|
Pyrantel Pamoate
Pyrantel is a medication used to treat a number of parasitic worm infections. This includes ascariasis, hookworm infections, enterobiasis (pinworm infection), trichostrongyliasis, and trichinellosis. It is taken by mouth. Side effects include nausea, headache, dizziness, trouble sleeping, and rash. A lower dose should be used in people with liver disease. While it does not appear to be harmful during pregnancy, it has not been studied for this use. It is unclear if it is safe for use during breastfeeding. It is in the antihelmintic family of medications. It works by paralyzing worms. Pyrantel was initially described in 1965. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Pyrantel is available as a generic medication. It may also be used to treat worms in a number of other animals. Pregnancy and breastfeeding Pyrantel pamoate is considered a pregnancy category C drug for use during pregnancy for humans, but is in category A for canines and felines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Worm Infection
Helminthiasis, also known as worm infection, is any macroparasitic disease of humans and other animals in which a part of the body is infected with parasitic worms, known as helminths. There are numerous species of these parasites, which are broadly classified into tapeworms, flukes, and roundworms. They often live in the gastrointestinal tract of their hosts, but they may also burrow into other organs, where they induce physiological damage. Soil-transmitted helminthiasis and schistosomiasis are the most important helminthiases, and are among the neglected tropical diseases. These group of helminthiases have been targeted under the joint action of the world's leading pharmaceutical companies and non-governmental organizations through a project launched in 2012 called the London Declaration on Neglected Tropical Diseases, which aimed to control or eradicate certain neglected tropical diseases by 2020. Helminthiasis has been found to result in poor birth outcome, poor cognitive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generic Medication
A generic drug is a pharmaceutical drug that contains the same chemical substance as a drug that was originally protected by chemical patents. Generic drugs are allowed for sale after the patents on the original drugs expire. Because the active chemical substance is the same, the medical profile of generics is equivalent in performance compared to their performance at the time when they were patented drugs. A generic drug has the same active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) as the original, but it may differ in some characteristics such as the manufacturing process, pharmaceutical formulation, formulation, excipients, color, taste, and packaging. Although they may not be associated with a particular company, generic drugs are usually subject to government regulations in the countries in which they are dispensed. They are labeled with the name of the manufacturer and a generic non-proprietary name such as the United States Adopted Name (USAN) or International nonproprietary name, Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
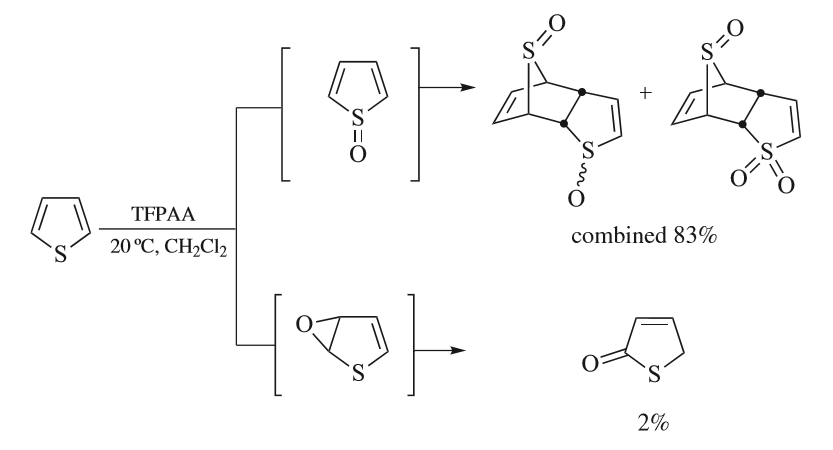
Thiophenes
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a planar five-membered ring, it is aromaticity, aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. It is a colorless liquid with a benzene-like odor. In most of its reactions, it resembles benzene. Compounds analogous to thiophene include furan (C4H4O), selenophene (C4H4Se) and pyrrole (C4H4NH), which each vary by the heteroatom in the ring. Isolation and occurrence Thiophene was discovered by Viktor Meyer in 1882 as a contaminant in benzene. It was observed that isatin (an indole) forms a blue dye if it is mixed with sulfuric acid and crude benzene. The formation of the blue indophenin had long been believed to be a reaction of benzene itself. Viktor Meyer was able to isolate thiophene as the actual substance responsible for this reaction. Thiophene and especially its derivatives occur in petroleum, sometimes in concentrations up to 1–3%. The thiophenic content of Petroleum, oil and coal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidines
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 4 positions) and pyridazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 2 positions). In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Occurrence and history The pyrimidine ring system has wide occurrence in nature as substituted and ring fused compounds and derivatives, including the nucleotides cytosine, thymine and uracil, thiamine (vitamin B1) and alloxan. It is also found in many synthetic compounds such as barbiturates and the HIV drug zidovudine. Although pyrimidine derivatives such as alloxan were known in the early 19th century, a laboratory synthesis of a pyrimidine was not carried out until 1879, when Grimaux reported the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinic Agonists
A nicotinic agonist is a drug that mimics the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The nAChR is named for its affinity for nicotine. Examples include nicotine (by definition), acetylcholine (the endogenous agonist of nAChRs), choline, epibatidine, lobeline, varenicline and cytisine. History Nicotine has been known for centuries for its intoxicating effect. It was first isolated in 1828 from the tobacco plant by German chemists Posselt and Reimann. The discovery of positive effects from nicotine on animal memory was discovered by in vivo researches in the mid 1980s. Those researches led to a new era in studies of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) and their stimulation but until then the focus had mainly been on nicotine addiction. The development of nAChR agonists began in the early 1990s after the discovery of nicotine's positive effects. Some research showed a possible therapy option in preclinical researches. ABT-418 was one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Worm
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in their mammalian hosts for many years due to their ability to manipulate the host's immune respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depolarizing Neuromuscular Blocking Agent
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs, or Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs), block transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors. In clinical use, neuromuscular block is used adjunctively to anesthesia to produce paralysis, firstly to paralyze the vocal cords, and permit endotracheal intubation, and secondly to optimize the surgical field by inhibiting spontaneous ventilation, and causing relaxation of skeletal muscles. Because the appropriate dose of neuromuscular-blocking drug may paralyze muscles required for breathing (i.e., the diaphragm), mechanical ventilation should be available to maintain adequate respiration. This class of medications helps to reduce patient movement, breathing, or ventilator dyssynchrony and allows lower insufflation pressures during laparoscopy. It has several indications for use in the intense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy Category
The pregnancy category of a medication is an assessment of the risk of fetal injury due to the pharmaceutical, if it is used as directed by the mother during pregnancy. It does ''not'' include any risks conferred by pharmaceutical agents or their metabolites in breast milk. Every drug has specific information listed in its product literature. The British National Formulary used to provide a table of drugs to be avoided or used with caution in pregnancy, and did so using a limited number of key phrases, but now Appendix 4 (which was the Pregnancy table) has been removed. Appendix 4 is now titled "Intravenous Additives". However, information that was previously available in the former Appendix 4 (pregnancy) and Appendix 5 (breastfeeding) is now available in the individual drug monographs. United States American law requires that certain drugs and biological products must be labelled very specificallyTitle 21, Part 201.57 (9)(i)of the Code of Federal Regulations lists specific requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both Developed country, developed and Developing country, developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
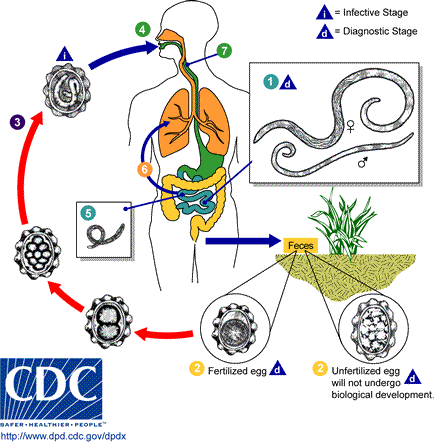
Ascariasis
Ascariasis is a disease caused by the parasitic roundworm ''Ascaris lumbricoides''. Infections have no symptoms in more than 85% of cases, especially if the number of worms is small. Symptoms increase with the number of worms present and may include shortness of breath and fever at the beginning of the disease. These may be followed by symptoms of abdominal swelling, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Children are most commonly affected, and in this age group the infection may also cause poor weight gain, malnutrition, and learning problems. Infection occurs by ingesting food or drink contaminated with ''Ascaris'' eggs from feces. The eggs hatch in the intestines, the larvae burrow through the gut wall, and migrate to the lungs via the blood. There they break into the Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli and pass up the Vertebrate trachea, trachea, where they are coughed up and may be swallowed. The larvae then pass through the stomach a second time into the intestine, where they become adul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antihelmintic
Anthelmintics or antihelminthics are a group of antiparasitic drugs that expel parasitic worms (helminths) and other internal parasites from the body by either stunning or killing them without causing significant damage to the host. They may also be called vermifuges (those that stun) or vermicides (those that kill). Anthelmintics are used to treat people who are infected by helminths, a condition called helminthiasis. These drugs are also used to treat infected animals, particularly small ruminants such as goats and sheep. Anthelmintic medication is also used in mass deworming campaigns of school-aged children in many developing countries. Anthelmintics are also used for mass deworming of livestock. The drugs of choice for soil-transmitted helminths are mebendazole and albendazole; for schistosomiasis and tapeworms it is praziquantel. Types Many early treatments were herbal, such as the oil of herbs of the genus ''Chenopodium'' that were given as anthelmintic treatment for centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
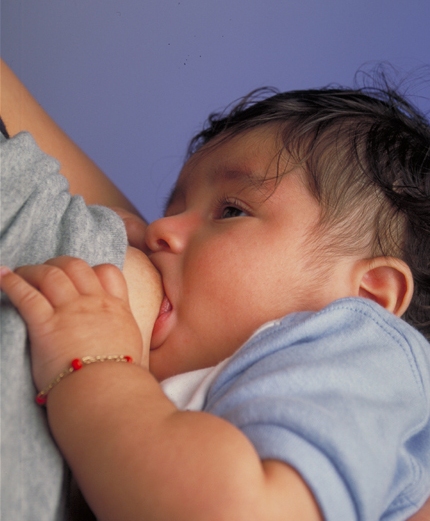
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommend that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's birth and continue as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. The WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. Breastfee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |