|
Protestantism In Switzerland
The Reformed branch of Protestantism in Switzerland was started in Zürich by Huldrych Zwingli and spread within a few years to Basel ( Johannes Oecolampadius), Bern (Berchtold Haller and Niklaus Manuel), St. Gallen,( Joachim Vadian), to cities in southern Germany and via Alsace (Martin Bucer) to France. Since 1920, the Swiss Reformed Churches have been organized in 26 member churches of the Federation of Swiss Protestant Churches. In the 2000 Swiss census, 33% of Swiss population were reported as registered members of a Reformed cantonal church. By 2022, this was 22.5%, with 2.7% of the populations belonging to other Protestant denominations. History After the early death of Zwingli in 1531, his work was continued by Heinrich Bullinger, the love of the Second Helvetic Confession. The French-speaking cities Neuchâtel, Geneva and Lausanne changed to the Reformation ten years later under William Farel and John Calvin coming from France. The Zwingli and Calvin branches had eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
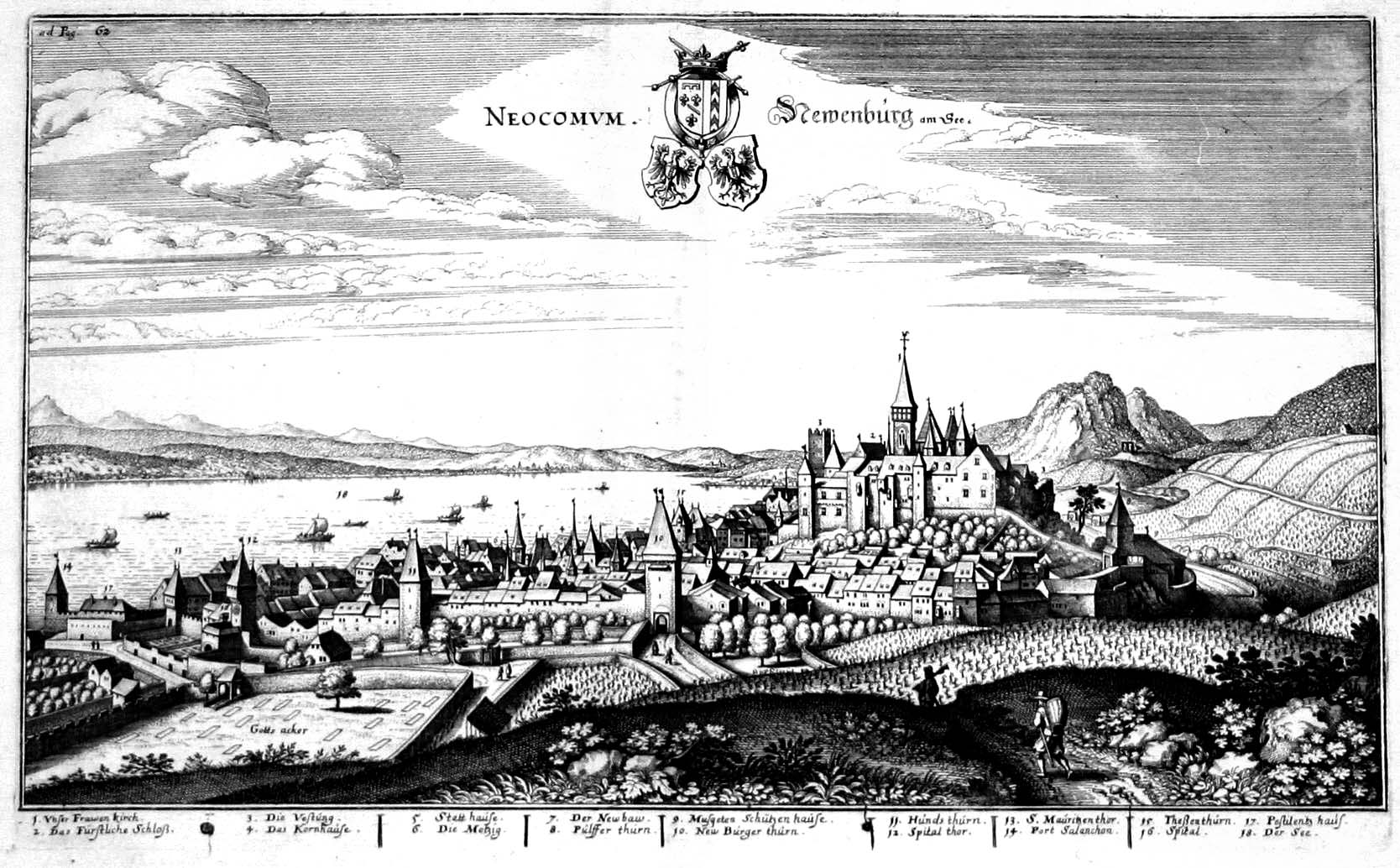
Neuchâtel
Neuchâtel (, ; ; ) is a list of towns in Switzerland, town, a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality, and the capital (political), capital of the cantons of Switzerland, Swiss canton of Neuchâtel (canton), Neuchâtel on Lake Neuchâtel. Since the fusion in 2021 of the municipalities of Neuchâtel, Corcelles-Cormondrèche, Peseux, Neuchâtel, Peseux, and Valangin, the city has approximately 33,000 inhabitants (80,000 in the metropolitan area). The city is sometimes referred to historically by the German name ; both the French and German names mean "New Castle". The castle after which the city is named was built by Rudolph III of Burgundy and completed in 1011. Originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, the city was absorbed into the Holy Roman Empire in 1033. The domain of the counts of Neuchatel was first referred to as a city in 1214. The city came under Prussian control from 1707 until 1848, with an interruption during the Napoleonic Wars from 1806 to 1814. In 1848, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation in 1517. The Lutheran Churches adhere to the Bible and the Ecumenical Creeds, with Lutheran doctrine being explicated in the Book of Concord. Lutherans hold themselves to be in continuity with the apostolic church and affirm the writings of the Church Fathers and the first four ecumenical councils. The schism between Roman Catholicism and Lutheranism, which was formalized in the Diet of Worms, Edict of Worms of 1521, centered around two points: the proper source of s:Augsburg Confession#Article XXVIII: Of Ecclesiastical Power., authority in the church, often called the formal principle of the Reformation, and the doctrine of s:Augsburg Confession#Article IV: Of Justification., justification, the material principle of Luther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baptist Church
Baptists are a denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers ( believer's baptism) and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul competency (the responsibility and accountability of every person before God), '' sola fide'' (salvation by faith alone), '' sola scriptura'' (the Bible is the sole infallible authority, as the rule of faith and practice) and congregationalist church government. Baptists generally recognize two ordinances: baptism and communion. Diverse from their beginning, those identifying as Baptists today may differ widely from one another in what they believe, how they worship, their attitudes toward other Christians, and their understanding of what is important in Christian discipleship. Baptist missionaries have spread various Baptist churches to every continent. The largest Baptist communion of churches is the Baptist World Alliance, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Mennonite Conference
The Swiss Mennonite Conference (also ''Konferenz der Mennoniten der Schweiz'' or ''Conférence Mennonite Suisse'') is an Anabaptist Christian body in Switzerland. The Swiss Mennonites are the oldest and were possibly the most influential body of Anabaptists at some time. The earliest recorded Anabaptist movement during Reformation times originated in the village of Zollikon near Zürich in 1525. Conrad Grebel (ca. 1496–1526) and Felix Manz (ca. 1496–1527), followers of Huldrych Zwingli, divided from Zwingli on the issue of infant baptism versus believers baptism. They organized in the home of Manz on January 21, 1525. Though Grebel and Manz were dead within two years—Grebel of the plague and Manz drowned by the Council of Zürich—the believers' baptism movement quickly spread through German-speaking Switzerland. On the day of Manz' execution, another leader, George Blaurock, was beaten and expelled from the city. From there, he travelled to Bern and eventually left Switz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Reformation
The Protestant Reformation in Switzerland was promoted initially by Huldrych Zwingli, who gained the support of the magistrate, Mark Reust, and the population of Zürich in the 1520s. It led to significant changes in civil life and state matters in Zürich and spread to several other cantons of Switzerland, cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy. Seven cantons remained Catholic, however, which led to intercantonal wars known as the Wars of Kappel. After the victory of the Catholic cantons in 1531, they proceeded to institute Counter-Reformation policies in some regions. The schism and distrust between the Catholic and the Protestant cantons defined their interior politics and paralysed any common foreign policy until well into the 18th century. Despite their religious differences and an exclusively Catholic defence alliance of the seven cantons (''Goldener Bund''), no other major armed conflicts directly between the cantons occurred. Soldiers from both sides fought in the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anabaptist
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek language, Greek : 're-' and 'baptism'; , earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. The term (translation: "Baptizers") is now used, which is considered more impartial. From the perspective of their persecutors, the "Baptizers" baptized for the second time those "who as infants had already been baptized". The denigrative term Anabaptist, given to them by others, signifies rebaptizing and is considered a polemical term, so it has been dropped from use in modern German. However, in the English-speaking world, it is still used to distinguish the Baptizers more clearly from the Baptists, a Protestant sect that developed later in England. Compare their self-designation as "Brethren in Christ" or "Church of God": . is a List of Christian movements, Christian movement which traces its origins to the Radical Reformation in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calvinist
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterianism, Presbyterian, Congregationalism, Congregational, and Waldensians traditions, as well as parts of the Calvinistic Methodist, Methodist, Reformed Anglican Church, Anglican (known as "Episcopal" in some regions) and Reformed Baptists, Baptist traditions. Reformed theology emphasizes the Biblical authority, authority of the Bible and the Sovereignty of God in Christianity, sovereignty of God, as well as covenant theology, a framework for understanding the Bible based on God's covenants with people. Reformed churches emphasize simplicity in worship. Several forms of ecclesiastical polity are exercised by Reformed churches, including presbyterian polity, presbyterian, Congregational polity, congregational, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theology Of Huldrych Zwingli
The theology of Ulrich Zwingli was based on an interpretation of the Bible, taking scripture as the inspired word of God and placing its authority higher than what he saw as human sources such as the ecumenical councils and the Church Fathers. He also recognised the human element within the inspiration, noting the differences in the canonical gospels. Zwinglianism is the Reformed confession based on the Second Helvetic Confession promulgated by Zwingli's successor Heinrich Bullinger in the 1560s. Zwingli's views on baptism were largely a response to Anabaptism, a movement which criticized the practice of infant baptism. He defended the baptism of children by describing it as a sign of a Christian's covenant with disciples and God just as God made a covenant with Abraham. He denied the Catholic doctrine of transubstantiation and following Cornelius Henrici Hoen, he agreed that the bread and wine of the institution signify and do not literally become the body and blood of Jesus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Canton
The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the Federated state, member states of the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the form of the first three confederate allies used to be referred to as the . Two important periods in the development of the Old Swiss Confederacy are summarized by the terms ('Eight Cantons'; from 1353 to 1481) and ('Thirteen Cantons', from 1513 to 1798).rendered "the 'confederacy of eight'" and "the 'Thirteen-Canton Confederation'", respectively, in: Each canton of the Old Swiss Confederacy, formerly also ('lieu/locality', from before 1450), or ('estate', from ), was a fully sovereignty, sovereign state with its own border controls, army, and currency from at least the Treaty of Westphalia (1648) until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848, with a brief period of centralised government during the Helvetic Republic (1798–1803). The term has been widely used since the 19th century. "" The number of canton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consensus Tigurinus
The ''Consensus Tigurinus'' or Consensus of Zurich was a Protestant document written in 1549 by John Calvin and Heinrich Bullinger. The document was intended to bring unity to the Protestant churches on their doctrines of the sacraments, particularly the Lord's Supper. Calvin’s views stood between the Lutheran view of Real Presence and the Zwinglian view of symbolism. He wrote the first draft of the document in November 1548, with notes by Bullinger. Content The document covered 26 Articles of Reformed Sacramentology. Calvin emphasized that there is great meaning in sacramental symbols but it does not have power to act on its own. The document taught: :that the Sacraments are not in and of themselves effective and conferring grace, but that God, through the Holy Spirit, acts through them as means; that the internal effect appears only in the elect; that the good of the Sacraments consists in leading us to Christ, and being instruments of the grace of God, which is since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Calvin
John Calvin (; ; ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French Christian theology, theologian, pastor and Protestant Reformers, reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of Christian theology later called Calvinism, including its doctrines of predestination and of God's Monergism, absolute sovereignty in the Christian soteriology, salvation of the human soul from death and Damnation, eternal damnation. Calvinist doctrines were Augustinian soteriology, influenced by and elaborated upon the Augustinian and other Christian traditions. Various Reformed Christianity, Reformed Church like Continental Reformed, Congregationalism, Presbyterianism, Waldensians, Reformed Baptists, Baptist Reformed, Calvinistic Methodism, Calvinist Methodism, and Reformed Anglican Churches, which look to Calvin as the chief expositor of their beliefs, have spread throughout the world. Calvin was a tireless polemicist and Christian apolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |