|
Quintus Caecilius Metellus (consul 206 BC)
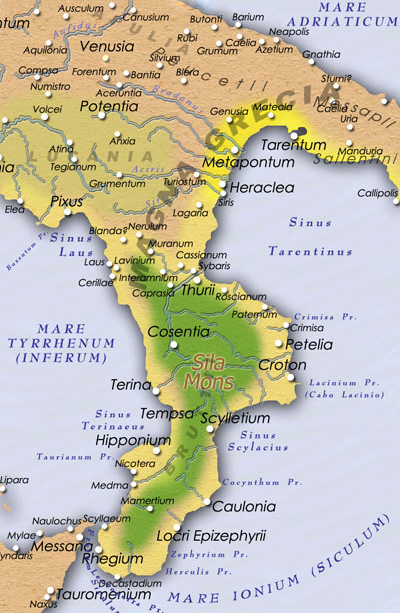
Quintus Caecilius Metellus (c. 250 BC – 175 BC) was a pontiff in 216 BC, aedile of the plebeians in 209 BC, curule aedile in 208 BC, magister equitum in 207 BC, consul in 206 BC, dictator in 205 BC, proconsul of Bruttium in 204 BC, and an ambassador at the court of Philip V of Macedon in 185 BC. He served as a legate in the army of Gaius Claudius Nero and fought in the war against Hannibal. He was a political ally of Scipio Africanus, the man who eventually defeated Hannibal.Adrian Goldsworthy, The Fall of Carthage, p. 300. He was also distinguished as an orator, the funeral sermon he pronounced at his father's funeral being counted among his best speeches. He was the father of Quintus Caecilius Metellus Macedonicus and Lucius Caecilius Metellus Calvus. Family background Quintus Caecilius Metellus was the son of Lucius Caecilius Metellus, a successful general who defeated Hasdrubal at Panormus in the First Punic War. Both father and son were members of the famed gens C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denarius
The ''denarius'' (; : ''dēnāriī'', ) was the standard Ancient Rome, Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War to the reign of Gordian III (AD 238–244), when it was gradually replaced by the ''antoninianus''. It continued to be minted in very small quantities, likely for ceremonial purposes, until and through the Tetrarchy (293–313). The word ''dēnārius'' is derived from the Latin ''dēnī'' "containing ten", as its value was originally of 10 ''As (Roman coin), assēs''.Its value was increased to 16 assēs in the middle of the 2nd century BC. The word for "money" descends from it in Italian (''denaro''), Slovene (''denar''), Portuguese (''dinheiro''), and Spanish (''dinero''). Its name also survives in the dinar currency. Its symbol is represented in Unicode as 𐆖 (U+10196), a numeral monogram that appeared on the obverse in the Republican period, denoting the 10 ''asses'' ("X") to 1 ''denarius'' ("I") conversion rate. However it can also be re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plebeians
In ancient Rome, the plebeians or plebs were the general body of free Roman citizens who were not Patrician (ancient Rome), patricians, as determined by the Capite censi, census, or in other words "commoners". Both classes were hereditary. Etymology The precise origins of the group and the term are unclear, but may be related to the Greek, ''plēthos'', meaning masses. In Latin, the word is a grammatical number, singular collective noun, and its genitive is . Plebeians were not a monolithic social class. In ancient Rome In the annalistic tradition of Livy and Dionysius of Halicarnassus, Dionysius, the distinction between patricians and plebeians was as old as Rome itself, instituted by Romulus' appointment of the first hundred senators, whose descendants became the patriciate. Modern hypotheses date the distinction "anywhere from the regal period to the late fifth century" BC. The 19th-century historian Barthold Georg Niebuhr believed plebeians were possibly foreigners im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caecilia Gens
The gens Caecilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are mentioned in history as early as the fifth century BC, but the first of the Caecilii who obtained the consulship was Lucius Caecilius Metellus Denter, in 284 BC.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', vol. I, p. 526 (" Caecilia Gens"). The Caecilii Metelli were one of the most powerful families of the late Republic, from the decades before the First Punic War down to the time of Augustus. Origin Like other Roman families in the later times of the Republic, the Caecilii traced their origin to a mythical personage, Caeculus, the founder of Praeneste. He was said to be the son of Vulcan, and engendered by a spark; a similar story was told of Servius Tullius. He was exposed as an infant, but preserved by his divine father, and raised by maidens. He grew up amongst the shepherds, and became a highwayman. Coming of age, he called upon the people of the countryside to build a new to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orator
An orator, or oratist, is a public speaker, especially one who is eloquent or skilled. Etymology Recorded in English c. 1374, with a meaning of "one who pleads or argues for a cause", from Anglo-French ''oratour'', Old French ''orateur'' (14th century), Latin ''orator'' ("speaker"), from ''orare'' ("speak before a court or assembly; plead"), derived from a Proto-Indo-European base *''or-'' ("to pronounce a ritual formula"). The modern meaning of the word, "public speaker", is attested from c. 1430. History In ancient Rome, the art of speaking in public (''Ars Oratoria'') was a professional competence especially cultivated by politicians and lawyers. As the Greeks were still seen as the masters in this field, as in philosophy and most sciences, the leading Roman families often either sent their sons to study these subjects under a famous master in Greece (as was the case with the young Julius Caesar), or engaged a Greek teacher (under pay or as a slave). In the young rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Zama
The Battle of Zama was fought in 202 BC in what is now Tunisia between a Roman Republic, Roman army commanded by Scipio Africanus and a Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian army commanded by Hannibal. The battle was part of the Second Punic War and resulted in such a severe defeat for the Carthaginians that they Capitulation (surrender), capitulated, while Hannibal was forced into exile. The Roman army of approximately 30,000 men was outnumbered by the Carthaginians who fielded either 40,000 or 50,000; the Romans were stronger in cavalry, but the Carthaginians had 80 war elephants. At the outset of the Second Punic War, in 218 BC, a Carthaginian army led by Hannibal invaded mainland Italy, where it Military campaign, campaigned for the next 16 years. In 210 BC Scipio took command of the faltering Roman war effort in Iberia (modern Spain and Portugal) and cleared the peninsula of Carthaginians in five years. He returned to Rome and was appointed Roman consul, consul in 205 BC. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–) was a Roman general and statesman who was one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Ancient Carthage, Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the honorific epithet ''Africanus'', literally meaning 'the African', but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa (Roman province), Africa. Scipio's conquest of Carthaginian Iberia culminated in the Battle of Ilipa in 206 BC against Hannibal's brother Mago Barca. Although considered a hero by the Roman people, primarily for his victories against Carthage, Scipio had many opponents, especially Cato the Elder, who hated him deeply. In 187 BC, he was tried in a show trial alongside his brother for bribes they supposedly received from the Seleucid king Antiochus III ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannibal
Hannibal (; ; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Punic people, Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Ancient Carthage, Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War. Hannibal's father, Hamilcar Barca, was a leading Carthaginian general during the First Punic War. His younger brothers were Mago Barca, Mago and Hasdrubal Barca, Hasdrubal; his brother-in-law was Hasdrubal the Fair, who commanded other Carthaginian armies. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the Mediterranean Basin, triggered by the emergence of the Roman Republic as a great power with its defeat of Carthage in the First Punic War. Revanchism prevailed in Carthage, symbolized by the pledge that Hannibal made to his father to "never be a friend of Rome". In 218 BC, Hannibal attacked Saguntum (modern Sagunto, Spain), an ally of Rome, in Hispania, sparking the Second Punic War. Hannibal invaded Italy by Hannibal's crossing of the Alps, cross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Claudius Nero
Gaius Claudius Nero (c. 237 BCc. 189 BC) was a Ancient Rome, Roman general active during the Second Punic War against the invading Carthage, Carthaginian force, led by Hannibal, Hannibal Barca. During a military career that began as Legatus, legate in 214 BC, he was praetor in 212 BC, Promagistrate, propraetor in 211 BC during the Battle of Capua, siege of Capua, before being sent to Spain that same year. He became Roman consul, consul in 207 BC. He is most renowned for his part in the Battle of the Metaurus, fought alongside his co-consul and great rival Marcus Livius Salinator against Hannibal's brother Hasdrubal Barca, Hasdrubal, for which he was awarded an ovation. The Roman victory at Metaurus River in 207 BC is widely seen as a daring strategic masterstroke by Claudius who surreptitiously left the main force of his army, which was holding Hannibal at bay in the south of Italy, to lead a small contingent of troops north to bolster Livius' forces, taking Hasdrubal by surprise. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legatus
A legate (Latin: , ) was a high-ranking Roman military officer in the Roman army, equivalent to a high-ranking general officer of modern times. Initially used to delegate power, the term became formalised under Augustus as the officer in command of a Roman legion. From the times of the Roman Republic, legates received large shares of the military's rewards at the end of a successful campaign. This made the position a lucrative one, so it could often attract even distinguished consuls or other high-ranking political figures within Roman politics (e.g., the consul Lucius Julius Caesar volunteered late in the Gallic Wars as a legate under his first cousin, Gaius Julius Caesar). Diplomats and envoys sent by Rome were also given the title of legate. History Roman Republic The rank of legate existed as early as the Samnite Wars, but it was not until 190 BC that it started to be standardized, meant to better manage the higher numbers of soldiers the Second Punic War had forced t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip V Of Macedon
Philip V (; 238–179 BC) was king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by the Social War (220–217 BC), Social War in Greece (220-217 BC) and a struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon against Rome in the First Macedonian War, First (212-205 BC) and Second Macedonian War, Second (200-196 BC) Macedonian Wars. While he lost the latter, Philip later allied with Rome against Antiochus III the Great, Antiochus III in the Roman–Seleucid war, Roman-Seleucid War. He died in 179 BC from illness after efforts to recover the military and economic condition of Macedonia and passed the throne onto his elder son, Perseus of Macedon. Early life Philip was the son of Demetrius II of Macedon, and either Phthia of Macedon or Chryseis. Philip was nine years old when his father died in 229 BC. His elder paternal half-sister was Apama III. Philip's grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |