|
Putah Creek
Putah Creek ( Patwin: ''Liwaito'') is a major stream in Northern California, a tributary of the Yolo Bypass, and ultimately, the Sacramento River. The creek has its headwaters in the Mayacamas Mountains, a part of the Coast Range, and flows east through two dams. First, Monticello Dam forms Lake Berryessa, below which Putah Creek forms the border of Yolo and Solano Counties, and then flows to the Putah Diversion Dam and Lake Solano. After several drought years in the late 1980s, the majority of Putah Creek went dry, prompting a landmark lawsuit that resulted in the signing of the Putah Creek Accord in 2000. The Accord established releases from the dams to maintain stream flows in Putah Creek, with natural flow regimes which spike in winter/spring and ebb in summer/fall. The restoration of natural flow regimes has resulted in a doubling of riparian bird species and a return of spawning native steelhead trout and Chinook salmon, as well as protecting the liveliho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monticello Dam
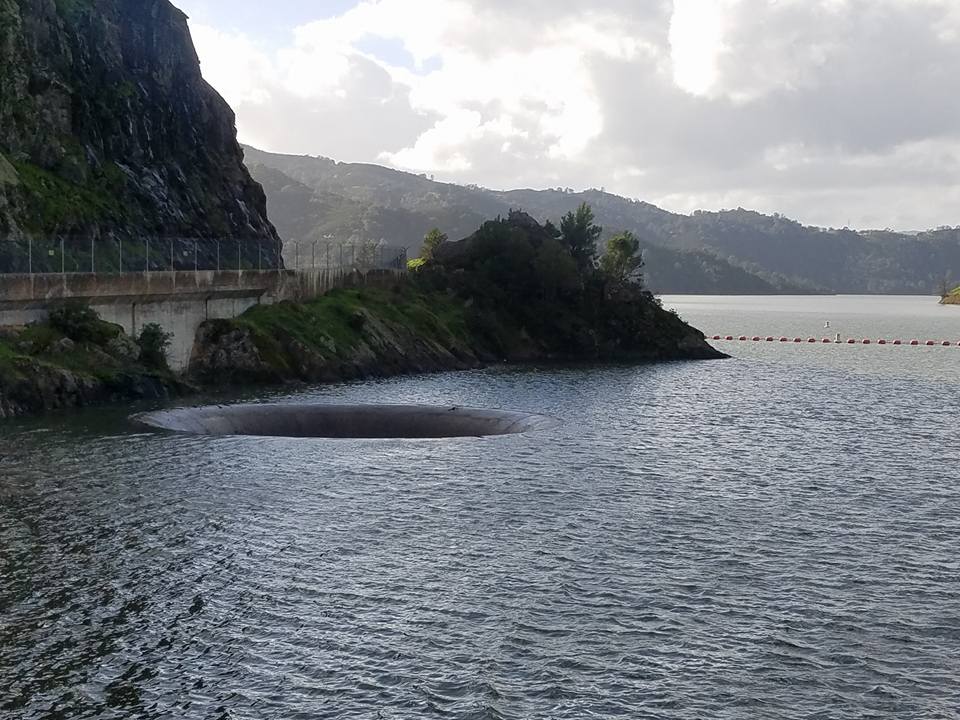
Monticello Dam is a high concrete arch dam in Napa County, California, Napa County, California, United States, constructed between 1953 and 1957. The dam impounded Putah Creek to create Lake Berryessa in the Vaca Mountains. Lake Berryessa is currently the seventh-largest Reservoir, man-made lake in California. Water from the reservoir primarily supplies agriculture in the Sacramento Valley downstream. The dam is noted for its classic, uncontrolled morning-glory-type spillway. The diameter at the lip is . To the south is Putah Creek State Wildlife Area. Statistics Although the dam and its long reservoir are located entirely in eastern Napa County, the dam lies less than west of the boundary with Yolo County, California, Yolo and Solano County, California, Solano Counties. In addition, parts of the lake's Drainage basin, watershed extend into Lake County, California, Lake County. Monticello is a concrete medium thick arch dam high from the foundations, long and above the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern California
Northern California (commonly shortened to NorCal) is a geocultural region that comprises the northern portion of the U.S. state of California, spanning the northernmost 48 of the state's List of counties in California, 58 counties. Northern California in its largest definition is determined by dividing the state into two regions, the other being Southern California. The main northern population centers include the San Francisco Bay Area (anchored by the cities of San Jose, California, San Jose, San Francisco, and Oakland, California, Oakland), the Greater Sacramento area (anchored by the state capital Sacramento, California, Sacramento), the Redding, California, area south of the Cascade Range, and the Metropolitan Fresno area (anchored by the city of Fresno, California, Fresno). Northern California also contains Sequoia sempervirens, redwood forests, along with most of the Sierra Nevada, including Yosemite Valley and part of Lake Tahoe, Mount Shasta (the second-highest peak in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a world language, global language with 483 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain, and about 558 million speakers total, including second-language speakers. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries, as well as one of the Official languages of the United Nations, six official languages of the United Nations. Spanish is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Board On Geographic Names
The United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) is a Federal government of the United States, federal body operating under the United States Secretary of the Interior. The purpose of the board is to establish and maintain uniform usage of geography, geographic names throughout the federal government of the United States. History Following the American Civil War, more and more American pioneer, American settlers began moving westward, prompting the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government to pursue some sort of consistency for referencing landmarks on maps and in official documents. As such, on January 8, 1890, Thomas Corwin Mendenhall, superintendent of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey Office, wrote to 10 noted geographers "to suggest the organization of a Board made up of representatives from the different Government services interested, to which may be referred any disputed question of geographical orthography." President Benjamin Harrison si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinook Salmon
The Chinook salmon (''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') is the largest and most valuable species of Oncorhynchus, Pacific salmon. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other vernacular names for the species include king salmon, quinnat salmon, spring salmon, blackmouth, and tyee salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name ''chavycha'' (чавыча). Chinook are anadromous fish native to the North Pacific Ocean and the river systems of western North America, ranging from California to Alaska, as well as Asian rivers ranging from northern Japan to the Palyavaam River in Arctic northeast Siberia. They have been introduced to other parts of the world, including New Zealand and Patagonia. Introduced Chinook salmon are thriving in Lake Michigan and Michigan's western rivers. A large Chinook is a prized and sought-after catch for a sporting angler. The flesh of the salmon is also highly valued for its dietary nutritional content, which includes h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steelhead Trout
Steelhead, or occasionally steelhead trout, is the anadromous form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout (''O. m. gairdneri'', also called redband steelhead). Steelhead are native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific basin in Northeast Asia and North America. Like other sea-run (anadromous) trout and salmon, steelhead spawn in freshwater, smolts migrate to the ocean to forage for several years and adults return to their natal streams to spawn. Steelhead are iteroparous, although their survival rate is approximately only 10–20%. Description The freshwater form of the steelhead is the rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss''). The difference between these forms of the species is that steelhead migrate to the ocean and return to freshwater tributaries to spawn, whereas non-anadromous rainbow trout do not leave freshwater. Steelhead are also larger and less colorful than rainbow trout. Steelhead can weigh up to and reach in length. They can live u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
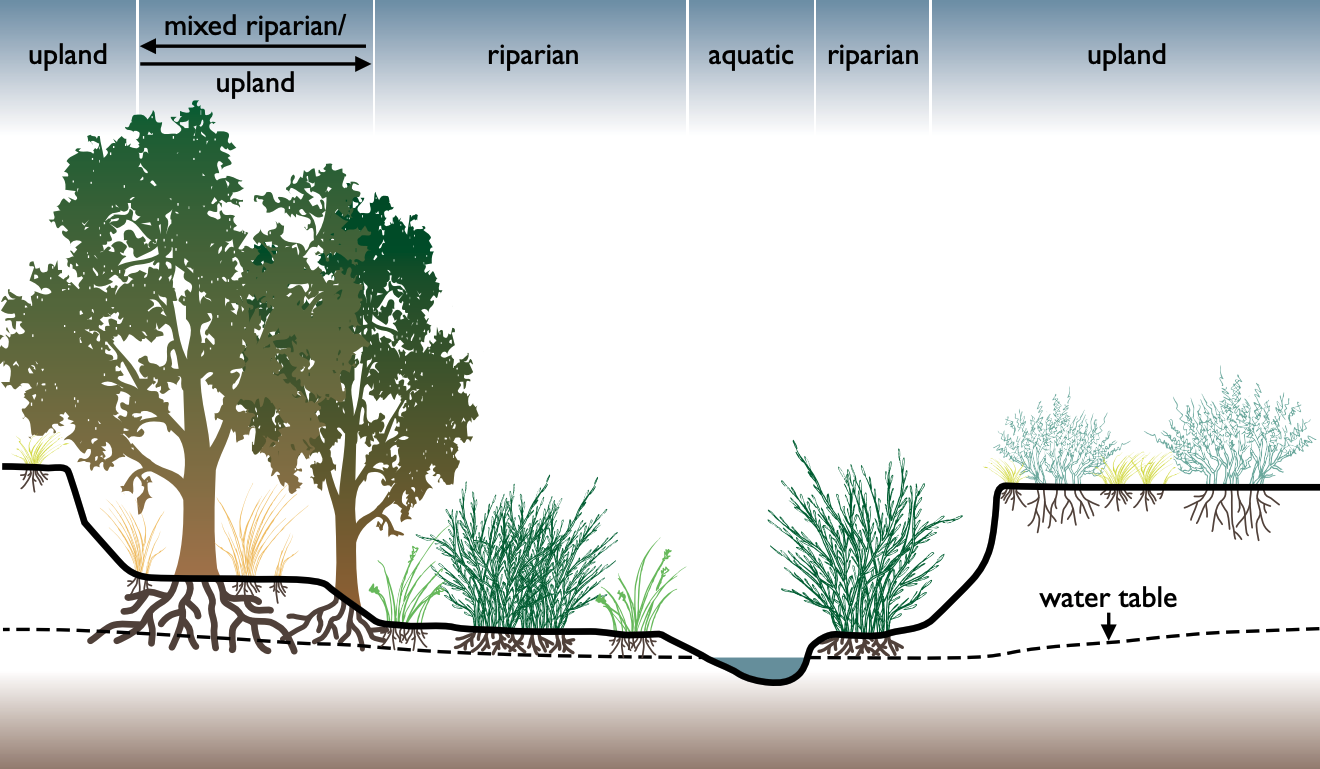
Riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin '' ripa'', meaning " river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Regime (hydrology)
Discharge regime, flow regime, or hydrological regime (commonly termed river regime, but that term is also used for other measurements) is the long-term pattern of annual changes to a Stream, stream's Discharge (hydrology), discharge at a particular point. Hence, it shows how the discharge of a stream at that point is expected to change over the year. It is thus the Hydrology, hydrological equivalent of climate. The main factor affecting the regime is climate, along with Terrain, relief, bedrock, soil and vegetation, as well as human activity. Like general trends can be grouped together into certain named groups, either by what causes them and the part of the year they happen (most classifications) or by the climate in which they most commonly appear (Beckinsale classification). There are many different classifications; however, most of them are localized to a specific area and cannot be used to classify all the rivers of the world. When interpreting such records of discharge, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Solano
Lake Solano is a reservoir formed by Putah Diversion Dam impounding Putah Creek, located in the Vaca Mountains within Yolo County and northern Solano County, California. The California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment has issued a safe eatinadvisoryfor any fish caught in Putah Creak including Lake Solano due to elevated levels of mercury. Geography The reservoir is long with a capacity of 750 acre-feet. It serves to divert water into the Putah South Canal to supply agricultural and urban users. It is downstream from Monticello Dam, also on Putah Creek. The city of Winters is downstream from the Putah Diversion Dam in the western Sacramento Valley The Sacramento Valley is the area of the Central Valley of the U.S. state of California that lies north of the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta and is drained by the Sacramento River. It encompasses all or parts of ten Northern California .... Recreation The lake and the surrounding land is used for recrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solano County
Solano County () is a county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, its population was 453,491. The county seat is Fairfield. Solano County comprises the Vallejo–Fairfield metropolitan statistical area, which is also included in the San Jose–San Francisco–Oakland, combined statistical area. Solano County is the northeastern county in the nine-county San Francisco Bay Area region. A portion of the South Campus at the University of California, Davis, is in Solano County. History Solano County was one of the original counties of California, created in 1850 at the time of statehood. At the request of General Mariano Guadalupe Vallejo, the county was named for Chief Solano of the Suisun people, a Native American tribe of the region and Vallejo's close ally. Chief Solano at one time led the tribes between the Petaluma River and the Sacramento River. The chief was also called ''Sem-Yeto'', which signifies "brave or fierce hand". The chief wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yolo County
Yolo County (; Wintun: ''Yo-loy''), officially the County of Yolo, is a county located in the northern portion of the U.S. state of California. Yolo County was one of the original counties of California, created in 1850 at the time of statehood. As of the 2020 census, its population was 216,403. Its county seat is Woodland. Yolo County is included in the greater Sacramento metropolitan area in the Sacramento Valley. Etymology In the original act of 1850, the name was spelled "Yola". ''Yolo'' is a Patwin Native American name variously believed to be a corruption of a tribal name, ''Yo-loy'', meaning "a place abounding in rushes", the village of Yodoi, believed to be in the vicinity of Knights Landing, California, or the name of the chief of said village, ''Yodo''. History Yolo County was one of the original counties of California, created in 1850 at the time of statehood. Government The county is governed by a board of five district supervisors as well the governments of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |