|
Qinghai Normal University
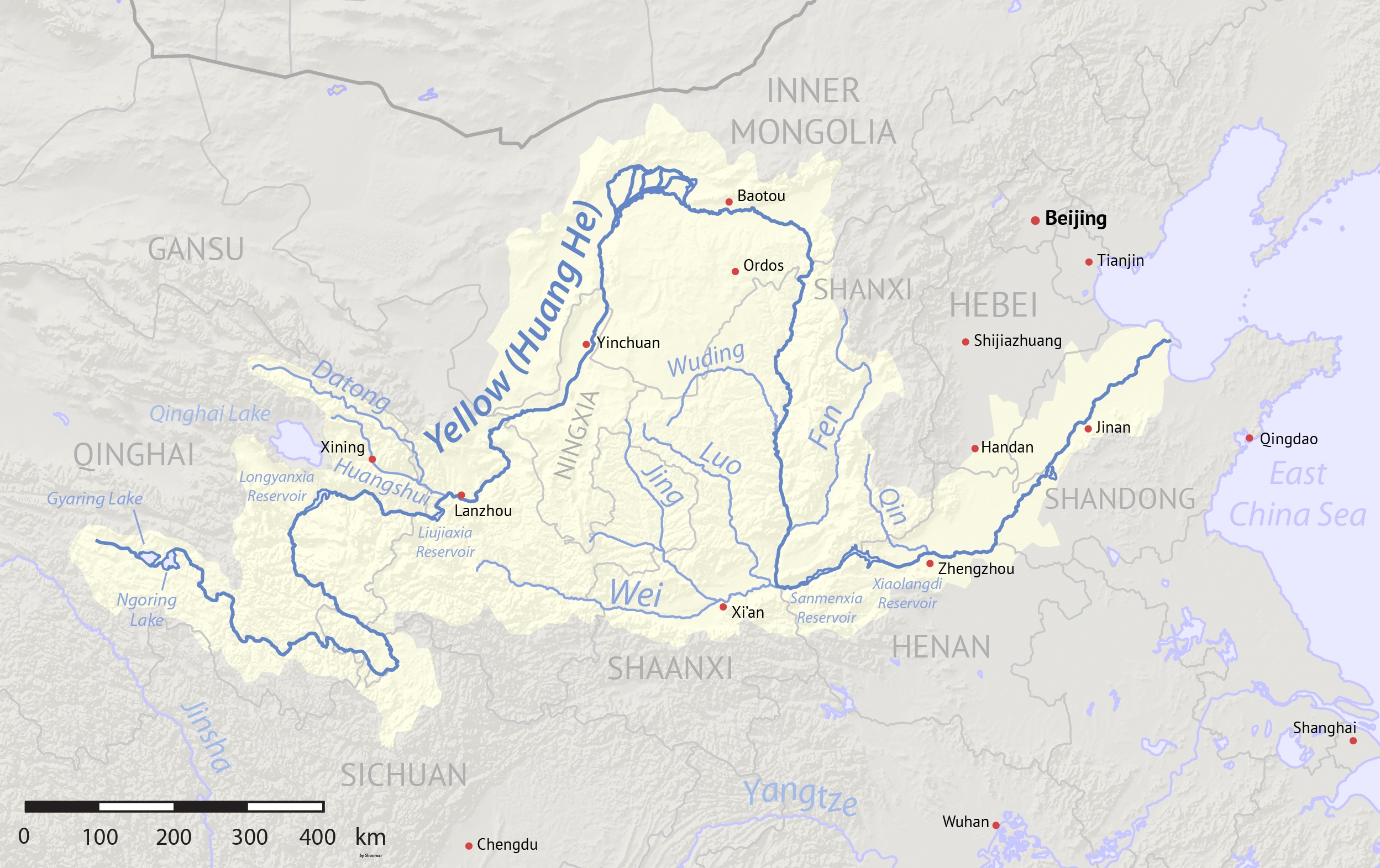
Qinghai Normal University () is a university in Xining, Qinghai, China. Founded in 1956, it lies on the Huangshui River The Huangshui River or Huang Shui is a river in Qinghai and Gansu, China. The river is a left tributary of the Yellow River and its total length is with a basin area of . Etymology The Huangshui River () is also referred to simply as Huang Riv ... and has 2 colleges, 14 departments, 3 branches and a research institute. ReferencesOfficial site Teachers colleges in China Universities and colleges in Qinghai Xining Educational institutions established in 1956 1956 establishments in China {{china-university-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
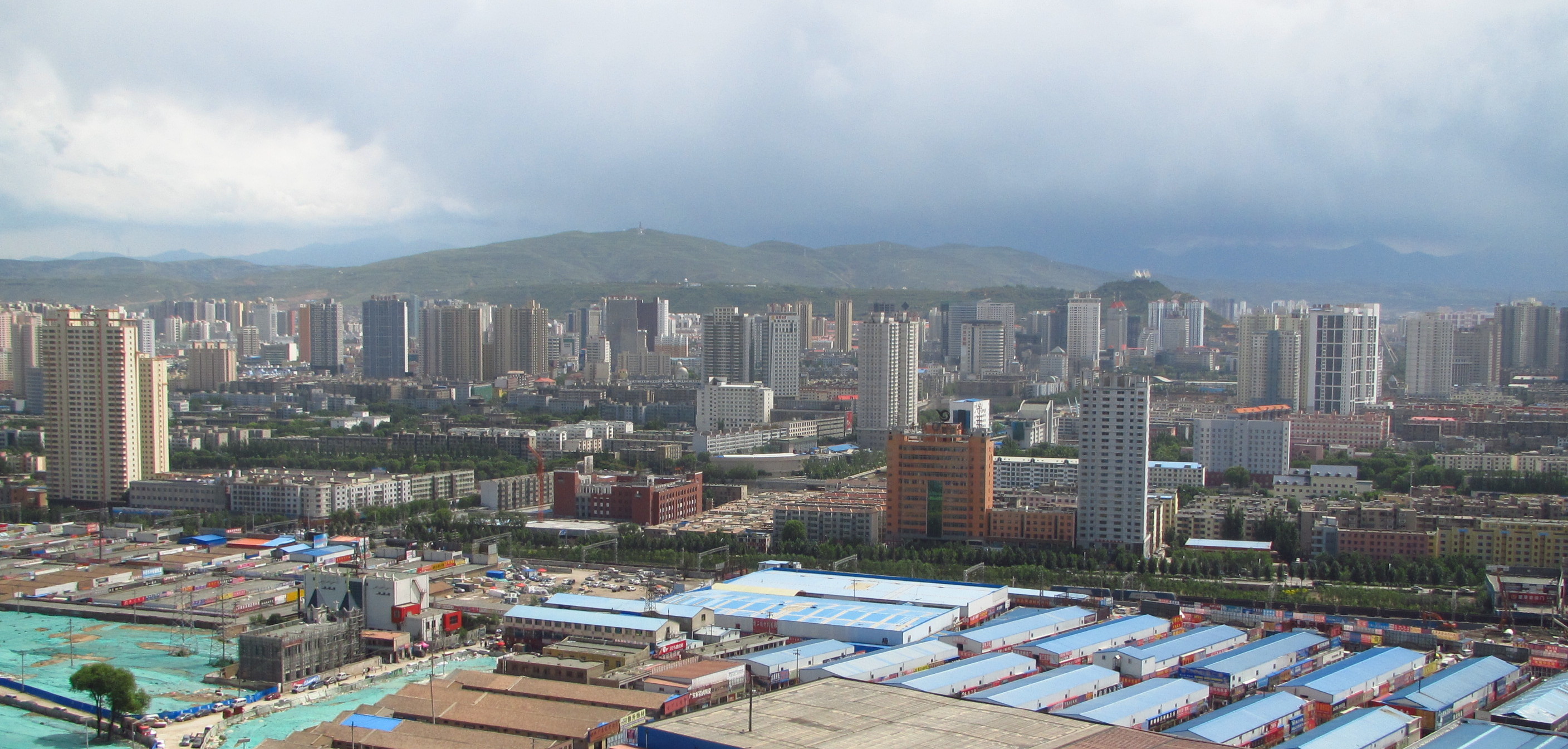
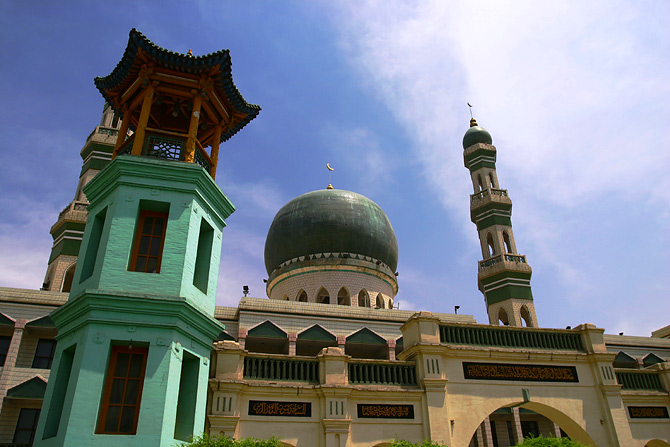
Xining
Xining (; ), alternatively known as Sining, is the capital of Qinghai province in western China and the largest city on the Tibetan Plateau. The city was a commercial hub along the Northern Silk Road's Hexi Corridor for over 2000 years, and was a stronghold of the Han, Sui, Tang, and Song dynasties' resistance against nomadic attacks from the west. Although long a part of Gansu province, Xining was added to Qinghai in 1928. Xining holds sites of religious significance to Muslims and Buddhists, including the Dongguan Mosque and Ta'er Monastery. The city lies in the Huangshui River valley, and owing to its high altitude, has a cool climate on the borderline between cool semi-arid and dry winter humid continental. It is connected by rail to Lhasa, Tibet and connected by high-speed rail to Lanzhou, Gansu and Ürümqi, Xinjiang. The city is home to Qinghai University, a comprehensive university and the only Project 211 university in Xining. History Xining has a hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Manchu Relations in Five Phases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land, the List of countries and territories by land borders, most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces of China, provinces, five autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, four direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and two special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the List of cities in China by population, most populous cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huangshui River
The Huangshui River or Huang Shui is a river in Qinghai and Gansu, China. The river is a left tributary of the Yellow River and its total length is with a basin area of . Etymology The Huangshui River () is also referred to simply as Huang River () in China. The river was formerly romanized as the Hwong-Choui. In Amdo Tibetan, the Huangshui is known as the Tsong Chu. History The Huangshui River valley has long been important as a route between Chinese, Tibetan, and Mongolian cultures. As one of the few fertile valleys on the northeast edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the river's basin has supported agriculture for various Neolithic and Bronze Age civilizations including the Majiayao culture, Qijia culture, Xindian culture, and Kayue culture. Huangshui's valley was also one of the routes utilized by travelers on the Northern Silk Road. The city of Xining formed on the Huangshui due to its strategic importance. Geography The Huangshui River, in name, is a short river t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai Normal University
Qinghai Normal University () is a university in Xining, Qinghai, China. Founded in 1956, it lies on the Huangshui River The Huangshui River or Huang Shui is a river in Qinghai and Gansu, China. The river is a left tributary of the Yellow River and its total length is with a basin area of . Etymology The Huangshui River () is also referred to simply as Huang Riv ... and has 2 colleges, 14 departments, 3 branches and a research institute. ReferencesOfficial site Teachers colleges in China Universities and colleges in Qinghai Xining Educational institutions established in 1956 1956 establishments in China {{china-university-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teachers Colleges In China
A teacher, also called a schoolteacher or formally an educator, is a person who helps students to acquire knowledge, competence, or virtue, via the practice of teaching. ''Informally'' the role of teacher may be taken on by anyone (e.g. when showing a colleague how to perform a specific task). In some countries, teaching young people of school age may be carried out in an informal setting, such as within the family (homeschooling), rather than in a formal setting such as a school or college. Some other professions may involve a significant amount of teaching (e.g. youth worker, pastor). In most countries, ''formal'' teaching of students is usually carried out by paid professional teachers. This article focuses on those who are ''employed'', as their main role, to teach others in a ''formal'' education context, such as at a school or other place of ''initial'' formal education or training. Duties and functions A teacher's role may vary among cultures. Teachers may provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universities And Colleges In Qinghai
The following is List of Universities and Colleges in Qinghai. As of 2012, there are 14 institutions of higher learning in the province, out of which 3 offer Bachelor's degree studies. Notation Note: The list is arranged in the default order followethe one provided by MOE References External links— Ministry of EducationList of Chinese universities including official links {{Qinghai topics Qinghai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Institutions Established In 1956
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Various researchers emphasize the role of critical thinking in order to distinguish education from indoctrination. Some theorists require that education results in an improvement of the student while others prefer a value-neutral definition of the term. In a slightly different sense, education may also refer, not to the process, but to the product of this process: the mental states and dispositions possessed by educated people. Education originated as the transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. Today, educational goals increasingly encompass new ideas such as the liberation of learners, skills needed for modern society, empathy, and complex vocational skills. Types of education are commonly divided into form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |