|
Pterodon (mammal)
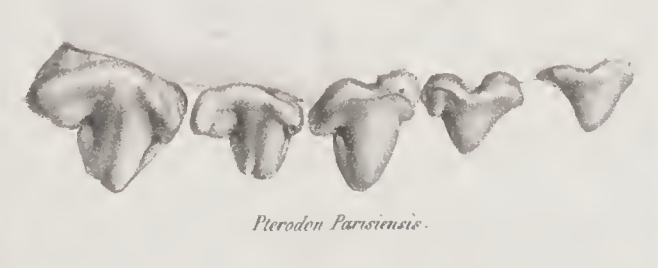
''Pterodon'' (Ancient Greek: (wing) + (tooth) meaning "wing tooth") is an extinct genus of hyaenodont in the family Hyainailouridae, containing two species. The type species ''Pterodon dasyuroides'' is known exclusively from the late Eocene to the earliest Oligocene of western Europe. The genus was first erected by the French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1839, who said that Georges Cuvier presented one of its fossils to a conference in 1828 but died before he could make a formal description of it. It was the second hyaenodont genus with taxonomic validity after ''Hyaenodon'', but this resulted in taxonomic confusion over the validities of the two genera by other taxonomists. Although the taxonomic status of ''Pterodon'' was revised during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, it became a wastebasket taxon for other hyaenodont species found in Africa and Asia. Today, only the type species is recognized as belonging to the genus while just one is pending reass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', 'Eos, Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a relatively undeveloped state and then nurtured within a pouch on their mother's abdomen. Extant marsupials encompass many species, including Kangaroo, kangaroos, Koala, koalas, Opossum, opossums, Phalangeriformes, possums, Tasmanian devil, Tasmanian devils, Wombat, wombats, Wallaby, wallabies, and Bandicoot, bandicoots. Marsupials constitute a clade stemming from the last common ancestor of extant Metatheria, which encompasses all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to Placentalia, placentals. The evolutionary split between placentals and marsupials occurred 125-160 million years ago, in the Middle Jurassic-Early Cretaceous period. Presently, close to 70% of the 334 extant marsupial species are concentrated on the Australian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esprit Requien
Esprit Requien (6 May 1788, Avignon – 30 May 1851, Bonifacio, Corse-du-Sud) was a French naturalist, who made contributions in the fields of conchology, paleontology and especially botany. From the age of 18, he was associated with the botanical garden in the city of Avignon. He performed extensive studies of flora native to Corsica and in the environs of Mont Ventoux. During his lifetime, he amassed an herbarium of 300,000 specimens.Prosopo Les sociétés savantes In the fields of conchology and palaeontology, he conducted collecting expeditions to the Pyrenees, and |
Paul Gervais
Paul Gervais (full name: François Louis Paul Gervais) (26 September 1816 – 10 February 1879) was a French palaeontologist and entomologist. Biography Gervais was born in Paris, where he obtained the diplomas of doctor of science and of medicine, and in 1835 he began palaeontological research as assistant in the laboratory of comparative anatomy at the ''Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle''. In 1841 he obtained the chair of zoology and comparative anatomy at the Faculty of Sciences in Montpellier, of which he was in 1856 appointed dean. In 1848–1852 appeared his important work ''Zoologie et paléontologie françaises'', supplementary to the palaeontological publications of Georges Cuvier and Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville; of this a second and greatly improved edition was issued in 1859. In 1865 he accepted the professorship of zoology at the Sorbonne, vacant through the death of Louis Pierre Gratiolet; this post he left in 1868 for the chair of comparative anatomy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste Pomel
Nicolas Auguste Pomel (20 September 1821 – 2 August 1898) was a French geologist, paleontologist and botanist. He worked as a mines engineer in Algeria and became a specialist in north African vertebrate fossils. He was Senator of Algeria for Oran from 1876 to 1882. Life Nicolas-Auguste Pomel was born in Issoire, Puy-de-Dôme, on 20 September 1821. He studied at the Lycée de Clermont and earned his '' licence ès sciences''. He was conscripted into the army when he was prepared to enter the École des mines. He became a civil engineer after being released. After the coup d'état of 2 December 1851 his Republican beliefs earned him deportation. He became a ''Garde des mines'' in Oran in 1866, and was promoted to the 1st class in 1872. From 1876 to 1882 he was member of the Senate (Oran division). In 1882 he was tasked with geological mapping of Algeria. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodon Dasyuroides Cranial Fossils 1876
Pterodon may refer to: * ''Pteranodon ''Pteranodon'' (; from and ) is a genus of pterosaur that included some of the largest known flying reptiles, with ''P. longiceps'' having a wingspan of over . They lived during the late Cretaceous geological period of North America in presen ...'', a pterosaur, sometimes misspelled as "Pterodon" * ''Pterodon'' (mammal), an extinct genus of hyaenodonts * ''Pterodon'' (plant), a genus of legumes in the family Fabaceae * Pterodon (company), a Czech game developer {{Disambiguation, genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in the European Union and the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2022. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, culture, Fashion capital, fashion, and gastronomy. Because of its leading role in the French art, arts and Science and technology in France, sciences and its early adoption of extensive street lighting, Paris became known as the City of Light in the 19th century. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 inhabitants in January 2023, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasyurus
Quolls (; genus ''Dasyurus'') are carnivorous marsupials native to Australia and New Guinea. They are primarily nocturnal, and spend most of the day in a den. Of the six species of quoll, four are found in Australia and two in New Guinea. Another two species are known from fossil remains in Pliocene and Pleistocene deposits in Queensland. Genetic evidence indicates that quolls evolved around 15 million years ago in the Miocene, and that the ancestors of the six species had all diverged by around four million years ago. The six species vary in weight and size, from to . They have brown or black fur and pink noses. They are largely solitary, but come together for a few social interactions, such as mating, which occurs during the winter season. A female gives birth to up to 30 pups, but the number that can be raised to adulthood is limited by the number of teats (6–7). They have a life span of 1–5 years (species dependent). Quolls eat smaller mammals, small birds, lizards, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placental
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished from monotremes and marsupials in that the fetus (biology), fetus is carried in the uterus of its mother to a relatively late stage of development. The name is something of a misnomer, considering that marsupials also nourish their fetuses via a placenta, though for a relatively briefer period, giving birth to less-developed young, which are then nurtured for a period inside the mother's pouch (marsupial), pouch. Placentalia represents the only living group within Eutheria, which contains all mammals that are more closely related to placentals than they are to marsupials. Anatomical features Placental mammals are anatomically distinguished from other mammals by: * a sufficiently wide opening at the bottom of the pelvis to allow the birt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Basin
The Paris Basin () is one of the major geological regions of France. It developed since the Triassic over remnant uplands of the Variscan orogeny (Hercynian orogeny). The sedimentary basin, no longer a single drainage basin, is a large sag in the craton, bordered by the Armorican Massif to the west, the Ardennes-Brabant axis to the north, the Massif des Vosges to the east, and the Massif Central to the south.Duval, B.C., 1992, Villeperdue Field, In Giant Oil and Gas Fields of the Decade, 1978-1988, AAPG Memoir 54, Halbouty, M.T., editor, Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Extent The region usually regarded as the Paris Basin is rather smaller than the area formed by the geological structure. The former occupies the centre of the northern half of the country, excluding Eastern France. The latter extends from the hills just south of Calais to Poitiers and from Caen to the brink of the middle Rhine Valley, east of Saarbrücken. Geography The landscape i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thylacine
The thylacine (; binomial name ''Thylacinus cynocephalus''), also commonly known as the Tasmanian tiger or Tasmanian wolf, was a carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmania and New Guinea. The thylacine died out in New Guinea and mainland Australia around 3,600–3,200 years ago, prior to the arrival of Europeans, possibly because of the introduction of the dingo, whose earliest record dates to around the same time, but which never reached Tasmania. Prior to European settlement, around 5,000 remained in the wild on the island of Tasmania. Beginning in the nineteenth century, they were perceived as a threat to the livestock of farmers and bounty (reward), bounty hunting was introduced. The last known of its species died in 1936 at Hobart Zoo in Tasmania. The thylacine is widespread in popular culture and is a cultural icon in Australia. The thylacine was known as the Tasmanian tiger because of the dark trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Academy Of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (, ) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific method, scientific research. It was at the forefront of scientific developments in Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries, and is one of the earliest Academy of Sciences, Academies of Sciences. Currently headed by Patrick Flandrin (President of the academy), it is one of the five Academies of the . __TOC__ History The Academy of Sciences traces its origin to Colbert's plan to create a general academy. He chose a small group of scholars who met on 22 December 1666 in the King's library, near the present-day Bibliothèque nationale de France, Bibliothèque Nationale, and thereafter held twice-weekly working meetings there in the two rooms assigned to the group. The first 30 years of the academy's existence were relatively informal, since no statutes had as yet been laid down for the ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |