|
Pseudochampsa
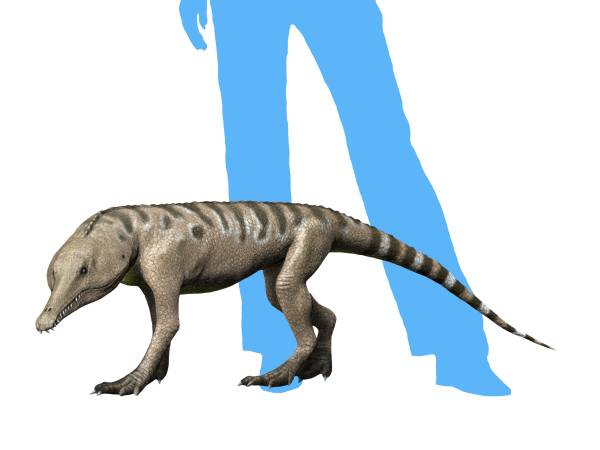
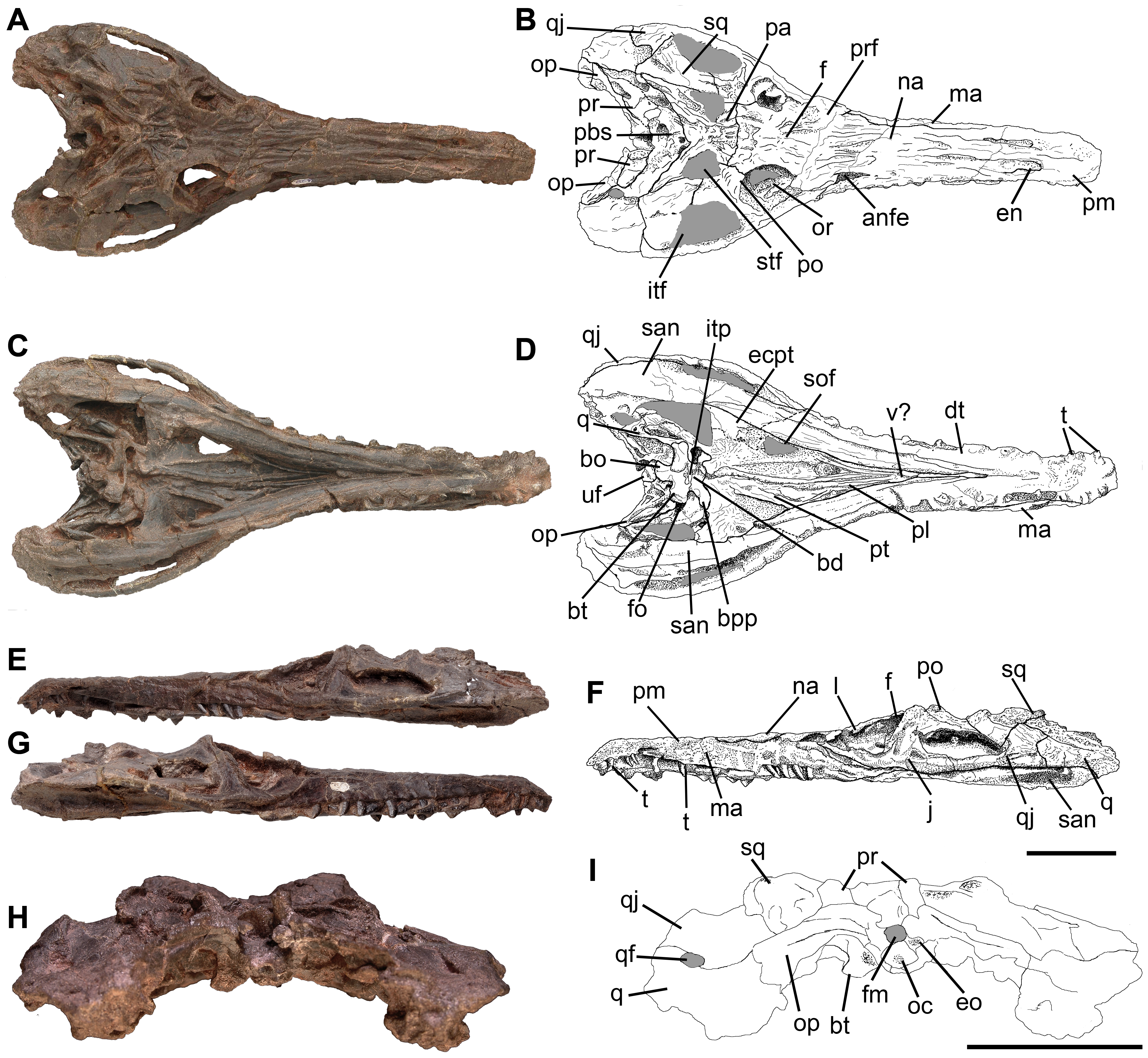
''Pseudochampsa'' is an extinct genus of proterochampsid archosauriform known from the Late Triassic (Carnian) Cancha de Bochas Member of the Ischigualasto Formation of San Juan Province, Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina. It contains a single species, ''Pseudochampsa ischigualastensis'', originally named as a second species of the closely related '' Chanaresuchus'', based on a fairly complete articulated skeleton and skull.Trotteyn et al., 2012 A revision of the remains concluded that it was best to move to species to its own genus, as no traits were found to unite ''P. ischigualastensis'' and the type species of ''Chanaresuchus'' to the exclusion of other proterochampsids. A phylogenetic analysis places both species in a polytomy with '' Gualosuchus'' as the most advanced members of Proterochampsia.Trotteyn & Ezcurra, 2014 Discovery ''Pseudochampsa'' is known solely from the holotype PVSJ 567, a nearly complete and articulated individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudochampsa Skull
''Pseudochampsa'' is an extinct genus of proterochampsid archosauriform known from the Late Triassic ( Carnian) Cancha de Bochas Member of the Ischigualasto Formation of San Juan Province, Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina. It contains a single species, ''Pseudochampsa ischigualastensis'', originally named as a second species of the closely related ''Chanaresuchus'', based on a fairly complete articulated skeleton and skull.Trotteyn et al., 2012 A revision of the remains concluded that it was best to move to species to its own genus, as no traits were found to unite ''P. ischigualastensis'' and the type species of ''Chanaresuchus'' to the exclusion of other proterochampsids. A phylogenetic analysis places both species in a polytomy with ''Gualosuchus'' as the most advanced members of Proterochampsia.Trotteyn & Ezcurra, 2014 Discovery ''Pseudochampsa'' is known solely from the holotype PVSJ 567, a nearly complete and articulated individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterochampsid
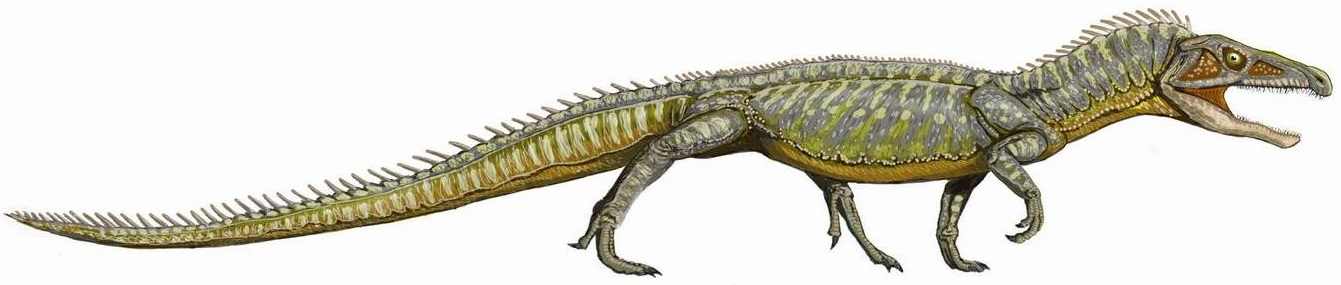
Proterochampsidae is a family of proterochampsian archosauriforms. Proterochampsids may have filled an ecological niche similar to modern crocodiles, and had a general crocodile-like appearance. They lived in what is now South America in the Middle and Late Triassic. Description Proterochampsids have long, crocodile-like skulls. The posterior portion of the skull is wide while the snout is very narrow. Most proterochampsids also have downturned snouts. Like many early archosauriforms, they also have dermal armour. Proterochampsids have small holes called dorsal fenestrae at the top of their skulls. Unlike other early archosauromorphs, they do not have a parietal foramin, which in many reptiles holds a parietal eye. The postorbital bones behind the eye sockets have thick, jagged crests. As another diagnostic feature of the group, the holes that allow the passage of the internal carotid artery through the braincase open at the sides of a bony projection called the basipterygoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischigualasto Formation
The Ischigualasto Formation is a Late Triassic fossiliferous formation and Lagerstätte in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin of the southwestern La Rioja Province and northeastern San Juan Province in northwestern Argentina. The formation dates to the Carnian and Norian ages and ranges between 231.7 and 225 Ma, based on ash bed dating. The up to thick formation is part of the Agua de la Peña Group, overlies Los Rastros Formation and is overlain by Los Colorados Formation. The formation is subdivided into four members, from old to young; La Peña, Cancha de Bochas, Valle de la Luna and Quebrada de la Sal. The sandstones, mudstones, conglomerates and tuffs of the formation were deposited in a humid alluvial to fluvial floodplain environment, characterized by strongly seasonal rainfall. The Ischigualasto Formation is an important paleontological unit and considered a Lagerstätte, as it preserves several genera of early dinosaurs, other archosaurs, synapsids, and temnospo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanaresuchus
''Chanaresuchus'' is an extinct genus of proterochampsian archosauriform. It was of modest size for a proterochampsian, being on average just over a meter in length. Fossils are known from the Middle and Late Triassic of La Rioja Province, Argentina and Rio Grande do Sul (geoparque Paleorrota), Brazil. The type species and only currently known species is ''Chanaresuchus bonapartei'' was named from the Ladinian-age Chañares Formation in 1971. A second species ''C. ischigualastensis'' named in 2012 from the late Carnian-age Ischigualasto Formation, was briefly assigned to ''Chanaresuchus'' before being moved to its own genus '' Pseudochampsa'' in 2014. ''C. bonapartei'' has recently been found in the Carnian Santa Maria Formation in Brazil. ''Chanaresuchus'' appears to be one of the most common archosauriforms from the Chanares Formation due to the abundance of specimens referred to the genus. Much of the material has been found by the La Plata-Harvard expedition of 1964-65. ''Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2012 In Paleontology
Note: In 2012, the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature was amended, with new regulations allowing the publication of new names and nomenclatural acts in zoology after 2011, in works "produced in an edition containing simultaneously obtainable copies by a method that assures (...) widely accessible electronic copies with fixed content and layout", provided that the work is registered in ZooBank before it is published, the work itself states the date of publication with evidence that registration has occurred, and the ZooBank registration states both the name of an electronic archive intended to preserve the work and the ISSN or ISBN associated with the work. New scientific names appearing in electronic works are not required to be registered in ZooBank, only the works themselves are. Works containing descriptions of some of the taxa listed below were not printed on paper in 2012; however, the taxa that were described in works which were registered in ZooBank in 2012 are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterochampsia
Proterochampsia is a clade of early archosauriform reptiles from the Triassic period. It includes the Proterochampsidae (e.g. ''Proterochampsa'', ''Chanaresuchus'' and ''Tropidosuchus'') and probably also the Doswelliidae. Nesbitt (2011) defines Proterochampsia as a stem-based taxon that includes ''Proterochampsa'' and all forms more closely related to it than ''Euparkeria'', ''Erythrosuchus'', ''Passer domesticus'' (the House Sparrow), or ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile). Therefore, the inclusion of Doswelliidae in it is dependent upon whether ''Doswellia'' and ''Proterochampsa'' form a monophyletic group to the exclusion of Archosauria and other related groups. Description Nesbitt (2011) found that Proterochampsians share several distinguishing characteristics, or synapomorphies. A prominent ridge runs along the length of the jugal, a bone below the eye. Another ridge is present on the quadratojugal, a bone positioned toward the back of the skull behind the juga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauriform
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles that developed from archosauromorph ancestors some time in the Latest Permian (roughly 252 million years ago). It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria (the group that contains crocodiles, pterosaurs and dinosaurs ncluding birds; Phil Senter">bird">ncluding_bird<_a>s.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing ''Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. These reptiles, which include members of the Family (biology), family Proterosuchidae and more advanced forms, were originally superficially crocodile-like animals with sprawling gaits and long snouts. Unlike the bulk of their therapsid contemporaries, the proterosuchids survived the catastrophe at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsus (skeleton)
In the human body, the tarsus is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot (cuboid, medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform, and navicular) and hindfoot ( talus and calcaneus). The tarsus articulates with the bones of the metatarsus, which in turn articulate with the proximal phalanges of the toes. The joint between the tibia and fibula above and the tarsus below is referred to as the ankle joint proper. In humans the largest bone in the tarsus is the calcaneus, which is the weight-bearing bone within the heel of the foot. Human anatomy Bones The talus bone or ankle bone is connected superiorly to the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and fibula, to form the ankle joint or talocrural joint; inferiorly, at the subtalar joint, to the calcaneus or heel bone. Together, the talus and calcaneus form the hindfoot.Podiatry Channel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibulae
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint. Structure The bone has the following components: * Lateral malleolus * Interosseous membrane connecting the fibula to the tibia, forming a syndesmosis joint * The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. * The inferior tibiofibular articulation (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the lower end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibiae
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute ''tibia''. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body. Structure In human anatomy, the tibia is the second largest bone next to the femur. As in other vertebrates the tibia is one of two bones in the lower leg, the other being the fibula, and is a component of the knee and ankle joints. The ossification or formation of the bone st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femora
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with the tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap), forming the knee joint. By most measures the two (left and right) femurs are the strongest bones of the body, and in humans, the largest and thickest. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper leg. The two femurs converge medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle of convergence of the femora is a major factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. Human females have thicker pelvic bones, causing their femora to converge more than in males. In the condition ''genu valgum'' (knock knee) the femurs converge so much that the knees touch one another. The opposite extreme is ''genu varum'' (bow-leggedness). In the general population o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humeri
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes (trochlea & capitulum), and 3 fossae ( radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from la, humerus, umerus meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic ''ams'' shoulder and Greek ''ōmos''. Structure Upper extremity The upper o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |