|
Pumped-storage
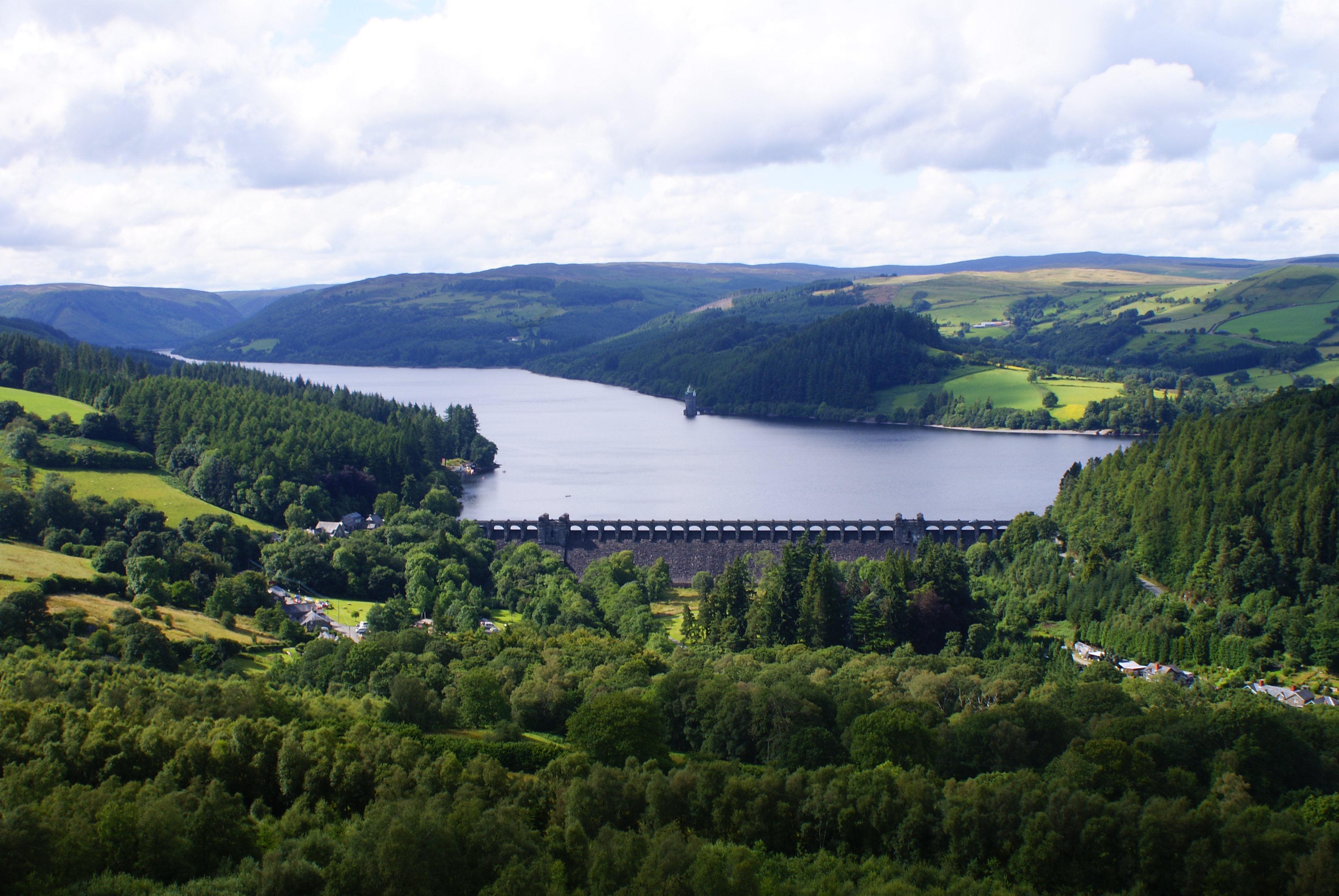
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. A PSH system stores energy in the form of gravitational potential energy of water, pumped from a lower elevation reservoir to a higher elevation. Low-cost surplus off-peak electric power is typically used to run the pumps. During periods of high electrical demand, the stored water is released through turbines to produce electric power. Pumped-storage hydroelectricity allows energy from intermittent sources (such as solar, wind, and other renewables) or excess electricity from continuous base-load sources (such as coal or nuclear) to be saved for periods of higher demand. The reservoirs used with pumped storage can be quite small, when contrasted with the lakes of conventional hydroelectric plants of similar power capacity, and generating periods are often less than half a day. The round-trip effic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an Accumulator (energy), accumulator or Battery (electricity), battery. Energy comes in multiple forms including radiation, chemical energy, chemical, gravitational potential energy, gravitational potential, Electric potential energy, electrical potential, electricity, elevated temperature, latent heat and kinetic energy, kinetic. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store to more conveniently or economically storable forms. Some technologies provide short-term energy storage, while others can endure for much longer. Bulk energy storage is currently dominated by hydroelectric dams, both conventional as well as pumped. Grid energy storage is a collection of methods used for energy storage on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Common e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
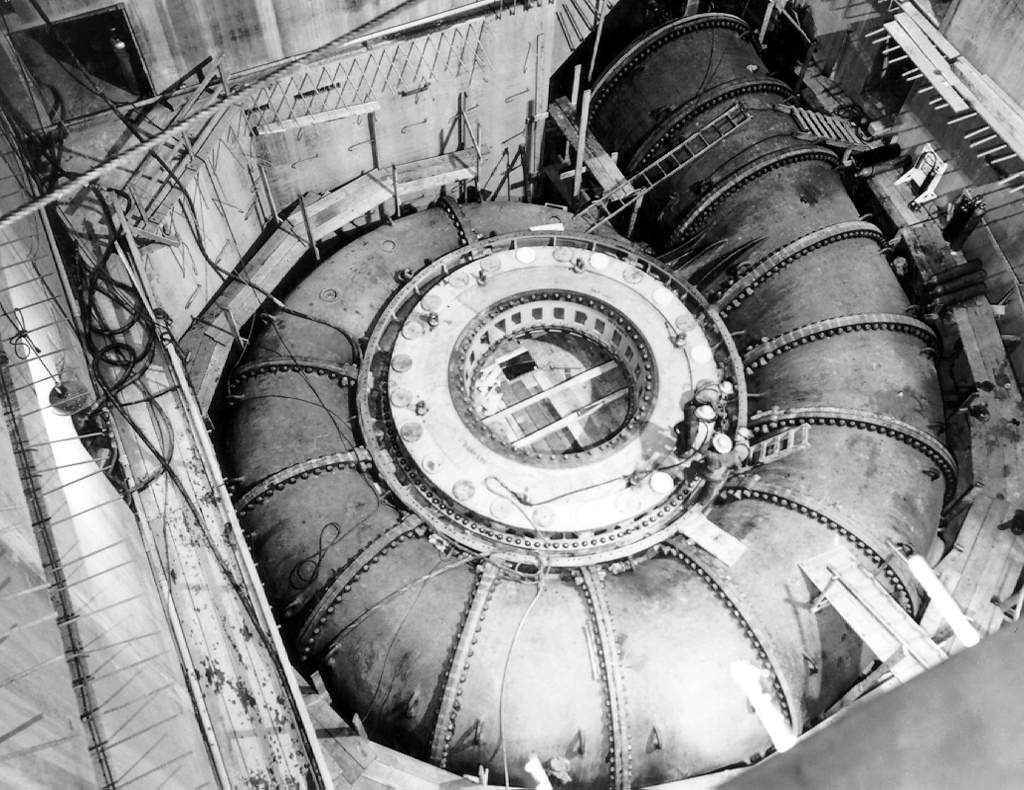
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pump As Turbine
A pump as turbine (PAT), also known as a pump in reverse, is an unconventional type of reaction water turbine, which behaves in a similar manner to that of a Francis turbine. The function of a PAT is comparable to that of any turbine, to convert kinetic and pressure energy of the fluid into mechanical energy of the runner. They are commonly commercialized as composite pump and motor/generator units, coupled by a fixed shaft to an asynchronous induction type motor unit. Unlike other conventional machines which require being manufactured according to the client’s specifications, pumps are a very common piece of equipment widely available in different sizes and functionality anywhere around the globe. When used as a turbine, the rotor moves in the opposite direction, or in reverse, as to when it is operating as a pump. In this manner, it allows the motor to generate electrical power. History First mentions of the possibility of using pumps as turbines (PAT) dates back to the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raccoon Mountain Pumped-Storage Plant
Raccoon Mountain Pumped-Storage Plant is a pumped-storage hydroelectric underground power station in Marion County, just west of Chattanooga in the U.S. state of Tennessee. Owned and operated by the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), the plant can generate a maximum of 1,652 megawatts of electricity. The reservoir at the top of the mountain covers , with a dam that is high and long, the largest rock-fill dam ever built by TVA. The plant serves as an important element for peak power generation and grid balancing in the TVA system. Construction was started in 1970 and was completed in 1978. The plant was idled in March 2012 due to cracks in the generators' rotors. The plant came entirely back on line in April 2014. Operation During periods of high electric demand, water flows from reservoir into a tunnel drilled through the center of the mountain, driving electric generators in the underground powerhouse. During periods of low demand and excess generation, the generators ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grid Energy Storage
Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, are technologies connected to the electrical power grid that store energy for later use. These systems help balance supply and demand by storing excess electricity from variable renewables such as solar and inflexible sources like nuclear power, releasing it when needed. They further provide essential grid services, such as helping to restart the grid after a power outage. , the largest form of grid storage is pumped-storage hydroelectricity, with utility-scale batteries and behind-the-meter batteries coming second and third. Lithium-ion batteries are highly suited for shorter duration storage up to 8 hours. Flow batteries and compressed air energy storage may provide storage for medium duration. Two forms of storage are suited for long-duration storage: green hydrogen, produced via electrolysis and thermal energy storage. Energy storage is one option to making grids more flexible. An other solution i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round-trip Efficiency
Energy conversion efficiency (''η'') is the ratio between the useful output of an energy conversion machine and the input, in energy terms. The input, as well as the useful output may be chemical, electric power, mechanical work, light (radiation), or heat. The resulting value, ''η'' (eta), ranges between 0 and 1. Overview Energy conversion efficiency depends on the usefulness of the output. All or part of the heat produced from burning a fuel may become rejected waste heat if, for example, work is the desired output from a thermodynamic cycle. Energy converter is an example of an energy transformation. For example, a light bulb falls into the categories energy converter. \eta = \frac Even though the definition includes the notion of usefulness, efficiency is considered a technical or physical term. Goal or mission oriented terms include effectiveness and efficacy. Generally, energy conversion efficiency is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1.0, or 0% to 100%. Effi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to convert light into an electric current. Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors and solar tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight to a hot spot, often to drive a steam turbine. Photovoltaics (PV) were initially solely used as a source of electricity for small and medium-sized applications, from the calculator powered by a single solar cell to remote homes powered by an off-grid rooftop PV system. Commercial concentrated solar power plants were first developed in the 1980s. Since then, as the cost of solar panels has fallen, grid-connected solar PV systems' capacity and production has doubled about every three years. Three-quarters of new generation capacity is solar, with both millions of rooftop installatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermittent Energy Source
Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable energy sources, such as dammed hydroelectricity or bioenergy, or relatively constant sources, such as geothermal power. The use of small amounts of intermittent power has little effect on grid operations. Using larger amounts of intermittent power may require upgrades or even a redesign of the grid infrastructure. Options to absorb large shares of variable energy into the grid include using storage, improved interconnection between different variable sources to smooth out supply, using dispatchable energy sources such as hydroelectricity and having overcapacity, so that sufficient energy is produced even when weather is less favourable. More connections between the energy sector and the building, transport and industrial sectors may also h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Turbine
A water turbine is a rotary machine that converts kinetic energy and potential energy of water into mechanical work. Water turbines were developed in the 19th century and were widely used for industrial power prior to electrical grids. Now, they are mostly used for electric power generation. Water turbines are mostly found in dams to generate electric power from water potential energy. History Water wheels have been used for hundreds of years for industrial power. Their main shortcoming is size, which limits the flow rate and head (hydraulic), head that can be harnessed. The migration from water wheels to modern turbines took about one hundred years. Development occurred during the Industrial Revolution, using scientific principles and methods. They also made extensive use of new materials and manufacturing methods developed at the time. Swirl The word turbine was introduced by the French engineer Claude Burdin in the early 19th century and is derived from the Greek w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reservoir
A reservoir (; ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam, usually built to water storage, store fresh water, often doubling for hydroelectric power generation. Reservoirs are created by controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrupting a watercourse to form an Bay, embayment within it, excavating, or building any number of retaining walls or levees to enclose any area to store water. Types Dammed valleys Dammed reservoirs are artificial lakes created and controlled by a dam constructed across a valley and rely on the natural topography to provide most of the basin of the reservoir. These reservoirs can either be ''on-stream reservoirs'', which are located on the original streambed of the downstream river and are filled by stream, creeks, rivers or rainwater that surface runoff, runs off the surrounding forested catchments, or ''off-stream reservoirs'', which receive water diversion, diverted water from a nearby stream or aqueduct (water supply), aq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |