|
Ascariasis
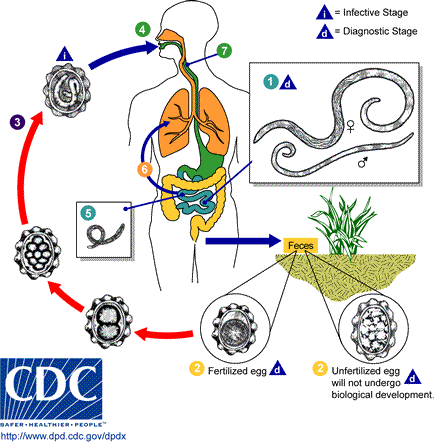
Ascariasis is a disease caused by the parasitic roundworm ''Ascaris lumbricoides''. Infections have no symptoms in more than 85% of cases, especially if the number of worms is small. Symptoms increase with the number of worms present and may include shortness of breath and fever at the beginning of the disease. These may be followed by symptoms of abdominal swelling, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Children are most commonly affected, and in this age group the infection may also cause poor weight gain, malnutrition, and learning problems. Infection occurs by ingesting food or drink contaminated with ''Ascaris'' eggs from feces. The eggs hatch in the intestines, the larvae burrow through the gut wall, and migrate to the lungs via the blood. There they break into the Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli and pass up the Vertebrate trachea, trachea, where they are coughed up and may be swallowed. The larvae then pass through the stomach a second time into the intestine, where they become adul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascaris Lumbricoides
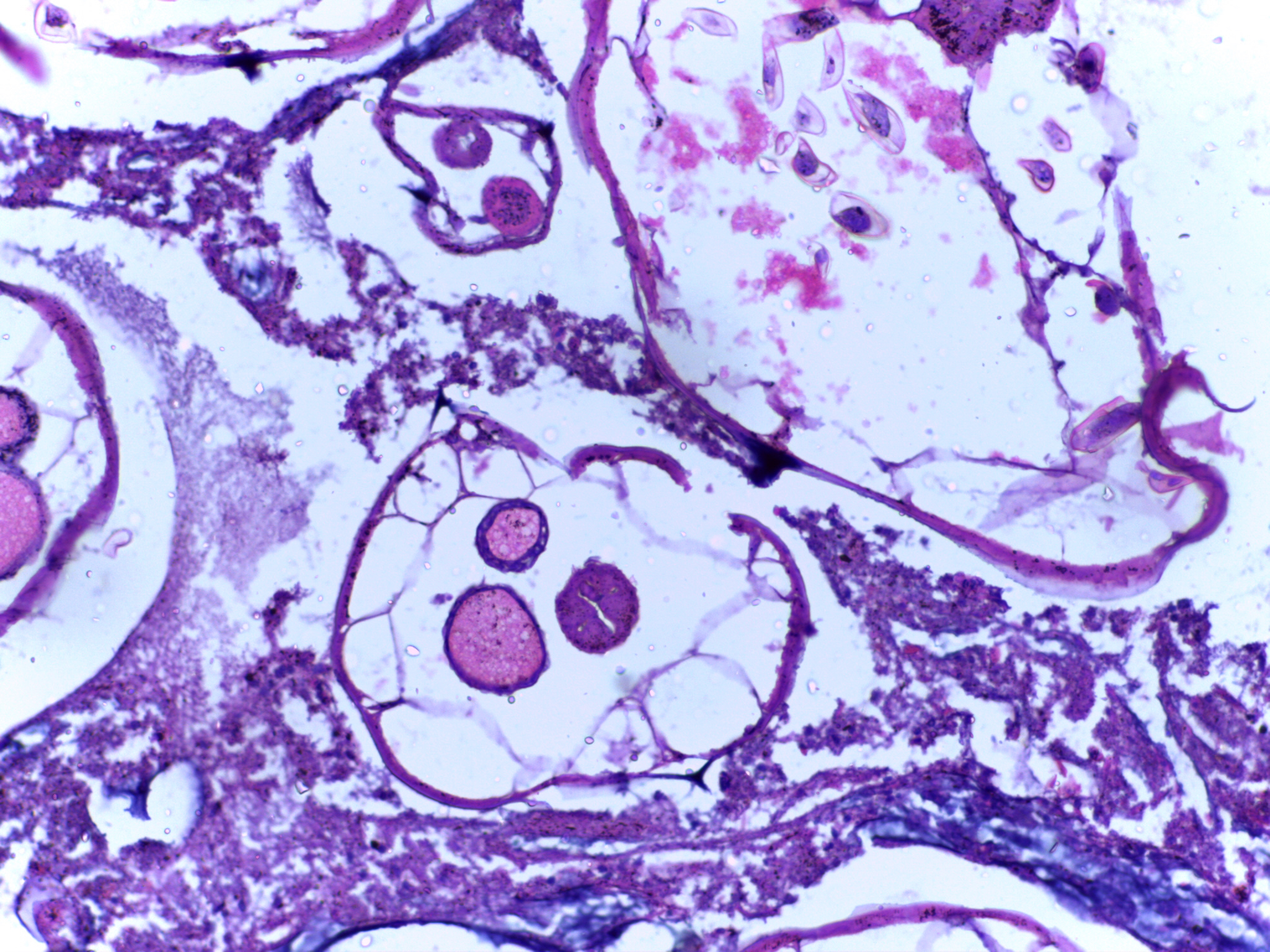
''Ascaris lumbricoides'' is a large parasitic worm, parasitic Nematoda, roundworm of the genus ''Ascaris.'' It is the most common parasitic worm in humans. An estimated 807 million–1.2 billion people are infected with ''Ascaris lumbricoides'' worldwide. People living in tropics, tropical and subtropics, subtropical countries are at greater risk of infection. Infection by ''Ascaris lumbricoides'' is known as ascariasis. It has been proposed that ''Ascaris lumbricoides'' and ''Ascaris suum'' (pig roundworm) are the same species. Life cycle ''Ascaris lumbricoides'', a roundworm, infects humans via the fecal-oral route. Eggs released by adult females are shed in feces. Unfertilized eggs are often observed in fecal samples but never become infective. Fertilized eggs embryonate and become infectious after 18 days to several weeks in soil, depending on the environmental conditions (optimum: moist, warm, shaded soil).Parasites - Ascariasis. (14 February 2018). Retrieved from https:/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil-transmitted Helminthiasis
Soil-transmitted helminthiasis is a type of worm infection (helminthiasis) caused by different species of roundworms. It is caused specifically by worms transmitted through soil contaminated with faecal matter and are known as soil-transmitted helminths. Three types of soil-transmitted helminthiasis can be distinguished: ascariasis, hookworm infection and whipworm infection. These three types of infection are therefore caused by the large roundworm '' A. lumbricoides, ''the hookworms'' Necator americanus ''or'' Ancylostoma duodenale'' and by the whipworm '' Trichuris trichiura''. It has become the most common parasitic disease of humans worldwide. Approximately two billion people (about a fourth of global population) are infected as of the latest estimate, and four billion at risk, surpassing even the all-time most prevalent parasitic disease, malaria. The largest numbers of cases occur in impoverished rural areas of Sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America, Southeast Asia, and Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascaris
''Ascaris'' is a nematode genus of parasitic worms known as the "small intestinal roundworms". One species, ''Ascaris lumbricoides'', affects humans and causes the disease ascariasis. Another species, ''Ascaris suum'', typically infects pigs. Other ascarid genera infect other animals, such as '' Parascaris equorum'', the equine roundworm, and '' Toxocara'' and '' Toxascaris'', which infect dogs and cats. Their eggs are deposited in feces and soil. Plants with the eggs on them infect any organism that consumes them. ''A. lumbricoides'' is the largest intestinal roundworm and is the most common helminth infection of humans worldwide. Infestation can cause morbidity by compromising nutritional status, affecting cognitive processes, inducing tissue reactions such as granuloma to larval stages, and by causing intestinal obstruction, which can be fatal. Morphology and Anatomy * Adult: cylindrical shape, creamy white or pinkish in color * Male: average ; more slender than the fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neglected Tropical Disease
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and parasitic worms (helminths). These diseases are contrasted with the "big three" infectious diseases (HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria), which generally receive greater treatment and research funding. In sub-Saharan Africa, disease burden, the effect of neglected tropical diseases as a group is comparable to that of malaria and tuberculosis. NTD co-infection can also make HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis more deadly. Some treatments for NTDs are relatively inexpensive. For example, praziquantel for schistosomiasis costs about US $0.20 per child per year. Nevertheless, in 2010 it was estimated that control of neglected diseases would require funding of between US$2 billion and $3 billion over the subsequent five to sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascaris
''Ascaris'' is a nematode genus of parasitic worms known as the "small intestinal roundworms". One species, ''Ascaris lumbricoides'', affects humans and causes the disease ascariasis. Another species, ''Ascaris suum'', typically infects pigs. Other ascarid genera infect other animals, such as '' Parascaris equorum'', the equine roundworm, and '' Toxocara'' and '' Toxascaris'', which infect dogs and cats. Their eggs are deposited in feces and soil. Plants with the eggs on them infect any organism that consumes them. ''A. lumbricoides'' is the largest intestinal roundworm and is the most common helminth infection of humans worldwide. Infestation can cause morbidity by compromising nutritional status, affecting cognitive processes, inducing tissue reactions such as granuloma to larval stages, and by causing intestinal obstruction, which can be fatal. Morphology and Anatomy * Adult: cylindrical shape, creamy white or pinkish in color * Male: average ; more slender than the fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helminthiases
Helminthiasis, also known as worm infection, is any macroparasitic disease of humans and other animals in which a part of the body is infected with parasitic worms, known as helminths. There are numerous species of these parasites, which are broadly classified into tapeworms, flukes, and roundworms. They often live in the gastrointestinal tract of their hosts, but they may also burrow into other organs, where they induce physiological damage. Soil-transmitted helminthiasis and schistosomiasis are the most important helminthiases, and are among the neglected tropical diseases. These group of helminthiases have been targeted under the joint action of the world's leading pharmaceutical companies and non-governmental organizations through a project launched in 2012 called the London Declaration on Neglected Tropical Diseases, which aimed to control or eradicate certain neglected tropical diseases by 2020. Helminthiasis has been found to result in poor birth outcome, poor cognitiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albendazole
Albendazole is a broad-spectrum antihelmintic and antiprotozoal agent of the benzimidazole type. It is used for the treatment of a variety of intestinal parasite infections, including ascariasis, pinworm infection, hookworm infection, trichuriasis, strongyloidiasis, taeniasis, clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis, cutaneous larva migrans, giardiasis, and gnathostomiasis, among other diseases. Common side effects include nausea, abdominal pain, and headache. Rare but potentially serious side effects include bone marrow suppression which usually improves on discontinuing the medication. Hepatitis, Liver inflammation has been reported and those with prior liver problems are at greater risk. It is pregnancy category D in Australia, meaning it may cause harm if taken by pregnant women. Albendazole was developed in 1975. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Albendazole is available in a fixed-dose combination with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helminthiasis
Helminthiasis, also known as worm infection, is any macroparasite, macroparasitic disease of humans and other animals in which a part of the body is infected with parasitism, parasitic worms, known as helminths. There are numerous species of these parasites, which are broadly classified into cestoda, tapeworms, trematoda, flukes, and nematode, roundworms. They often live in the gastrointestinal tract of their host (biology), hosts, but they may also burrow into other organ (anatomy), organs, where they induce physiological damage. Soil-transmitted helminthiasis and schistosomiasis are the most important helminthiases, and are among the neglected tropical diseases. These group of helminthiases have been targeted under the joint action of the world's leading pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical companies and non-governmental organizations through a project launched in 2012 called the London Declaration on Neglected Tropical Diseases, which aimed to control or eradicate certain n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitazoxanide
Nitazoxanide, sold under the brand name Alinia among others, is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic and broad-spectrum antiviral medication that is used in medicine for the treatment of various helminthic, protozoal, and viral infections. It is indicated for the treatment of infection by '' Cryptosporidium parvum'' and '' Giardia lamblia'' in immunocompetent individuals and has been repurposed for the treatment of influenza. Nitazoxanide has also been shown to have ''in vitro'' antiparasitic activity and clinical treatment efficacy for infections caused by other protozoa and helminths; evidence suggested that it possesses efficacy in treating a number of viral infections as well. Chemically, nitazoxanide is the prototype member of the thiazolides, a class of drugs which are synthetic nitrothiazolyl- salicylamide derivatives with antiparasitic and antiviral activity. Tizoxanide, an active metabolite of nitazoxanide in humans, is also an antiparasitic drug of the thiazolid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribendimidine
Tribendimidine is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic agent developed in China, at the National Institute of Parasitic Diseases in Shanghai. It is a derivative of amidantel.Free full text In clinical trials, it was highly effective in treating ankylostomiasis, ascariasis and enterobiasis. It is also effective against clonorchiasis. However, animal studies suggest it is ineffective in treating ''Schistosoma mansoni'' or ''Fasciola hepatica'' disease. The drug has also performed well in trials against opisthorchiasis, curing about 70% of cases. Tribendimidine is manufactured by Shandong Xinhua Pharmaceutical Company Limited in Zibo, Shandong, China. It was approved by the China Food and Drug Administration in 2007. References Anthelmintics Amidines Imines ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and dependent territories in Africa, African countries and territories that are situated fully in that specified region, the term may also include polities that only have part of their territory located in that region, per the definition of the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations (UN). This is considered a non-standardised geographical region with the number of countries included varying from 46 to 48 depending on the organisation describing the region (e.g. United Nations, UN, World Health Organization, WHO, World Bank, etc.). The Regions of the African Union, African Union (AU) uses a different regional breakdown, recognising all 55 member states on the continent—grouping them into five distinct and standard regions. The te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |