|
Public Sector
The public sector, also called the state sector, is the part of the economy composed of both public services and public enterprises. Public sectors include the public goods and governmental services such as the military, law enforcement, public infrastructure, public transit, public education, along with public health care and those working for the government itself, such as elected officials. The public sector might provide services that a non-payer cannot be excluded from (such as street lighting), services which benefit all of society rather than just the individual who uses the service. Public enterprises, or state-owned enterprises, are self-financing commercial enterprises that are under public ownership which provide various private goods and services for sale and usually operate on a commercial basis. Organizations that are not part of the public sector are either part of the private sector or voluntary sector. The private sector is composed of the economic sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Employment In The UK Public Sector, December 2013
Employment is a relationship between two party (law), parties Regulation, regulating the provision of paid Labour (human activity), labour services. Usually based on a employment contract, contract, one party, the employer, which might be a corporation, a not-for-profit organization, a co-operative, or any other entity, pays the other, the employee, in return for carrying out assigned work. Employees work in return for wage, wages, which can be paid on the basis of an hourly rate, by piecework or an annual salary, depending on the type of work an employee does, the prevailing conditions of the sector and the bargaining power between the parties. Employees in some sectors may receive gratuity, gratuities, bonus payments or employee stock option, stock options. In some types of employment, employees may receive benefits in addition to payment. Benefits may include health insurance, housing, and disability insurance. Employment is typically governed by Labour law, employment laws, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State-owned Enterprise
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a business entity created or owned by a national or local government, either through an executive order or legislation. SOEs aim to generate profit for the government, prevent private sector monopolies, provide goods at lower prices, implement government policies, or serve remote areas where private businesses are scarce. The government typically holds full or majority ownership and oversees operations. SOEs have a distinct legal structure, with financial and developmental goals, like making services more accessible while earning profit (such as a state railway). They can be considered as government-affiliated entities designed to meet commercial and state capitalist objectives. Terminology The terminology around the term state-owned enterprise is murky. All three words in the term are challenged and subject to interpretation. First, it is debatable what the term "state" implies (e.g., it is unclear whether municipally owned corporations and ente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Servants (France)
The French civil service () is the set of civil servants (''fonctionnaires'') working for the Government of France. Not all employees of the state and public institutions or corporations are civil servants; however, the media often incorrectly equate "government employee" or "employee of a public corporation" with ''fonctionnaire''. For instance, most employees of the RATP and SNCF (metropolitan and national rail transport authorities) are not civil servants. The Civil Service is also sometimes incorrectly referred to as the ''administration'', but, properly speaking, the ''administration'' is the compound of public administrations and public administrative establishments, not their employees. Most employment positions in the French civil service are open to citizens of the European Union. Others, especially in police and justice, are specifically reserved for nationals, while a minority are open regardless of citizenship. About half of the civil servants are employed in the Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pay Review Body
A Review Body in the United Kingdom is a government mechanism to replace collective bargaining for certain groups of employees in the public sector, for example doctors and nurses in the National Health Service. A Review Body makes independent recommendations on pay after considering evidence from the relevant parties (typically government, employers and unions), with cherished expectations that the Government will honour those recommendations and the unions will not pursue national industrial action. Office of Manpower Economics The Office of Manpower Economics (OME) is a non-statutory body set up to provide an independent secretariat for each of the eight pay review bodies. It is funded by the Department for Business and Trade (DBT). Review bodies The Review Body system started in 1960 for doctors and dentists after the publication of The Royal Commission on Doctor's and Dentist's Remuneration. As of 2005 there were six Review Bodies overseen by OME which together covered appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Union
A trade union (British English) or labor union (American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers whose purpose is to maintain or improve the conditions of their employment, such as attaining better wages and Employee benefits, benefits, improving Work (human activity), working conditions, improving safety standards, establishing complaint procedures, developing rules governing status of employees (rules governing promotions, just-cause conditions for termination) and protecting and increasing the bargaining power of workers. Trade unions typically fund their head office and legal team functions through regularly imposed fees called ''union dues''. The union representatives in the workforce are usually made up of workplace volunteers who are often appointed by members through internal democratic elections. The trade union, through an elected leadership and bargaining committee, bargains with the employer on behalf of its members, known as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negotiation
Negotiation is a dialogue between two or more parties to resolve points of difference, gain an advantage for an individual or Collective bargaining, collective, or craft outcomes to satisfy various interests. The parties aspire to agree on matters of The Impact of Religion on International Negotiations, mutual interest. The agreement can be beneficial for all or some of the parties involved. The negotiators should establish their own needs and wants while also seeking to understand the wants and needs of others involved to increase their chances of closing deals, avoiding conflicts, forming relationships with other parties, or maximizing mutual gains. Distributive negotiations, or compromises, are conducted by putting forward a position and making concessions to achieve an agreement. The degree to which the negotiating parties Trust (social science), trust each other to implement the negotiated solution is a major factor in determining the success of a negotiation. People neg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications Network
A telecommunications network is a group of Node (networking), nodes interconnected by telecommunications links that are used to exchange messages between the nodes. The links may use a variety of technologies based on the methodologies of circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching, to pass messages and signals. Multiple nodes may cooperate to pass the message from an originating node to the destination node, via multiple network hops. For this routing function, each node in the network is assigned a network address for identification and locating it on the network. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space of the network. Examples of telecommunications networks include computer networks, the Internet, the public switched telephone network (PSTN), the global Telex network, the aeronautical ACARS network, and the wireless radio networks of cell phone telecommunication providers. Network structure this is the structure of network genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Grid
An electrical grid (or electricity network) is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power transmission to carry power over long distances, and finally electric power distribution to customers. In that last step, voltage is stepped down again to the required service voltage. Power stations are typically built close to energy sources and far from densely populated areas. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. From small to large there are microgrids, wide area synchronous grids, and super grids. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the ''power grid''. Grids are nearly always synchronous, meaning all distribution areas operate with three phase alternating current (AC) frequencies synchronized (so that voltage swings occur at almost the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from residences and from commercial, institutional and public facilities that exist in the locality. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a creativecommons:by/4.0/, Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License Sub-types of sewage are greywater (from sinks, bathtubs, showers, dishwashers, and clothes washers) and blackwater (waste), blackwater (the water used to flush toilets, combined with the human waste that it flushes away). Sewage also contains soaps and detergents. Food waste may be present from dishwashing, and food quantities may be increased where garbage disposal units are used. In regions where toilet paper is used rather than bidets, that paper is also added to the sewage. Sewage contains macro-pollu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
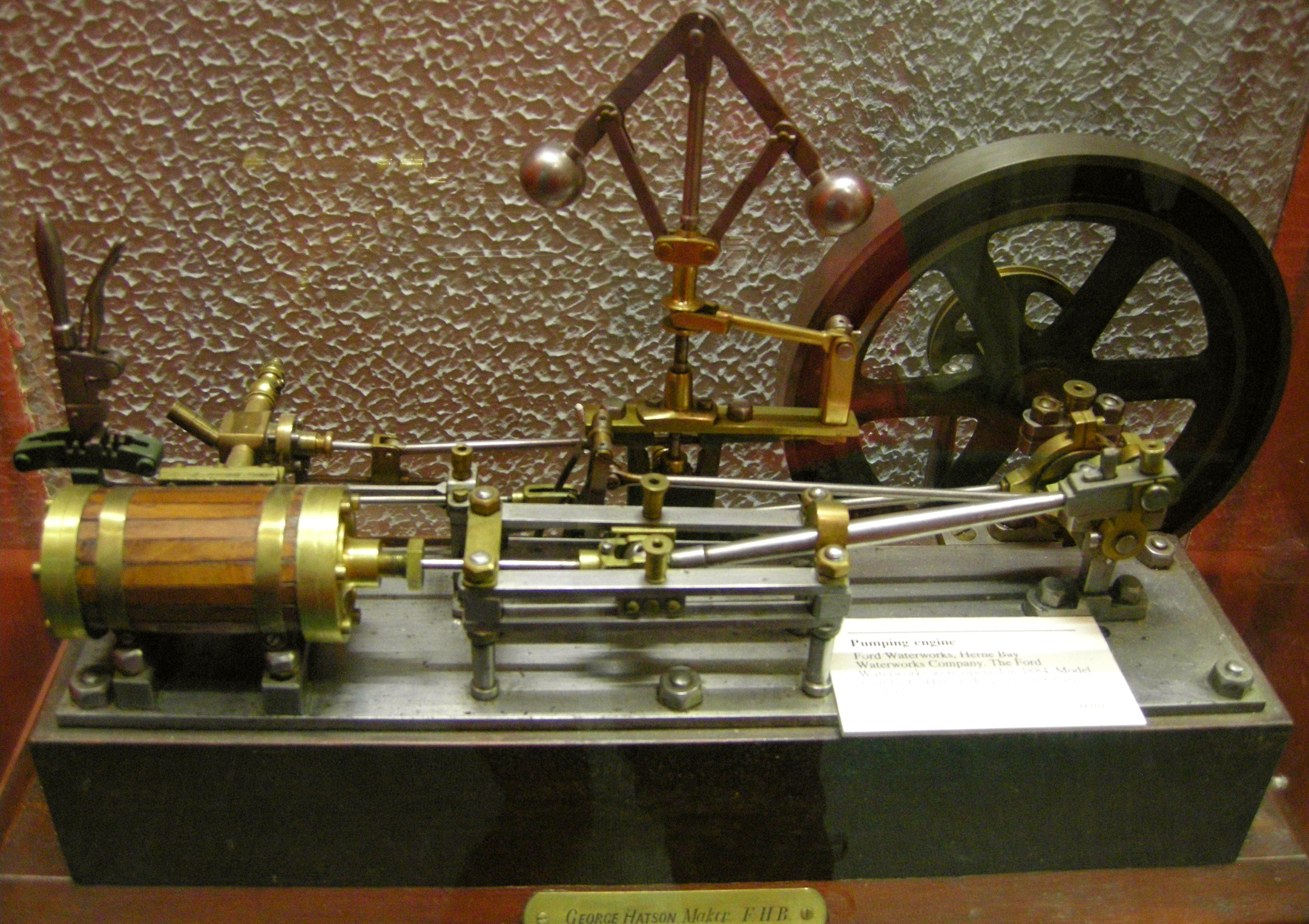
Water Supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. These systems are what supply drinking water to populations around the globe. Aspects of service quality include continuity of supply, water quality and water pressure. The institutional responsibility for water supply is arranged differently in different countries and regions (urban versus rural). It usually includes issues surrounding policy and regulation, service provision and standardization. The cost of supplying water consists, to a very large extent, of fixed costs (capital costs and personnel costs) and only to a small extent of variable costs that depend on the amount of water consumed (mainly energy and chemicals). Almost all service providers in the world charge tariffs to recover part of their costs. Water supply is a separat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunnel
A tunnel is an underground or undersea passageway. It is dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, or laid under water, and is usually completely enclosed except for the two portals common at each end, though there may be access and ventilation openings at various points along the length. A pipeline differs significantly from a tunnel, though some recent tunnels have used immersed tube construction techniques rather than traditional tunnel boring methods. A tunnel may be for foot or vehicular road traffic, for rail traffic, or for a canal. The central portions of a rapid transit network are usually in the tunnel. Some tunnels are used as sewers or aqueducts to supply water for consumption or for hydroelectric stations. Utility tunnels are used for routing steam, chilled water, electrical power or telecommunication cables, as well as connecting buildings for convenient passage of people and equipment.Salazar, Waneta. ''Tunnels in Civil Engineering''. Delhi, India : Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge
A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge, dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese is one of the oldest arch bridges in existence and use. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |