenetic taxonomy of 16S ribosomal RNA, a technique that has revolutionized microbiology. He also originated the RNA world hypothesis in 1967, although not by that name. Woese held the Stanley O. Ikenberry Chair and was professor of microbiology at the University of Illinois Urbana–Champaign. Life and education Woese was born in Syracuse, New York on July 15, 1928. His family was German American. Woese attended Deerfield Academy in Massachusetts. He received a bachelor's degree in mathematics and physics from Amherst College in 1950. During his time at Amherst, Woese took only one biology course (Biochemistry, in his senior year) and had "no scientific interest in plants and animals" until advised by William M. Fairbank, then an assistant professor of physics at A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslie Orgel
Leslie Eleazer Orgel FRS (12 January 1927 – 27 October 2007) was a British chemist and member of the National Academy of Sciences, known for his theories on the origin of life. Biography Leslie Orgel was born in London on . He received his Bachelor of Arts degree in chemistry with first-class honours from the University of Oxford in 1948. In 1951 he was elected a Fellow of Magdalen College, Oxford and in 1953 was awarded his PhD in chemistry. Orgel started his career as a theoretical inorganic chemist and continued his studies in this field at Oxford, the California Institute of Technology, and the University of Chicago. Together with Sydney Brenner, Jack Dunitz, Dorothy Hodgkin, and Beryl M. Oughton he was one of the first people in April 1953 to see the model of the structure of DNA, constructed by Francis Crick and James Watson, at the time he and the other scientists were working at Oxford University's Chemistry Department. According to the late Dr. Beryl Ought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the Nucleic acid double helix, helical structure of the DNA molecule. Crick and Watson's paper in ''Nature (journal), Nature'' in 1953 laid the groundwork for understanding DNA structure and functions. Together with Maurice Wilkins, they were jointly awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular geometry, molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material". Crick was an important theoretical molecular biologist and played a crucial role in research related to revealing the helical structure of DNA. He is widely known for the use of the term "central dogma" to summarise the idea that once information is transferred from nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) to prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Szent-Györgyi
Albert Imre Szent-Györgyi de Rapoltu Mare, Nagyrápolt (; September 16, 1893 – October 22, 1986) was a Hungarian biochemist who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1937. He is credited with first isolating vitamin C and discovering many of the components and reactions of the citric acid cycle and the molecular basis of muscle contraction. He was also active in the Hungarian resistance movement, Hungarian Resistance during World War II, and entered Hungarian politics after the war. Early life Szent-Györgyi was born in Budapest, Kingdom of Hungary, on September 16, 1893. His father, Miklós Szent-Györgyi, was a landowner, born in Târgu Mureş, Marosvásárhely, Transylvania (today Târgu Mureş, Romania), a Calvinism, Calvinist, and could trace his ancestry back to 1608 when Sámuel, a Calvinist Wiktionary:predicant, predicant, was ennobled. At the time of Szent-Györgyi's birth, being of the nobility was considered important and created opportunities that o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicken Or The Egg
The chicken or the egg causality dilemma is commonly stated as the question, "which came first: the chicken or the egg?" The dilemma stems from the observation that all chickens hatch from eggs and all chicken eggs are laid by chickens. "Chicken-and-egg" is a metaphoric adjective describing situations where it is not clear which of two events should be considered the ''cause'' and which should be considered the ''effect'', to express a scenario of infinite regress, or to express the difficulty of sequencing actions where each seems to depend on others being done first. Plutarch posed the question as a philosophical matter in his essay " The Symposiacs", written in the 1st century CE. Ancient legacy The question represents an ancient folk paradox addressing the problem of origins and first cause. Aristotle, writing in the fourth century BCE, concluded that this was an infinite sequence, with no true origin. Plutarch, writing four centuries later, specifically highlighted this que ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abiogenesis
Abiogenesis is the natural process by which life arises from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to living entities on Earth was not a single event, but a process of increasing complexity involving the formation of a habitable planet, the prebiotic synthesis of organic molecules, molecular self-replication, self-assembly, autocatalysis, and the emergence of cell membranes. The transition from non-life to life has never been observed experimentally, but many proposals have been made for different stages of the process. The study of abiogenesis aims to determine how pre-life chemical reactions gave rise to life under conditions strikingly different from those on Earth today. It primarily uses tools from biology and chemistry, with more recent approaches attempting a synthesis of many sciences. Life functions through the specialized chemistry of carbon and water, and builds largely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Cofactors typically differ from ligands in that they often derive their function by remaining bound. Cofactors can be classified into two types: inorganic ions and complex organic molecules called coenzymes. Coenzymes are mostly derived from vitamins and other organic essential nutrients in small amounts. (Some scientists limit the use of the term "cofactor" for inorganic substances; both types are included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a " prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or even covalently and, therefore, permanently) bound to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monomers
A monomer ( ; ''wikt:mono-, mono-'', "one" + ''wikt:-mer, -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can chemical reaction, react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization. Classification Chemistry classifies monomers by type, and two broad classes based on the type of polymer they form. By type: * natural vs synthetic, e.g. glycine vs caprolactam, respectively * polar vs nonpolar, e.g. vinyl acetate vs ethylene, respectively * cyclic vs linear, e.g. ethylene oxide vs ethylene glycol, respectively By type of polymer they form: * those that participate in condensation polymerization * those that participate in addition polymerization Differing stoichiometry causes each class to create its respective form of polymer. : The polymerization of one kind of monomer gives a polymer#Monomers and repeat units, homopolymer. Many polymers are copolymers, meaning that they are derived from two diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biocatalysis
Biocatalysis refers to the use of living (biological) systems or their parts to speed up ( catalyze) chemical reactions. In biocatalytic processes, natural catalysts, such as enzymes, perform chemical transformations on organic compounds. Both enzymes that have been more or less isolated and enzymes still residing inside living cells are employed for this task. Modern biotechnology, specifically directed evolution, has made the production of modified or non-natural enzymes possible. This has enabled the development of enzymes that can catalyze novel small molecule transformations that may be difficult or impossible using classical synthetic organic chemistry. Utilizing natural or modified enzymes to perform organic synthesis is termed chemoenzymatic synthesis; the reactions performed by the enzyme are classified as chemoenzymatic reactions. History Biocatalysis underpins some of the oldest chemical transformations known to humans, for brewing predates recorded history. The old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Storage
Information is an abstract concept that refers to something which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level, it pertains to the interpretation (perhaps formally) of that which may be sensed, or their abstractions. Any natural process that is not completely random and any observable pattern in any medium can be said to convey some amount of information. Whereas digital signals and other data use discrete signs to convey information, other phenomena and artifacts such as analogue signals, poems, pictures, music or other sounds, and currents convey information in a more continuous form. Information is not knowledge itself, but the meaning that may be derived from a representation through interpretation. The concept of ''information'' is relevant or connected to various concepts, including constraint, communication, control, data, form, education, knowledge, meaning, understanding, mental stimuli, pattern, perception, proposition, representa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |