|
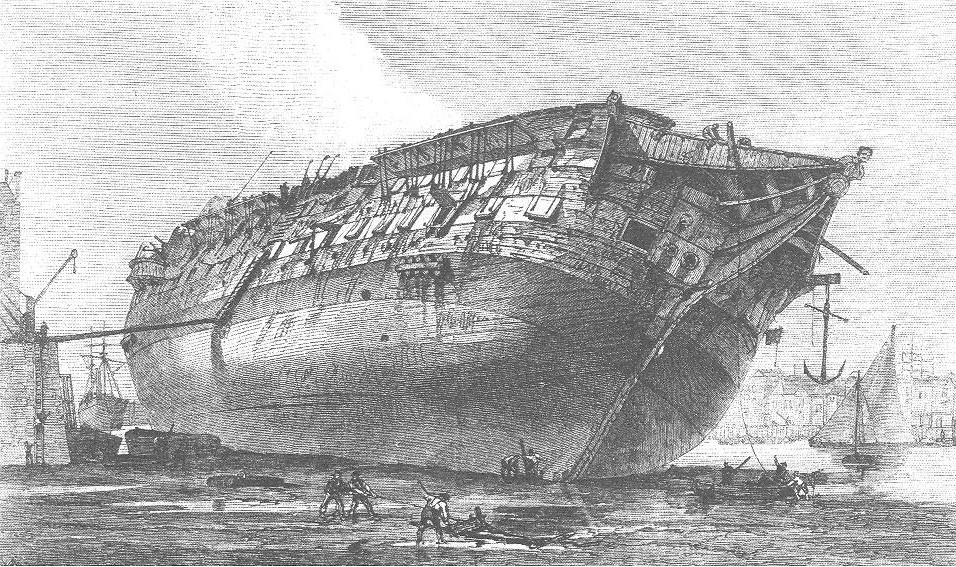
RMS Scythia
RMS ''Scythia'' was a Cunard ocean liner. She sailed on her maiden voyage in 1921, and became a troop and supply ship during the Second World War. ''Scythia'' was the longest serving Cunard liner until 4 September 2005, when her record was surpassed by ''Queen Elizabeth 2''. History After heavy losses during the First World War, Cunard Line embarked on an ambitious building programme. It decided to build "intermediate", ships rather than the large liners it had previously employed. ''Scythia'' was the first ship in this new fleet, and building began in 1919. ''Scythia'' was built for the services between Liverpool and Queenstown in the British Isles to New York and Boston, in the United States. A luxury liner designed to appeal to American tourists, in the mid-1920s, she began sailing from New York to the Mediterranean. ''Scythia'' was requisitioned at the end of 1939, left Liverpool on 24 September 1940 with 48 children bound for Boston, sponsored by readers of the ''Bosto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunard Line
The Cunard Line ( ) is a British shipping and an international cruise line based at Carnival House at Southampton, England, operated by Carnival UK and owned by Carnival Corporation & plc. Since 2011, Cunard and its four ships have been registered in Hamilton, Bermuda. In 1839, Samuel Cunard was awarded the first British transatlantic steamship mail contract, and the next year formed the British and North American Royal Mail Steam-Packet Company in Glasgow with shipowner Sir George Burns together with Robert Napier, the famous Scottish steamship engine designer and builder, to operate the line's four pioneer paddle steamers on the Liverpool–Halifax–Boston route. For most of the next 30 years, Cunard held the Blue Riband for the fastest Atlantic voyage. However, in the 1870s Cunard fell behind its rivals, the White Star Line and the Inman Line. To meet this competition, in 1879 the firm was reorganised as the Cunard Steamship Company Ltd, to raise capital. In 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Breaking
Ship breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship scrapping, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships either as a source of Interchangeable parts, parts, which can be sold for re-use, or for the extraction of raw materials, chiefly scrap. Modern ships have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years before corrosion, Fatigue (material), metal fatigue and a lack of parts render them uneconomical to operate. Ship-breaking allows the materials from the ship, especially steel, to be recycled and made into new products. This lowers the demand for mined iron ore and reduces energy use in the steelmaking process. Fixtures and other equipment on board the vessels can also be reused. While ship-breaking is sustainable, there are concerns about its use by poorer countries without stringent environmental legislation. It is also labour-intensive, and considered one of the world's most dangerous industries. In 2012, roughly 1,250 oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than long and wide, covering . It hosts key north European shipping lanes and is a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and a rich source of energy resources, including wind energy, wind and wave power. The North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe, from the Middle Ages to the modern era. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Viking Age, Vikings' rise. The Hanseatic League, the Dutch Golden Age, Dutch Republic, and Kingdom of Great Britain, Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refugees
A refugee, according to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), is a person "forced to flee their own country and seek safety in another country. They are unable to return to their own country because of feared persecution as a result of who they are, what they believe in or say, or because of armed conflict, violence or serious public disorder." Such a person may be called an asylum seeker until granted refugee status by a contracting state or by the UNHCR if they formally make a claim for asylum. Internally Displaced People (IDPs) are often called refugees, but they are distinguished from refugees because they have not crossed an international border, although their reasons for leaving their home may be the same as those of refugees. Etymology and usage In English, the term ''refugee'' derives from the root word ''refuge'', from Old French ''refuge'', meaning "hiding place". It refers to "shelter or protection from danger or distress", from Latin ''fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Refugee Organization
The International Refugee Organization (IRO) was an intergovernmental organization founded on 20 April 1946 to deal with the massive refugee problem created by World War II. A Preparatory Commission began operations fourteen months previously. In 1948, the treaty establishing the IRO formally entered into force and the IRO became a United Nations specialized agency. The IRO assumed most of the functions of the earlier United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration. In 1952, operations of the IRO ceased, and it was replaced by the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR). The Constitution of the International Refugee Organization, adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 15 December 1946, is the founding document of the IRO. The constitution specified the organization's field of operations. Controversially, the constitution defined "persons of German ethnic origin" who had been expelled, or were to be expelled from their countries o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pier 21
Pier 21 is a former ocean liner terminal and immigration shed from 1928 to 1971 in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. Nearly one million immigrants came to Canada through Pier 21, and it is the last surviving seaport immigration facility in Canada. The facility is often compared to the landmark American immigration gateway Ellis Island. The former immigration facility is now occupied by the Canadian Museum of Immigration, the Nova Scotia College of Art and Design as well as various retail and studio tenants. Background Halifax Harbour, along with Quebec City and Victoria, British Columbia were the major ports of entry for immigration to Canada in the steamship era. Pier 2 in Halifax's North End, also known as the "Deepwater Piers", was built in 1880 to process immigrants arriving on ocean liners. It also served as a major terminal for troopships and hospital ships in World War I. However, by 1913, the peak year of immigration in Canada, it was clear that the growing size of ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algiers
Algiers is the capital city of Algeria as well as the capital of the Algiers Province; it extends over many Communes of Algeria, communes without having its own separate governing body. With 2,988,145 residents in 2008Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques de l'Algérie (web). and an estimated 3,004,130 residents in 2025 in an area of , Algiers is the largest city in List of cities in Algeria, Algeria, List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, the third largest city on the Mediterranean, List of largest cities in the Arab world, sixth in the Arab World, and List of cities in Africa by population, 11th in Africa. Located in the north-central portion of the country, it extends along the Bay of Algiers surrounded by the Mitidja Plain and major mountain ranges. Its favorable location made it the center of Regency of Algiers, Ottoman and French Algeria, French cultural, political, and architectural influences for the region, shaping it to be the diverse met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harbour
A harbor (American English), or harbour (Commonwealth English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences), is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be Mooring, moored. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is a man-made facility built for loading and unloading Watercraft, vessels and dropping off and picking up passengers. Harbors usually include one or more ports. Alexandria Port in Egypt, meanwhile, is an example of a port with two harbors. Harbors may be natural or artificial. An artificial harbor can have deliberately constructed breakwater (structure), breakwaters, sea walls, or jetties or they can be constructed by dredging, which requires maintenance by further periodic dredging. An example of an artificial harbor is Long Beach Harbor, California, United States, which was an array of salt marshes and tidal flats too shallow for modern merchant ships before it was first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Torpedo
An aerial torpedo (also known as an airborne torpedo or air-dropped torpedo) is a torpedo launched from a torpedo bomber aircraft into the water, after which the weapon propels itself to the target. First used in World War I, air-dropped torpedoes were used extensively in World War II, and remain in limited use. Aerial torpedoes are generally smaller and lighter than submarine- and surface-launched torpedoes. History Origins The idea of dropping lightweight torpedoes from aircraft was conceived in the early 1910s by Bradley A. Fiske, an officer in the United States Navy.Hopkins, Albert Allis. ''The Scientific American War Book: The Mechanism and Technique of War'', Chapter XLV: Aerial Torpedoes and Torpedo Mines. Munn & Company, Incorporated, 1915 A patent for this was awarded in 1912.Hart, Albert Bushnell. ''Harper's pictorial library of the world war, Volume 4''. Harper, 1920, p. 335. Fiske worked out the mechanics of carrying and releasing the aerial torpedo from a bom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
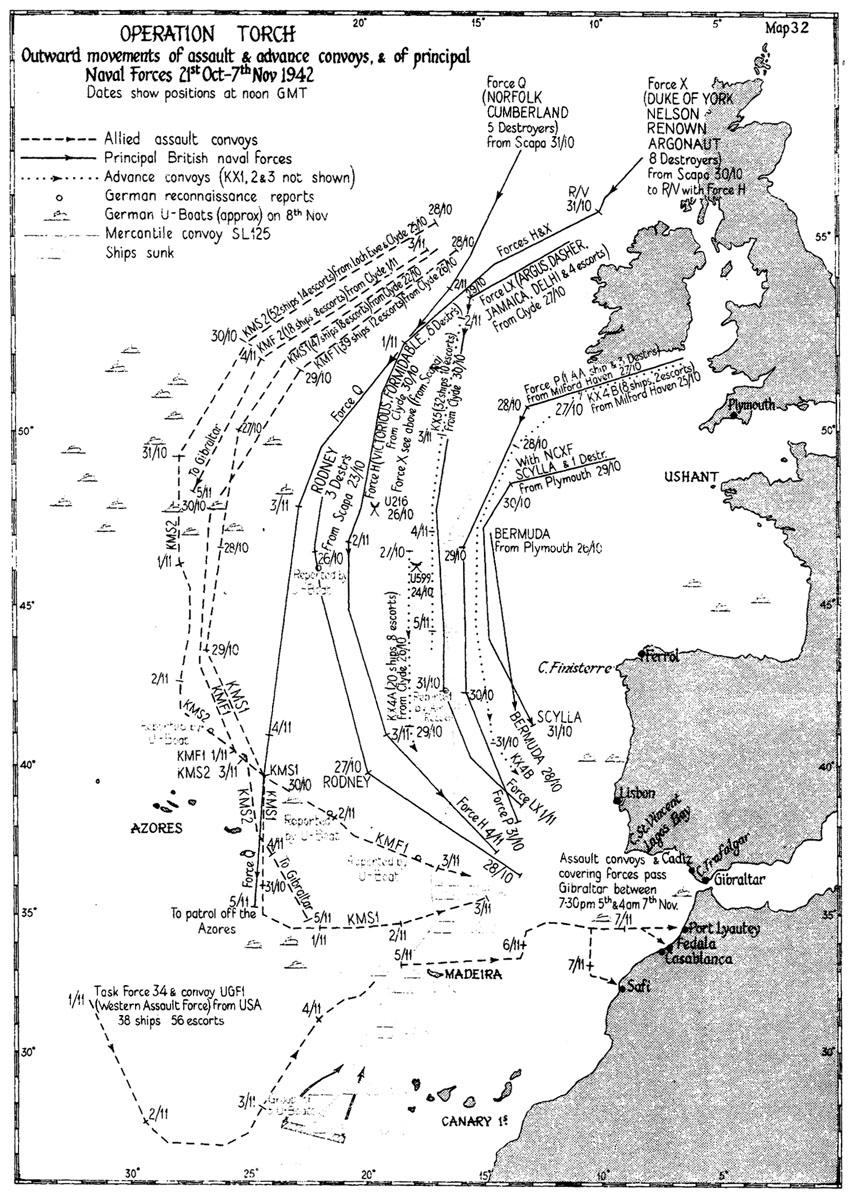
Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8–16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa while allowing American armed forces the opportunity to begin their fight against Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy on a limited scale. The French colonies were aligned with Germany via Vichy France but the loyalties of the population were mixed. Reports indicated that they might support the Allies. The American General Dwight D. Eisenhower, supreme commander of the Allied forces in Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II, Mediterranean theater of the war, approved plans for a three-pronged attack on Casablanca (Western), Oran (Centre) and Algiers (Eastern), then a rapid move on Tunis to catch Axis forces in North Africa from the west in conjunction with the British advance from Egypt. The Western Task Force encountered unexpected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st King's Dragoon Guards
The 1st King's Dragoon Guards was an armoured cavalry and dragoon guard regiment in the British Army. The regiment was raised by Sir John Lanier in 1685 as the 2nd Queen's Regiment of Horse, named in honour of Queen Mary, consort of King James II. It was renamed the 2nd King's Own Regiment of Horse in 1714 in honour of George I. The regiment attained the title 1st King's Dragoon Guards in 1751. The regiment served as horse cavalry until 1937 when it was mechanised with light tanks. The regiment became part of the Royal Armoured Corps in 1939. After service in the First World War and the Second World War, the regiment amalgamated with the 2nd Dragoon Guards (Queen's Bays) in 1959 to form the 1st The Queen's Dragoon Guards. History Early history The regiment was raised by Sir John Lanier in 1685 as Lanier's Regiment of Horse or the 2nd Queen's Regiment of Horse, named in honour of Queen Mary, consort of King James II, as part of the response to the Monmouth Rebellion. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |