Riparian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
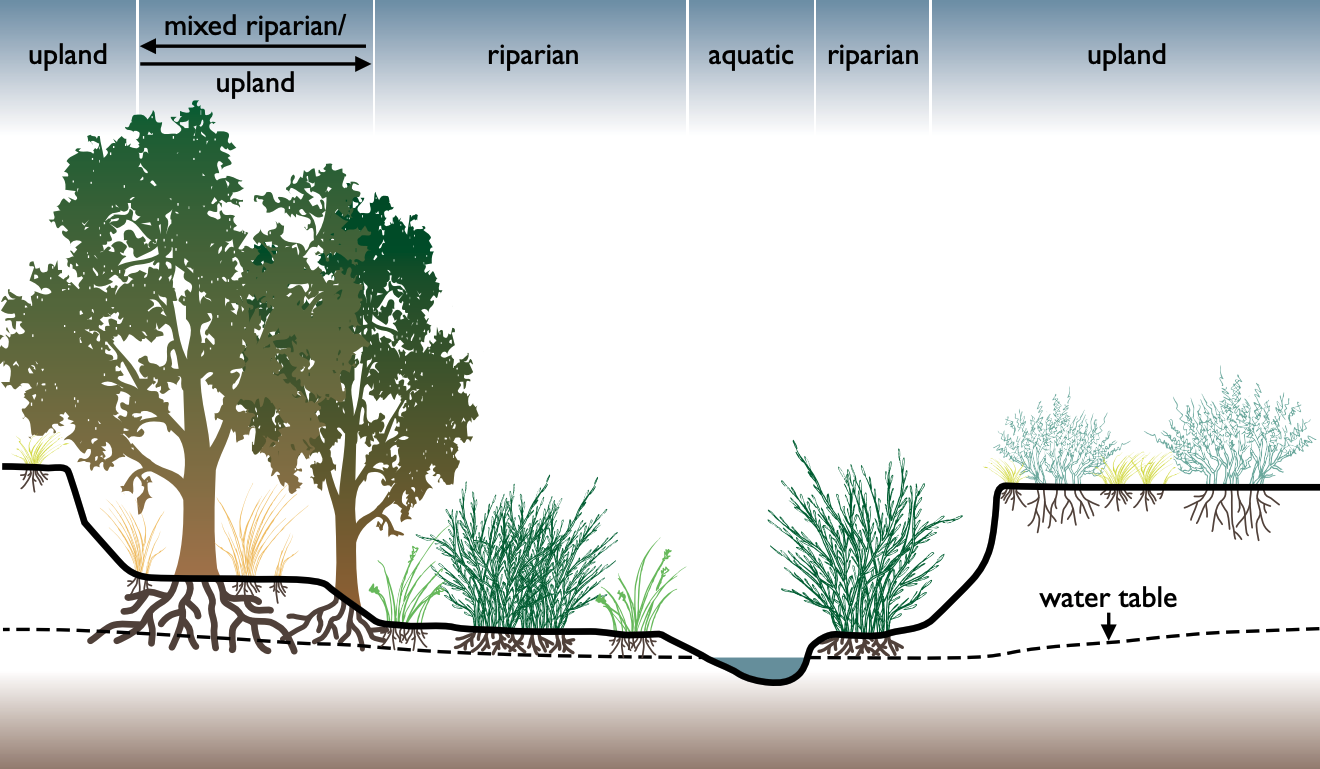 A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a
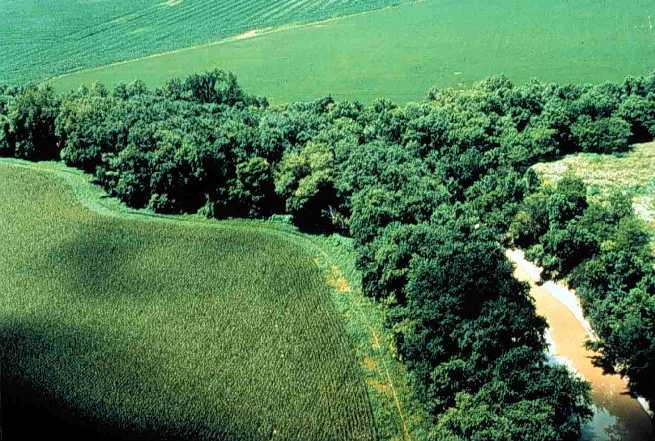

 Riparian zones dissipate stream energy. The
Riparian zones dissipate stream energy. The
 A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
or stream
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a strea ...
. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest
A riparian forest or riparian woodland is a forested or wooded area of land adjacent to a body of water such as a river, stream, pond, lake, marshland, estuary, canal, Sink (geography), sink, or reservoir. Due to the broad nature of the definitio ...
, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
'' ripa'', meaning " river bank".
Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biome
A biome () is a distinct geographical region with specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. It consists of a biological community that has formed in response to its physical environment and regional climate. In 1935, Tansley added the ...
s of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ...
, environmental resource management, and civil engineering
Civil engineering is a regulation and licensure in engineering, professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads ...
because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
, and the influence they have on terrestrial and semiaquatic
In biology, being semi-aquatic refers to various macroorganisms that live regularly in both aquatic and terrestrial environments. When referring to animals, the term describes those that actively spend part of their daily time in water (in ...
fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
as well as aquatic ecosystem
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem found in and around a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms—aquatic life—that are dependent on each other and on their environ ...
s, including grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominance (ecology), dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes such as clover, and other Herbaceo ...
s, woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants (trees and shrubs), or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunli ...
s, wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
s, and even non-vegetative areas.
Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zones are important natural biofilter
Biofiltration is a pollution control technique using a bioreactor containing living material to capture and biologically degrade pollutants. Common uses include processing waste water, capturing harmful chemicals or silt from surface runoff, a ...
s, protecting aquatic environments from excessive sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
ation, polluted surface runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow or terrestrial runoff) is the unconfined flow of water over the ground surface, in contrast to ''channel runoff'' (or ''stream flow''). It occurs when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other ...
, and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
. They supply shelter and food for many aquatic animal
An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in a body of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respirato ...
s and shade that limits stream temperature change. When riparian zones are damaged by construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
, agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
or silviculture
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, as well as quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production.
The name comes from the Latin ('forest') and ('growing'). The study of forests ...
, biological restoration can take place, usually by human intervention in erosion control
Erosion control is the practice of preventing or controlling wind or water erosion in agriculture, land development, coast, coastal areas, Bank (geography), river banks and construction. Effective erosion controls handle surface runoff and are ...
and revegetation. If the area adjacent to a watercourse
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a strea ...
has standing water or saturated soil for as long as a season, it is normally termed a wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
because of its hydric soil Hydric soil is soil which is permanently or seasonally saturated by water, resulting in anaerobic conditions, as found in wetlands.
Overview
Most soils are aerobic. This is important because plant roots respire (that is, they consume oxygen ...
characteristics. Because of their prominent role in supporting a diversity of species, riparian zones are often the subject of national protection in a biodiversity action plan. These are also known as a "plant or vegetation waste buffer".
Research shows that riparian zones are instrumental in water quality
Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through tr ...
improvement for both surface runoff and water flowing into streams through subsurface or groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
flow. Riparian zones can play a role in lowering nitrate contamination in surface runoff, such as manure and other fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
s from agricultural fields, that would otherwise damage ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s and human health. Particularly, the attenuation of nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
or denitrification
Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process where nitrate (NO3−) is reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products. Facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denitr ...
of the nitrates from fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
in this buffer zone is important. The use of wetland riparian zones shows a particularly high rate of removal of nitrate entering a stream and thus has a place in agricultural management. Also in terms of carbon transport from terrestrial ecosystems to aquatic ecosystems, riparian groundwater can play an important role. As such, a distinction can be made between parts of the riparian zone that connect large parts of the landscape to streams, and riparian areas with more local groundwater contributions.
Characteristics
Key features of a typical riparian forest include
1. Location and Hydrological Context
- Riparian forests are primarily situated alongside rivers or streams, with varying degrees of proximity to the water's edge. - These ecosystems are intimately connected with dynamic water flow and soil processes, influencing their characteristics.2.Diverse Ecosystem Components
- Riparian forests feature a diverse combination of elements, including: - Mesic terrestrial vegetation (vegetation adapted to moist conditions). - Dependent animal life, relying on the riparian environment for habitat and resources. - Local microclimate influenced by the presence of water bodies.3. Distinct Vegetation Structure
- The vegetation in riparian forests exhibits a multi-layered structure. - Moisture-dependent trees are the dominant feature, giving these forests a unique appearance, especially in savanna regions. - These moisture-dependent trees define the landscape, accompanied by a variety of mesic understorey, shrub, and ground cover species.4. Floristic Composition
- Riparian forests often host plant species that have high moisture requirements. - The flora typically includes species native to the region, adapted to the moist conditions provided by proximity to water bodies. In summary, riparian forests are characterized by their location along waterways, their intricate interplay with water and soil dynamics, a diverse array of vegetation layers, and a plant composition favoring moisture-dependent species.
Roles and functions
meander
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the Channel (geography), channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erosion, erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank (cut bank, cut bank or river cl ...
ing curves of a river, combined with vegetation and root systems, slow the flow of water, which reduces soil erosion and flood damage. Sediment is trapped, reducing suspended solids to create less turbid water, replenish soils, and build stream banks. Pollutants are filtered from surface runoff, enhancing water quality via biofiltration.
The riparian zones also provide wildlife
Wildlife refers to domestication, undomesticated animals and uncultivated plant species which can exist in their natural habitat, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wilderness, wild in an area without being species, introdu ...
habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
, increased biodiversity, and wildlife corridor
A wildlife corridor, also known as a habitat corridor, or green corridor, is a designated area habitat (ecology), that connects wildlife populations that have been separated by human activities or structures, such as development, roads, or land ...
s, enabling aquatic and riparian organisms to move along river systems avoiding isolated communities. Riparian vegetation can also provide forage
Forage is a plant material (mainly plant leaves and stems) eaten by grazing livestock. Historically, the term ''forage'' has meant only plants eaten by the animals directly as pasture, crop residue, or immature cereal crops, but it is also used m ...
for wildlife and livestock.
Riparian zones are also important for the fish that live within rivers, such as brook and charr. Impacts on riparian zones can affect fish, and restoration is not always sufficient to recover fish populations.
They provide native landscape
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or human-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. A landscape includes th ...
irrigation by extending seasonal or perennial flows of water. Nutrients from terrestrial vegetation (e.g. plant litter and insect drop) are transferred to aquatic food webs, and are a vital source of energy in aquatic food webs. The vegetation surrounding the stream helps to shade the water, mitigating water temperature changes. Thinning of riparian zones has been observed to cause increased maximum temperatures, higher fluctuations in temperature, and elevated temperatures being observed more frequently and for longer periods of time. Extreme changes in water temperature can have lethal effects on fish and other organisms in the area. The vegetation also contributes wood debris to streams, which is important to maintaining geomorphology
Geomorphology () is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features generated by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or near Earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand wh ...
.
Riparian zones also act as important buffers against nutrient loss in the wake of natural disasters, such as hurricanes
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
. Many of the characteristics of riparian zones that reduce the inputs of nitrogen from agricultural runoff also retain the necessary nitrogen in the ecosystem after hurricanes threaten to dilute and wash away critical nutrients.
From a social aspect, riparian zones contribute to nearby property values through amenity and views, and they improve enjoyment for footpaths and bikeways through supporting foreshoreway networks. Space is created for riparian sports such as fishing, swimming, and launching for vessels and paddle craft.
The riparian zone acts as a sacrificial erosion buffer to absorb impacts of factors including climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, increased runoff from urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
, and increased boat wake without damaging structures located behind a setback zone.
"Riparian zones play a crucial role in preserving the vitality of streams and rivers, especially when faced with challenges stemming from catchment land use, including agricultural and urban development. These changes in land utilization can exert adverse impacts on the health of streams and rivers and, consequently, contribute to a decline in their reproductive rates."
Role in logging
The protection of riparian zones is often a consideration inlogging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidder, skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or trunk (botany), logs onto logging truck, truckssoil eroded from the harvested area. Factors such as soil types and
 Typical riparian vegetation in temperate New South Wales,
Typical riparian vegetation in temperate New South Wales,
File:Cottonwood Creek, BLM, Oregon, 1988.jpg, alt=A rocky, brown stream bank mostly bare of vegetation, with a few aspen trees in the background, Cottonwood Creek riparian area in southeastern
Riparian Bibliography, National Agroforestry Center
Dissertation on riparian vegetation of Chalakudy RiverNational Riparian Service Team, Bureau of Land ManagementRed River Basin Riparian ProjectRiparian Forest Buffers, Kansas State University
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Riparian Zone Terrestrial biomes Environmental conservation Hydrology Water streams Rivers Habitats Habitat Water and the environment Freshwater ecology
root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
structures, climatic conditions, and vegetative cover determine the effectiveness of riparian buffering. Activities associated with logging, such as sediment input, introduction or removal of species, and the input of polluted water all degrade riparian zones.
Vegetation
The assortment of riparian zone trees varies from those of wetlands and typically consists of plants that are either emergent aquatic plants, orherb
Herbs are a widely distributed and widespread group of plants, excluding vegetables, with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicinal purposes, or for fragrances. Culinary use typically distingu ...
s, tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
s and shrub
A shrub or bush is a small to medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple ...
s that thrive in proximity to water. In South Africa's fynbos
Fynbos (; , ) is a small belt of natural shrubland or heathland vegetation located in the Western Cape and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa. The area is predominantly coastal and mountainous, with a Mediterranean climate. The fynbos ...
biome, Riparian ecosystem are heavily invaded by alien woody plants. Riparian plant communities along lowland streams exhibit remarkable species diversity, driven by the unique environmental gradients inherent to these ecosystems.
Riparian zones in Africa
Riparian forest can be found in Benin, West Africa. In Benin, where the savanna ecosystem prevails, "riparian forests" include various types of woodlands, such assemi-deciduous
Semi-deciduous or semi-evergreen is a botanical term which refers to plants that lose their foliage for a very short period, when old leaves fall off and new foliage growth is starting. This phenomenon occurs in tropical and sub-tropical wood ...
forests, dry forests, open forests, and woodland savannas. These woodlands can be found alongside rivers and streams. In Nigeria, you can also discover riparian zones within the Ibadan region of Oyo state. Ibadan, one of the oldest towns in Africa, covers a total area of 3,080 square kilometers and is characterized by a network of perennial water streams that create these valuable riparian zones. In the research conducted by Adeoye et al. (2012) on land use changes in Southwestern Nigeria, it was observed that 46.18 square kilometers of the area are occupied by water bodies. Additionally, most streams and rivers in this region are accompanied by riparian forests. Nevertheless, the study also identified a consistent reduction in the extent of these riparian forests over time, primarily attributed to a significant deforestation rate. In Nigeria, according to Momodu et al. (2011), there has been a notable decline of about 50% in the riparian forest coverage within the period of 1978 to 2000. This reduction is primarily attributed to alterations in land use and land cover. Additionally, their research indicates that if current trends continue, the riparian forests may face further depletion, potentially leading to their complete disappearance by the year 2040. Riparian zones can also be found in Cape Agulhas region of South Africa. Riparian areas along South African rivers have experienced significant deterioration as a result of human activities. Similar to many other developed and developing areas worldwide, the extensive building of dams in upstream river areas and the extraction of water for irrigation purposes have led to diminished water flows and changes in the riparian environment.
North America
Water's edge
Herbaceous Perennial: *'' Peltandra virginica'' – Arrow Arum *'' Sagittaria lancifolia'' – Arrowhead *'' Carex stricta'' – Tussock Sedge *'' Iris virginica'' – Southern Blue Flag IrisInundated riparian zone
Herbaceous Perennial: *'' Sagittaria latifolia'' – Duck Potato *''Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani
''Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani'' is a species of flowering plant in the Cyperaceae, sedge family known by the common names softstem bulrush, grey club-rush, and great bulrush. It can be found throughout much of the world; it has been reported f ...
'' – Softstem Bulrush
*'' Scirpus americanus'' – Three-square Bulrush
*'' Eleocharis quadrangulata'' – Square-stem Spikerush
*'' Eleocharis obtusa'' – Spikerush
Western
In western North America and the Pacific coast, the riparian vegetation includes: Riparian trees *''Sequoia sempervirens
''Sequoia sempervirens'' ()''Sunset Western Garden Book,'' 1995: 606–607 is the sole living species of the genus ''Sequoia (genus), Sequoia'' in the cypress family Cupressaceae (formerly treated in Taxodiaceae). Common names include coast ...
'' – Coast Redwood
*''Thuja plicata
''Thuja plicata'' is a large evergreen coniferous tree in the family Cupressaceae, native to the Pacific Northwest of North America. Its common name is western redcedar in the U.S. or western red cedar in the UK, and it is also called pacific re ...
'' – Western Redcedar
*'' Abies grandis'' – Grand Fir
*''Picea sitchensis
''Picea sitchensis'', the Sitka spruce, is a large, coniferous, evergreen tree growing to just over tall, with a trunk diameter at breast height that can exceed 5 m (16 ft). It is by far the largest species of spruce and the fifth-l ...
'' – Sitka Spruce
*'' Chamaecyparis lawsoniana'' – Port Orford-cedar
*'' Taxus brevifolia'' – Pacific Yew
*'' Populus fremontii'' – Fremont Cottonwood
*'' Populus trichocarpa'' – Black Cottonwood
*''Platanus racemosa
''Platanus racemosa'' is a species of plane tree known by several common names, including California sycamore, western sycamore, California plane tree, and in North American Spanish . ''Platanus racemosa'' is native to California and Baja Califo ...
'' – California Sycamore
*'' Alnus rhombifolia'' – White Alder
*'' Alnus rubra'' – Red Alder
*'' Acer macrophyllum'' – Big-leaf Maple
*'' Fraxinus latifolia'' – Oregon ash
*'' Prunus emarginata'' – Bitter Cherry
*'' Salix lasiolepis'' – Arroyo Willow
*'' Salix lucida'' – Pacific Willow
*'' Quercus agrifolia'' – Coast live oak
*'' Quercus garryana'' – Garry oak
*'' Populus tremuloides'' – Quaking Aspen
*'' Umbellularia californica'' – California Bay Laurel
*'' Cornus nuttallii'' – Pacific Dogwood
Riparian shrubs
*'' Acer circinatum'' – Vine Maple
*'' Ribes spp.'' – Gooseberies and Currants
*'' Rosa pisocarpa'' – Swamp Rose or Cluster Rose
*'' Symphoricarpos albus'' – Snowberry
*'' Spiraea douglasii'' – Douglas spirea
*'' Rubus spp.'' – Blackberries, Raspberries, Thimbleberry, Salmonberry
*'' Rhododendron occidentale'' – Western Azalea
*'' Oplopanax horridus'' – Devil's Club
*'' Oemleria cerasiformis'' – Indian Plum, Osoberry
*''Lonicera involucrata
''Lonicera involucrata'', the bearberry honeysuckle, bracted honeysuckle, twinberry honeysuckle, Californian Honeysuckle, twin-berry, or black twinberry, is a species of honeysuckle native to northern and western North America.
Description
It ...
'' – Twinberry
*'' Cornus stolonifera'' – Red-osier Dogwood
*'' Salix spp.'' – Willows
Other plants
*'' Polypodium'' – Polypody Ferns
*''Polystichum
''Polystichum'' is a genus of ferns in the family (biology), family Dryopteridaceae, subfamily Dryopteridoideae, according to the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I). The genus has about 500 species and has a cosmopolitan ...
'' – Sword Ferns
*'' Woodwardia'' – Giant Chain Ferns
*'' Pteridium'' – Goldback Ferns
*''Dryopteris
:''The moth genus ''Dryopteris'' is now considered a junior synonym of ''Oreta.
''Dryopteris'' , commonly called the wood ferns, male ferns (referring in particular to ''Dryopteris filix-mas''), or buckler ferns, is a fern genus in the family Dry ...
'' – Wood Ferns
*'' Adiantum'' – Maidenhair Ferns
*'' Carex spp.'' – Sedges
*'' Juncus spp.'' – Rushes
*'' Festuca californica'' – California Fescue bunchgrass
*'' Leymus condensatus'' – Giant Wildrye bunchgrass
*'' Melica californica'' – California Melic bunchgrass
*'' Mimulus spp.'' – Monkeyflower and varieties
*'' Aquilegia spp.'' – Columbine
Asia
InAsia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
there are different types of riparian vegetation, but the interactions between hydrology and ecology are similar as occurs in other geographic areas.
*'' Carex spp.'' – Sedges
*'' Juncus spp.'' – Rushes
Australia
 Typical riparian vegetation in temperate New South Wales,
Typical riparian vegetation in temperate New South Wales, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
include:
*'' Acacia melanoxylon'' – Blackwood
*'' Acacia pravissima'' – Ovens Wattle
*'' Acacia rubida'' – Red Stem Wattle
*'' Bursaria lasiophylla'' – Blackthorn
*'' Callistemon citrinus'' – Crimson Bottlebrush
*'' Callistemon sieberi'' – River Bottlebrush
*'' Casuarina cunninghamiana'' – River She-Oak
*'' Eucalyptus bridgesiana'' – Apple Box
*'' Eucalyptus camaldulensis'' – River Red Gum
*'' Eucalyptus melliodora'' – Yellow Box
*'' Eucalyptus viminalis'' – Manna Gum
*'' Kunzea ericoides'' – Burgan
*'' Leptospermum obovatum'' – River Tea-Tree
*'' Melaleuca ericifolia'' – Swamp Paperbark
Central Europe
Typical riparian zone trees inCentral Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
include:
*'' Acer campestre'' – Field Maple
*''Acer pseudoplatanus
''Acer pseudoplatanus'', known as the sycamore in the British Isles and as the sycamore maple in the United States, is a species of maple native to Central Europe and Western Asia. It is a large deciduous, broad-leaved tree, tolerant of wind an ...
'' – Sycamore Maple
*'' Alnus glutinosa'' – Black Alder
*''Carpinus betulus
Hornbeams are hardwood trees in the plant genus ''Carpinus'' in the family Betulaceae. Its species occur across much of the temperateness, temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
Common names
The common English name ''hornbeam'' derives ...
'' – European Hornbeam
*''Fraxinus excelsior
''Fraxinus excelsior'', known as the ash, or European ash or common ash to distinguish it from other types of ash, is a flowering plant species in the olive family Oleaceae. It is native throughout mainland Europe east to the Caucasus and Alb ...
'' – European Ash
*'' Juglans regia'' – Persian Walnut
*'' Malus sylvestris'' – European Wild Apple
*''Populus alba
''Populus alba'', commonly called silver poplar,Webb, C. J.; Sykes, W. R.; Garnock-Jones, P. J. 1988: Flora of New Zealand. Vol. IV. Naturalised Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms, Dicotyledons. 4. Christchurch, New Zealand, Botany Division, D.S.I.R. si ...
'' – White Poplar
*''Populus nigra
''Populus nigra'', the black poplar, is a species of Populus sect. Aigeiros, cottonwood poplar, the type species of section ''Aigeiros'' of the genus ''Populus'', native to Europe, southwest and central Asia, and northwest Africa.Flora Europaea' ...
'' – Black Poplar
*''Quercus robur
''Quercus robur'', the pedunculate oak, is a species of flowering plant in the beech and oak family, Fagaceae. It is a large tree, native plant, native to most of Europe and western Asia, and is widely cultivated in other temperate regions. It ...
'' – Pedunculate Oak
*''Salix alba
''Salix alba'', the white willow, is a species of willow native to Europe and western and Central Asia.Meikle, R. D. (1984). ''Willows and Poplars of Great Britain and Ireland''. BSBI Handbook No. 4. .Rushforth, K. (1999). ''Trees of Britain an ...
'' – White Willow
*'' Salix fragilis'' – Crack Willow
*''Tilia cordata
''Tilia cordata'', the small-leaved lime or small-leaved linden, is a species of tree in the family Malvaceae, native to much of Europe. Other common names include little-leaf or littleleaf linden, or traditionally in South East England, pry or p ...
'' – Small-leaved Lime
*'' Ulmus laevis'' – European White Elm
*''Ulmus minor
''Ulmus minor'' Mill., the field elm, is by far the most polymorphic of the European species, although its taxonomy remains a matter of contention. Its natural range is predominantly south European, extending to Asia Minor and Iran; its norther ...
'' – Field Elm
Repair and restoration
Land clearing followed by floods can quickly erode a riverbank, taking valuable grasses and soils downstream, and later allowing the sun to bake the land dry. Riparian zones can be restored through relocation (of human-made products), rehabilitation, and time. Natural Sequence Farming techniques have been used in the Upper Hunter Valley ofNew South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
, Australia, in an attempt to restore eroded farms to optimum productivity rapidly.
The Natural Sequence Farming technique involves placing obstacles in the water's pathway to lessen the energy of a flood and help the water to deposit soil and seep
A seep or flush is a moist or wet place where water, usually groundwater, reaches the Earth's surface from an underground aquifer.
Description
Seeps are usually not of sufficient volume to be flowing beyond their immediate above-ground location. ...
into the flood zone. Another technique is to quickly establish ecological succession
Ecological succession is the process of how species compositions change in an Community (ecology), ecological community over time.
The two main categories of ecological succession are primary succession and secondary succession. Primary successi ...
by encouraging fast-growing plants such as "weeds" ( pioneer species) to grow. These may spread along the watercourse and cause environmental degradation
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, referring respectively to all living and non-living things occurring naturally and the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism ...
, but may stabilize the soil, place carbon into the ground, and protect the land from drying. The weeds will improve the streambeds so trees and grasses can return and, ideally, replace the weeds. There are several other techniques used by government and non-government agencies to address riparian and streambed degradation, ranging from the installation of bed control structures such as log sills to the use of pin groynes or rock emplacement. Other possible approaches include control of invasive species, monitoring of herbivore activity, and cessation of human activity in a particular zone followed by natural re-vegetation. Conservation efforts have also encouraged incorporating the value of ecosystem services provided by riparian zones into management plans, as these benefits have traditionally been absent in the consideration and designing of these plans.
Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
before restoration, 1988
File:Cottonwood Creek, BLM, Oregon, 2000.jpg, alt=The same stream bank lined with short grasses, with more aspen trees in the background, Cottonwood Creek riparian area during recovery, 2000
File:Cottonwood Creek, BLM, Oregon, 2002.jpg, alt=The same stream bank lined with higher grasses that obscure most of the water, with a thicker aspen grove behind, Cottonwood Creek riparian area after restoration, 2002
See also
* Accropode *Aquatic ecosystem
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem found in and around a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms—aquatic life—that are dependent on each other and on their environ ...
* Bioswale
Bioswales are channels designed to concentrate and convey stormwater runoff while removing debris and pollution. Bioswales can also be beneficial in groundwater recharge, recharging groundwater.
Bioswales are typically vegetated, mulched, or xer ...
* Bosque
* Canebrake
* Constructed wetland
A constructed wetland is an artificial wetland to treat sewage, greywater, stormwater runoff or Industrial wastewater treatment, industrial wastewater. It may also be designed for land reclamation after mining, or as a Flood mitigation, mitigatio ...
* Endorheic basin
An endorheic basin ( ; also endoreic basin and endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water (e.g. rivers and oceans); instead, the water drainage flows into permanent ...
* Flood-meadow
* Floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river. Floodplains stretch from the banks of a river channel to the base of the enclosing valley, and experience flooding during periods of high Discharge (hydrolog ...
* Freshwater swamp forest
* Gallery forest
* Green belt
A green belt or greenbelt is a policy, and land-use zone designation used in land-use planning to retain areas of largely undeveloped, wilderness, wild, or agricultural landscape, land surrounding or neighboring urban areas. Similar concepts ...
* Marsh
In ecology, a marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous plants rather than by woody plants.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p More in genera ...
* Outwelling
* Riparian water rights
* Riparian-zone restoration
Riparian-zone restoration is the ecological restoration of riparian-zone habitats of streams, rivers, springs, lakes, floodplains, and other hydrologic ecologies. A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or st ...
* Riprap
* Várzea forest
* Vernal pool
* Vulnerable waters
* Water-meadow
* Wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
References
Further reading
* * *Parkyn, Stephanie. (2004). ''Review of Riparian Buffer Zone Effectiveness''. Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry (New Zealand), www.maf.govt.nz/publications. *Riparian Bibliography, National Agroforestry Center
External links
Dissertation on riparian vegetation of Chalakudy River
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Riparian Zone Terrestrial biomes Environmental conservation Hydrology Water streams Rivers Habitats Habitat Water and the environment Freshwater ecology