|
Pyotr Nesterov
Pyotr Nikolayevich Nesterov (russian: Пётр Николаевич Нестеров ( – ) was a Russian pilot, an aircraft designer and an aerobatics pioneer. Life and career Nesterov was born on 15 February 1887 in Nizhny Novgorod, into the family of an army officer, a cadet corps teacher. In August 1904, he left the military school in Nizhny Novgorod and went to Mikhailov artillery academy in St Petersburg. He became a second lieutenant and served in the 9th East Siberian Artillery Brigade in Vladivostok. By the laws of that time, an officer who married before the age of 28 had to contribute a so-called ‘reserve’ to the state treasury – a deposit of 5,000 rubles to provide for his family in the event of his death. The only exception was made for officers who served in the Far East; as Nesterov did not have the money, he took his young wife to the Far East. In 1909, Nesterov came into contact with aviation when he was posted to a balloon observation regiment as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, Нижний Новгород, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj ˈnovɡərət ), colloquially shortened to Nizhny, from the 13th to the 17th century Novgorod of the Lower Land, formerly known as Gorky (, ; 1932–1990), is the administrative centre of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast and the Volga Federal District. The city is located at the confluence of the Oka and the Volga rivers in Central Russia, with a population of over 1.2 million residents, up to roughly 1.7 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Nizhny Novgorod is the sixth-largest city in Russia, the second-most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. It is an important economic, transportation, scientific, educational and cultural center in Russia and the vast Volga-Vyatka economic region, and is the main center of river tourism in Russia. In the historic part of the city there are many universities, theaters, museums and churches. The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area of , with a population of 600,871 residents as of 2021. Vladivostok is the second-largest city in the Far Eastern Federal District, as well as the Russian Far East, after Khabarovsk. Shortly after the signing of the Treaty of Aigun, the city was founded on July 2, 1860 as a Russian military outpost on formerly Chinese land. In 1872, the main Russian naval base on the Pacific Ocean was transferred to the city, stimulating the growth of modern Vladivostok. After the outbreak of the Russian Revolution in 1917, Vladivostok was Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War, occupied in 1918 by White Russian and Allies_of_World_War_I, Allied forces, the last of whom from Japan were not withdrawn until 1922; by that tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morane-Saulnier Type G
The Morane-Saulnier G was a two-seat sport and racing monoplane produced in France before the First World War.Taylor 1989, 648"The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft", 2539 It was a development of the racing monoplanes designed by Léon Morane and Raymond Saulnier after leaving Borel and, like its predecessors, was a wire-braced, shoulder-wing monoplane. Construction was of fabric-covered wood throughout, except for the undercarriage struts which were of steel tube."The Latest Morane-Saulnier Monoplane", 564 The type was a sporting success. In April 1913, Roland Garros took second place in the inaugural Schneider Cup in a floatplane version, finishing with a time of 40 minutes 40 seconds."The Monaco Meeting", 450 On 26 June, Claude Grahame-White flew another float-equipped example from Paris to London via Le Havre, Boulogne-sur-Mer, and Dover,"Mr Grahame-Wnite's Seine—Thames Trip" covering some that day.Hartmann 2001, 10 Between 21 and 28 September the same year, two float-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adoption Of The Gregorian Calendar
The adoption of the Gregorian Calendar was an event in the early modern history of most cultures and societies, marking a change from their traditional (or "old style") dating system to the modern (or "new style") dating system the Gregorian calendar that is widely used around the world today. Some states adopted the new calendar from 1582, some did not do so before the early twentieth century, and others did so at various dates between. A number of jurisdictions continue to use a different civil calendar. For many the new style calendar is only used for civil purposes and the old style calendar remains used in religious contexts. Today, the Gregorian calendar is the world's most widely used civil calendar. During and for some time after the change between systems, it has been common to use the terms "Old Style" and "New Style" when giving dates, to indicate which calendar was used to reckon them. The Gregorian calendar was decreed in 1582 by the papal bull by Pope Grego ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Galicia
The Battle of Galicia, also known as the Battle of Lemberg, was a major battle between Russia and Austria-Hungary during the early stages of World War I in 1914. In the course of the battle, the Austro-Hungarian armies were severely defeated and forced out of Galicia, while the Russians captured Lemberg and, for approximately nine months, ruled Eastern Galicia until their defeat at Gorlice and Tarnów. Background When war came the Austro-Hungarian Chief-of-Staff Franz Conrad von Hötzendorf planned to launch an offensive into Russian Poland with his northern armies (the 1st and 4th). The Russians would far outnumber the Central Powers in the east (especially the Austro-Hungarian armies, which were Russia's primary target), Conrad believed that their best option was an early advance into southern Poland where the Russians would be concentrating their newly mobilized units. Conrad knew that his German allies were committed to an offensive in the West to defeat the Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
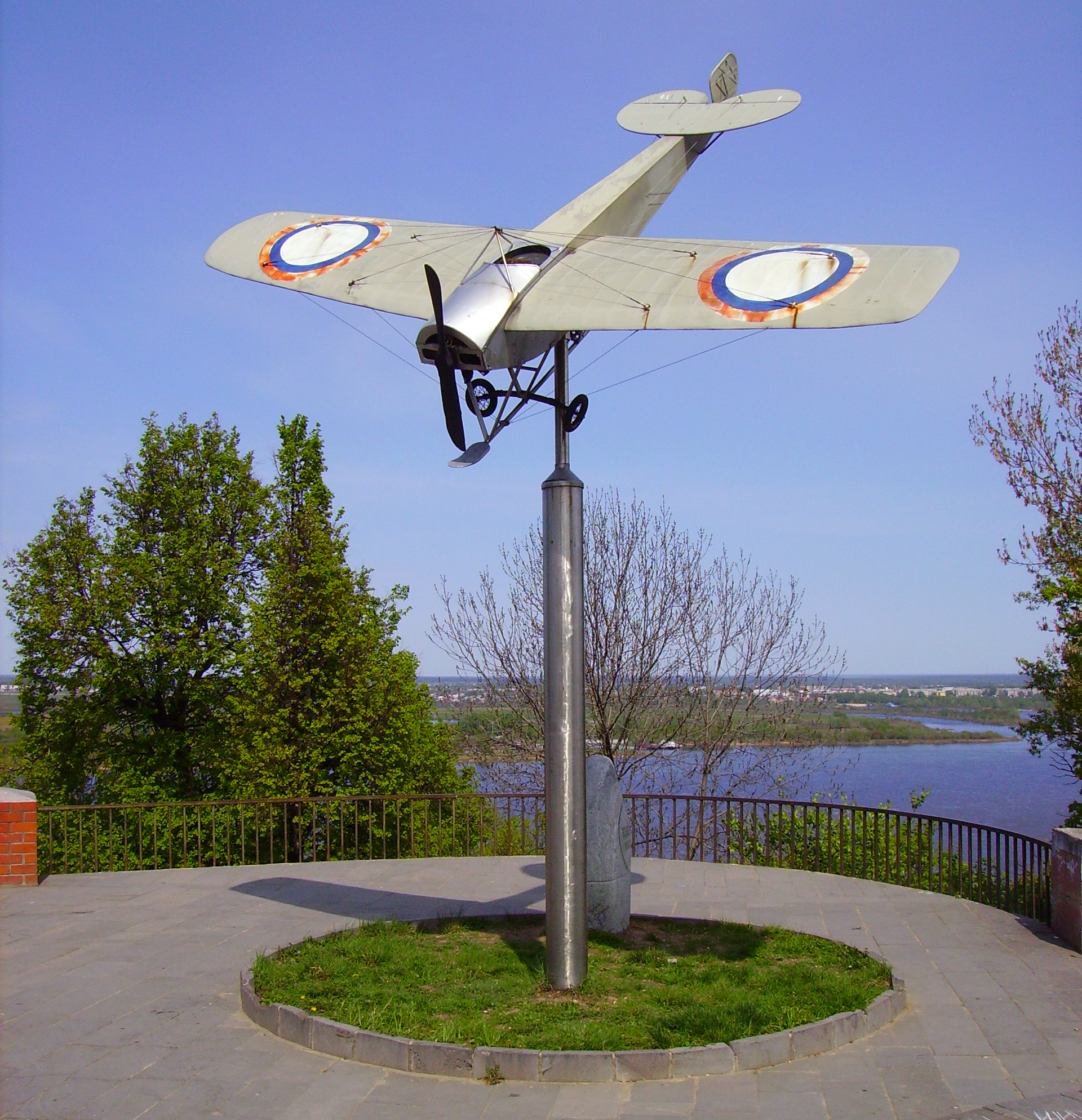
Nizhny Novgorod Nieuport Plane
Nizhny (russian: Ни́жний; masculine), Nizhnyaya (; feminine), or Nizhneye (russian: Ни́жнее; neuter), literally meaning "lower", is the name of several Russian localities. It may refer to: * Nizhny Novgorod, a Russian city colloquially referred to as "Nizhny" * Nizhny, Republic of Bashkortostan, a ''khutor'' in Chishminsky District of the Republic of Bashkortostan * Nizhny, Samara Oblast, a settlement in Isaklinsky District of Samara Oblast * Nizhnyaya, Kirov Oblast, a village in Pizhansky District of Kirov Oblast * Nizhnyaya, Leningrad Oblast, a village in Gatchinsky District of Leningrad Oblast * Nizhnyaya, Perm Krai, a village in Alexandrovsky District of Perm Krai * Nizhneye, Bryansk Oblast, a '' selo'' in Starodubsky District of Bryansk Oblast * Nizhneye, Kaluga Oblast, a ''selo'' in Zhukovsky District of Kaluga Oblast Kaluga Oblast (russian: Калу́жская о́бласть, translit=Kaluzhskaya oblast) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
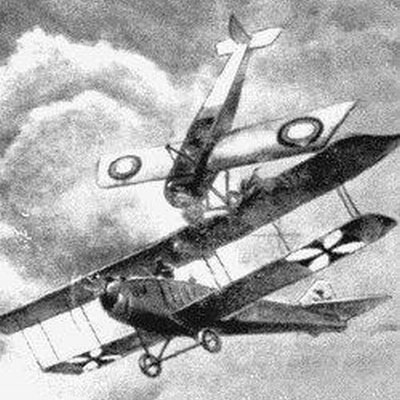
Aerial Ramming
Aerial ramming or air ramming is the ramming of one aircraft with another. It is a last-ditch tactic in air combat, sometimes used when all else has failed. Long before the invention of aircraft, ramming tactics in naval warfare and ground warfare were common. The first aerial ramming was performed by Pyotr Nesterov in 1914 during the First World War. In the early stages of World War II the tactic was employed by Soviet pilots, who called it ''taran'', the Russian word for "battering ram". A ramming pilot could use the weight of the aircraft as a ram, or they could try to make the enemy lose control of their plane, using the propeller or wing to damage the enemy's tail or a wing. Ramming took place when a pilot ran out of ammunition yet was still intent on destroying an enemy, or when the plane had already been damaged beyond saving. Most rammings occurred when the attacker's aircraft was economically, strategically or tactically less valuable than the enemy's, such as pilots flyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolphe Pégoud
Adolphe Célestin Pégoud (13 June 1889 – 31 August 1915) was a French aviator and flight instructor who became the first fighter ace in history during World War I. Biography Adolphe Célestin Pégoud was born 13 June 1889 in Montferrat, France. Pégoud served in the French Army from 1907 to 1913. Discharged on 13 February 1913, he immediately began flying, and earned his pilot's certificate 1 March 1913. Using a sacrifice aircraft, Pégoud was the first pilot to make a parachute jump from an airplane. During the first jump, observing the unexpected path of the plane and particularly a loop-like trajectory, he was convinced he could reproduce and control the same in flight. After landing, Pégoud addressed reporters: "I've seen him, alone, looping the loop. So you see that this is possible. Also, I will try!" As a test pilot for Louis Blériot, he devoted himself to this goal with a Blériot model XI monoplane in a series of test flights exploring the limits of airplane m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by population within city limits, seventh-most populous city in Europe. Kyiv is an important industrial, scientific, educational, and cultural center in Eastern Europe. It is home to many High tech, high-tech industries, higher education institutions, and historical landmarks. The city has an extensive system of Transport in Kyiv, public transport and infrastructure, including the Kyiv Metro. The city's name is said to derive from the name of Kyi, one of its four legendary founders. During History of Kyiv, its history, Kyiv, one of the oldest cities in Eastern Europe, passed through several stages of prominence and obscurity. The city probably existed as a commercial center as early as the 5th century. A Slavs, Slavic settlement on the great trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoplane
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration with a single mainplane, in contrast to a biplane or other types of multiplanes, which have multiple planes. A monoplane has inherently the highest efficiency and lowest drag of any wing configuration and is the simplest to build. However, during the early years of flight, these advantages were offset by its greater weight and lower manoeuvrability, making it relatively rare until the 1930s. Since then, the monoplane has been the most common form for a fixed-wing aircraft. Characteristics Support and weight The inherent efficiency of the monoplane is best achieved in the cantilever wing, which carries all structural forces internally. However, to fly at practical speeds the wing must be made thin, which requires a heavy structure to make it strong and stiff enough. External bracing can be used to improve structural efficiency, reducing weight and cost. For a wing of a given size, the weight reduction allows it to fly slower a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nieuport IV
The Nieuport IV was a French-built sporting, training and reconnaissance monoplane of the early 1910s. Design and development Societe Anonyme des Etablissements Nieuport was formed in 1909 by Édouard Nieuport. The Nieuport IV was a development of the single-seat Nieuport II and two seat Nieuport III.A. It was initially designed as a two-seat sporting and racing monoplane, but was also bought by the air forces of several countries. It was initially powered by a Gnome Omega rotary engine, which was later replaced by more powerful rotaries.Green, 1965, p.347 Operational history The first Nieuport IVs were built in 1911 and production continued well into World War I in Russia. The design was adopted in small numbers by most air arms of the period, although the Imperial Russian Air Service was the largest user. The IV.G was one of the principal aircraft used by the Imperial Russian Air Service during its formative years, with roughly 300 being produced locally by the Russo- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobatic Maneuver
Aerobatic maneuvers are flight paths putting aircraft in unusual attitudes, in air shows, dogfights or competition aerobatics. Aerobatics can be performed by a single aircraft or in formation with several others. Nearly all aircraft are capable of performing aerobatics maneuvers of some kind, although it may not be legal or safe to do so in certain aircraft. Aerobatics consist of five basic maneuvers: * Lines (both horizontal and vertical), * loops, * rolls, * spins, and * hammerheads. Most aerobatic figures are composites of these basic maneuvers with rolls superimposed. A loop is when the pilot pulls the plane up into the vertical, continues around until they are heading back in the same direction, like making a 360 degree turn, except it is in the vertical plane instead of the horizontal. The pilot will be inverted (upside down) at the top of the loop. A loop can also be performed by rolling inverted and making the same maneuver but diving towards the ground. It can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)


