|
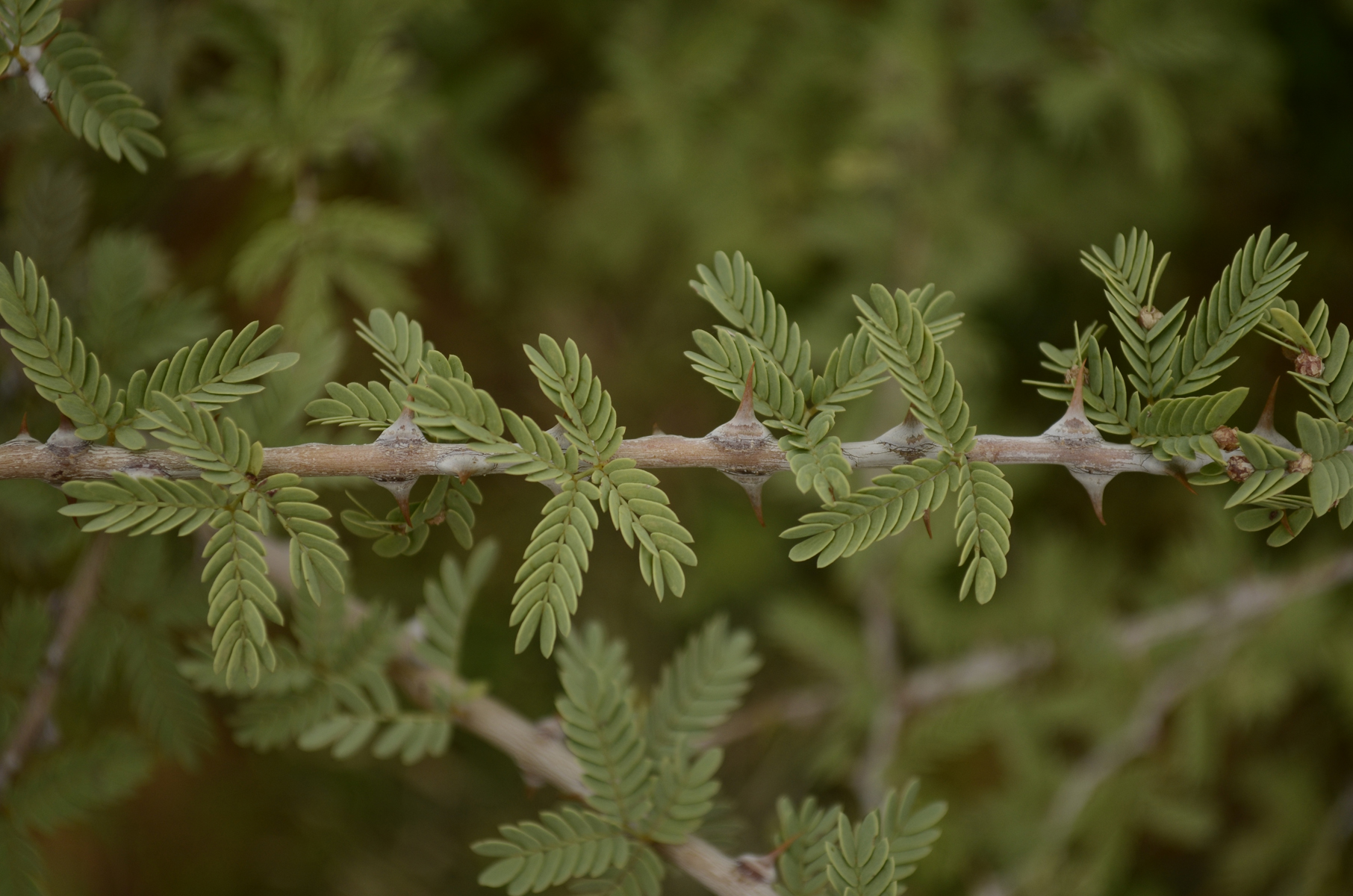
Prosopis Alpataco
''Prosopis'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. The current circumscription of the genus contains three species found in northern Africa, the Middle East, Central and South Asia. Previously it also contained around 40 species of spiny trees and shrubs found in subtropical and tropical regions of the Americas and Africa, now mostly placed in genera ''Strombocarpa'' and ''Neltuma''. They often thrive in arid soil and are resistant to drought, on occasion developing extremely deep root systems. Their wood is usually hard, dense and durable. Their fruits are pods and may contain large amounts of sugar. The generic name means "burdock" in late Latin and originated in the Greek language. Species The current circumscription of the genus contains three species, which are found in South Asia, the Middle East and northern Africa. * ''Prosopis cineraria'' ( L.) Druce – Persian mesquite, ghaf, khejri (Arabian Peninsula, Iran and South Asia) * ''Prosopis farcta'' (B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopis Cineraria
''Prosopis cineraria'', also known as Persian mesquite or ghaf or khejri, is a species of flowering tree in the pea family, Fabaceae. It is native to arid portions of Western Asia and the Indian Subcontinent, including Afghanistan, Bahrain, Iran, India, Oman, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Its leaves are bipinnate. It can survive extreme drought. It is an established introduced species in parts of Southeast Asia, including Indonesia. The ghaf is the national tree of the United Arab Emirates. Through the ''Give a Ghaf campaign'' its citizens are urged to plant it in their gardens to combat desertification and preserve their country's heritage. The desert village of Nazwa in the UAE is home to the Al Ghaf Conservation Reserve. ''Prosopis cineraria'' is also the state tree of Rajasthan (where it is known as khejri), Western Uttar Pradesh (where it is known as chhonkara) and Telangana (where it is known as jammi) in India. A large and well-known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere, such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree, it performs a mechanical-support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients among the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, woodchips, or fibers. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopis Koelziana
''Prosopis koelziana'' is a species of plant in the genus ''Prosopis''. It is found in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq and Iran. References Prosopis, koelziana Trees of Western Asia Forages Drought-tolerant trees {{Mimosoideae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Solander
Daniel Carlsson Solander or Daniel Charles Solander (19 February 1733 – 13 May 1782) was a Sweden, Swedish naturalist and an Apostles of Linnaeus, apostle of Carl Linnaeus. Solander was the first university-educated scientist to set foot on Australia, Australian soil. Biography Solander was born in Piteå, Norrbotten, Sweden, to Rev. Carl Solander a Lutheran principal, and Magdalena (née Bostadia). Solander enrolled at Uppsala University in July 1750 and initially studied languages, the humanities and law. The professor of botany was the celebrated Carl Linnaeus, who was soon impressed by young Solander's ability and accordingly persuaded his father to let him study natural history. Solander travelled to England in June 1760 to promote the new Linnean system of classification. In February 1763, he began librarian, cataloguing the natural history collections of the British Museum, and was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in June the following year. In 1768, Solander g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopis Farcta
''Prosopis farcta'', the Syrian mesquite, is a species of the genus '' Prosopis'', growing in and around the Middle East. Botanical details ''Prosopis farcta'' is a below-ground tree. Above ground, it looks like a shrub with a height of 20–100 cm (in rare cases up to 4m high). In addition, below ground the mesquite has a root system which is really a trunk with branches going as deep as 20 meters or more underground. So it is really a tree, and only the treetop protrudes above ground level. The "treetop" consists of a collection of shrubs which can extend over 1000 square meters or more, all of them connected to the same trunk. The shrubs grow noticeably in the warm summer months. The mesquite can survive difficult weather and soil conditions (including saline soil), and flourishes in Mediterranean heat, but dislikes shadows. The plant is common across the Middle East. It can be found as far north as southern Russia in the north, India in the east, and Algeria in the we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindhi Language
Sindhi ( ; or , ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by more than 30 million people in the Pakistani province of Sindh, where it has official status, as well as by 1.7 million people in India, where it is a Scheduled languages of India, scheduled language without state-level official status. Sindhi is primarily written in the Perso-Arabic script in Pakistan, while in India, both the Perso-Arabic script and Devanagari are used. Sindhi is a Northwestern Indo-Aryan languages, Northwestern Indo-Aryan language, and thus related to, but not mutually intelligible with, Saraiki language, Saraiki and Punjabi language, Punjabi. Sindhi has several regional dialects. The earliest written evidence of modern Sindhi as a language can be found in a translation of the Qur’an into Sindhi dating back to 883 AD. Sindhi was one of the first Indo-Aryan languages to encounter influence from Persian language, Persian and Arabic following the Umayyad campaigns in India, Umayyad conquest in 712 AD. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
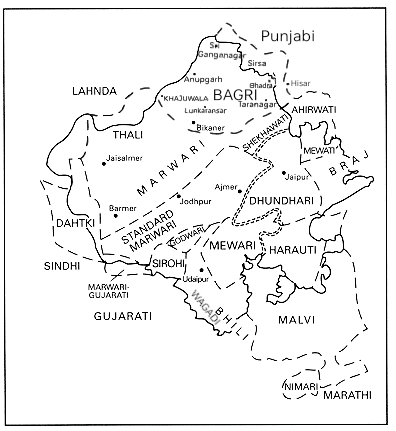
Rajasthani Language
The Rajasthani languages are a group of Western Indo-Aryan languages, primarily spoken in Rajasthan and Malwa, and adjacent areas of Haryana, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh in India and South Punjab and the adjacent areas of Sindh in Pakistan. They have also reached different corners of India, especially eastern and southern parts of India, due to the migrations of people of the Marwari community who use them for internal communication. Rajasthani languages are also spoken to a lesser extent in Nepal, where they are spoken by 25,394 people according to the 2011 Census of Nepal. The term Rajasthani is also used to refer to a literary language mostly based on Marwari.. Geographical distribution Most of the Rajasthani languages are chiefly spoken in the state of Rajasthan but are also spoken in Gujarat, Western Madhya Pradesh i.e. Malwa and Nimar, Haryana and Punjab. Rajasthani languages are also spoken in the Bahawalpur and Multan sectors of the Pakistani provinces of Punjab an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarati Language
Gujarati ( ; , ) is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian state of Gujarat and spoken predominantly by the Gujarati people. Gujarati is descended from Old Western Rājasthāni, Old Gujarati (). In India, it is one of the 22 Languages with official status in India, scheduled languages of the Union. It is also the official language in the state of Gujarat, as well as an official language in the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. As of 2011, Gujarati is the List of languages by number of native speakers in India, 6th most widely spoken language in India by number of native speakers, spoken by 55.5 million speakers which amounts to about 4.5% of the total Indian population. It is the List of languages by number of native speakers, 26th most widely spoken language in the world by number of native speakers as of 2007.Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007), in ''Nationalencyklopedin''. Asteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic (language)
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as ( "the eloquent Arabic") or simply ' (). Arabic is the third most widespread official language after English and French, one of six official languages of the United Nations, and the liturgical language of Islam. Arabic is widely taught in schools and universities around the world and is used to varying degrees in workplaces, governments and the media. During the Middle Ages, Arabic was a major vehicle of culture and learning, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Claridge Druce
George Claridge Druce (23 May 1850 – 29 February 1932) was an English botanist and a Mayor of Oxford. Personal life and education G. Claridge Druce was born at Potterspury on Watling Street in Northamptonshire. He was the illegitimate son of Jane Druce, born 1815 in Buckinghamshire. He went to school in the village of Yardley Gobion. At 16, he was apprenticed to P. Jeyes & Co., a pharmaceutical firm in Northampton. In 1872, he passed exams to become a pharmacist. In 1909, Druce moved to 9 Crick Road. He named the house "Yardley Lodge", after the village in which he spent his youth. He died at his home aged 81 and was buried in Holywell Cemetery. Career as a pharmacist In June 1879, Druce moved to Oxford and set up his own chemist's shop, Druce & Co., at 118 High Street, which continued until his death. He also featured as a shopkeeper in the Oxford novel '' Zuleika Dobson'' by Max Beerbohm. A plaque to Druce was erected on this shop by the Oxfordshire Blue Plaque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Latin
Late Latin is the scholarly name for the form of Literary Latin of late antiquity.Roberts (1996), p. 537. English dictionary definitions of Late Latin date this period from the 3rd to 6th centuries CE, and continuing into the 7th century in the Iberian Peninsula. This somewhat ambiguously defined version of Latin was used between the eras of Classical Latin and Medieval Latin. Scholars do not agree exactly when Classical Latin should end or Medieval Latin should begin. Being a written language, Late Latin is not the same as Vulgar Latin, or more specifically, the spoken Latin of the post-Imperial period. The latter served as the ancestor of the Romance languages. Although Late Latin reflects an upsurge in the use of Vulgar Latin vocabulary and constructs, it remains largely classical in its overall features, depending on the author who uses it. Some Late Latin writings are more literary and classical, but others are more inclined to the vernacular. As such it is an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burdock
''Arctium'' is a genus of biennial plants commonly known as burdock, family Asteraceae. Native to Europe and Asia, several species have been widely introduced worldwide. Burdock's clinging properties, in addition to providing an excellent mechanism for seed dispersal, led to the invention of the hook and loop fastener. Description Plants of the genus ''Arctium'' have dark green leaves that can grow up to long. They are generally large, coarse, and ovate, with the lower ones being heart-shaped. They are woolly underneath. The leafstalks are generally hollow. ''Arctium'' species generally flower from July through October. Burdock flowers provide essential pollen and nectar for honeybees around August, when clover is on the wane and before the goldenrod starts to bloom. Burdock's clinging properties make it an excellent mechanism for seed dispersal. Taxonomy A large number of species have been placed in genus ''Arctium'' at one time or another, but most of them are now class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |