|
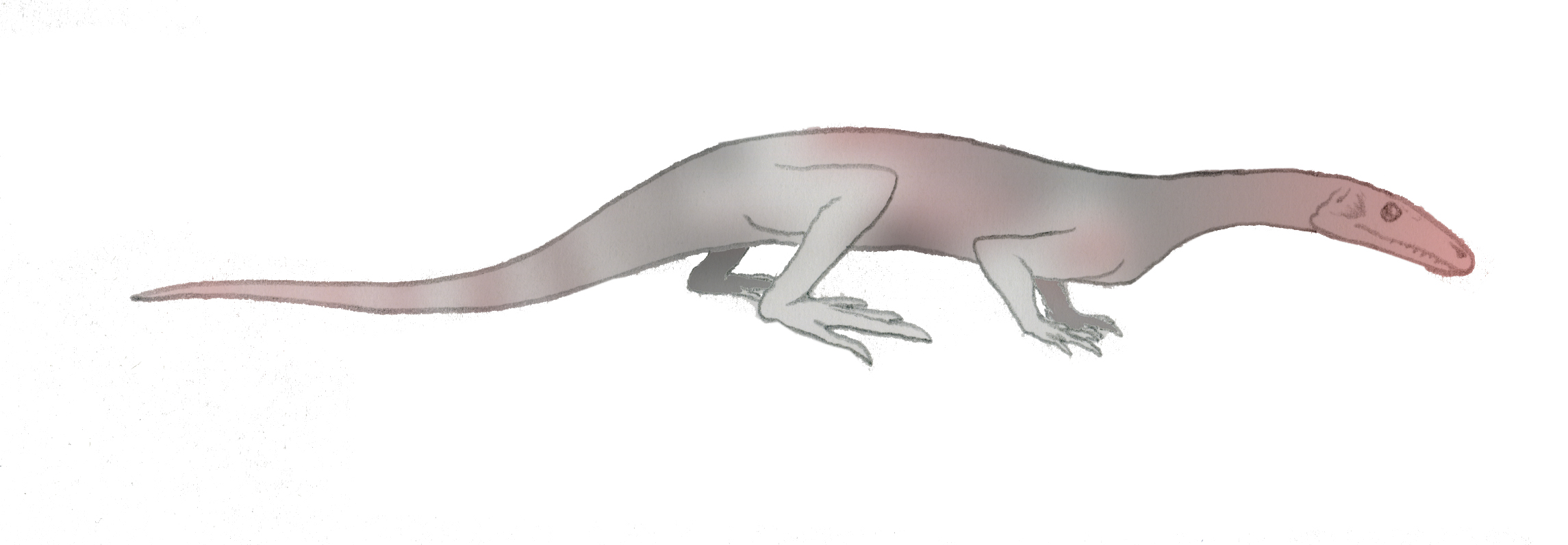
Prolacerta
''Prolacerta'' is a genus of archosauromorph from the lower Triassic of South Africa and Antarctica. The only known species is ''Prolacerta broomi''. The generic name ''Prolacerta'' is derived from Latin meaning “before lizard” and its species name ''broomi'' is in commemoration of the famous paleontologist Robert Broom, who discovered and studied many of the fossils found in rocks of the Karoo Supergroup. When first discovered, ''Prolacerta'' was considered to be ancestral to modern lizards, scientifically known as lacertilians. However, a study by Gow (1975) instead found that it shared more similarities with the lineage that would lead to archosaurs such as crocodilians and dinosaurs (including birds). ''Prolacerta'' is considered by modern paleontologists to be among the closest relatives of the Archosauriformes. History of discovery ''Prolacerta'' was first described by Francis Rex Parrington in 1935 from a single skull recovered near the small town, Middelburg, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha ( Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) rather than lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including '' Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and '' Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines ( turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone
The ''Lystrosaurus'' Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone which correlates to the upper Adelaide and lower Tarkastad Subgroups of the Beaufort Group, a fossiliferous and geologically important geological Group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. This biozone has outcrops in the south central Eastern Cape ( Middelburg, Queenstown, Aliwal North, Nieu-Bethesda) and in the southern and northeastern Free State ( Bethulie, Gariep Dam, Mthatha, Harrismith). The '' Lystrosaurus'' Assemblage Zone is one of eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group, and is considered to be Early Triassic in age. The name of the biozone refers to '' Lystrosaurus'', a small to medium-sized dicynodont therapsid. It is characterized by the appearance of further '' Lystrosaurus'' subspecies which are confined to this biozone. '' Lystrosaurus maccaigi'' and '' Lystrosaurus curvatus'' are the only two species found outside the ''Lystrosaurus'' Assemblage Zone in Upper Permian deposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
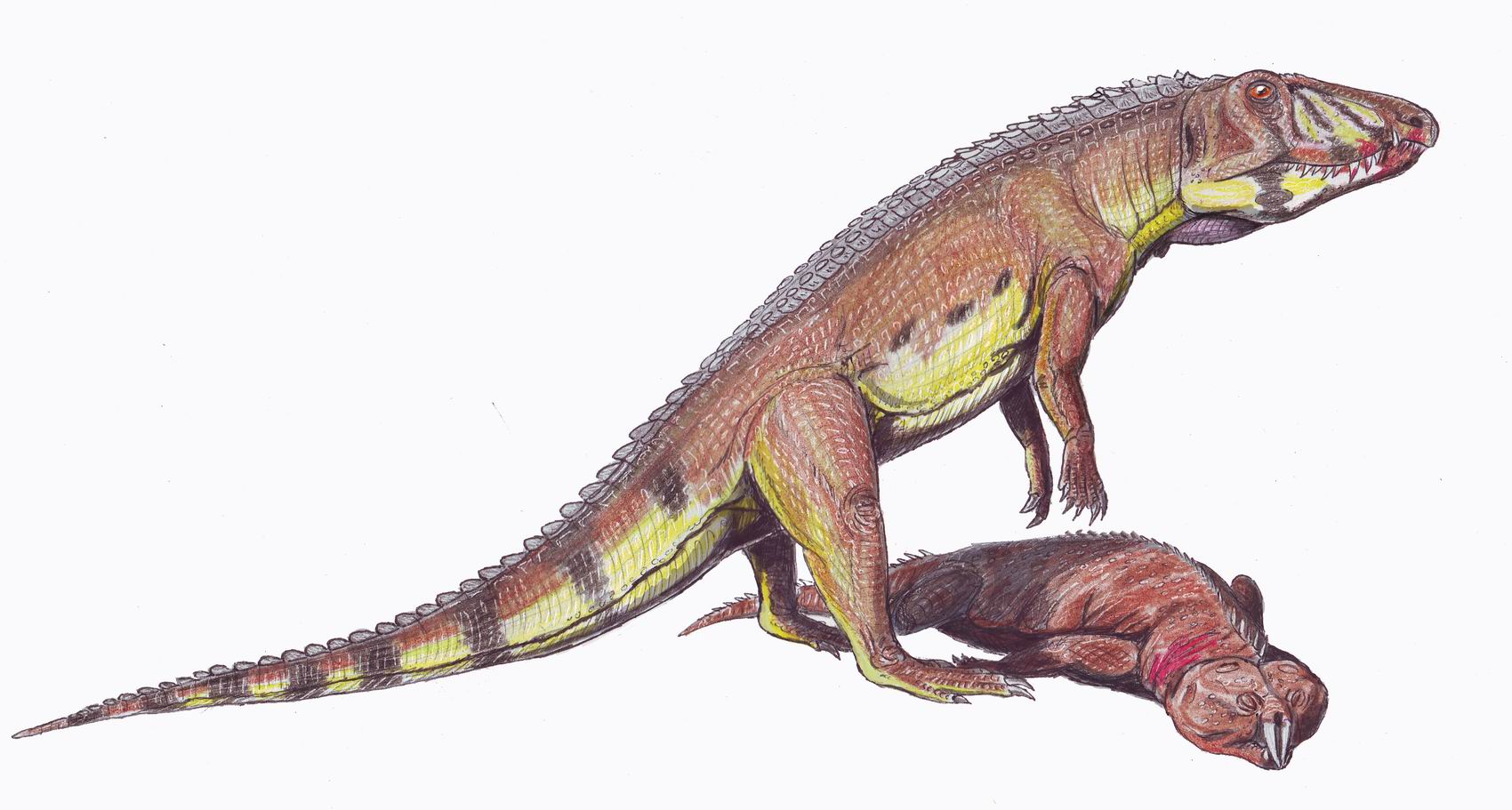
Archosauriformes
Archosauriformes ( Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles that developed from archosauromorph ancestors some time in the Latest Permian (roughly 252 million years ago). It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria (the group that contains crocodiles, pterosaurs and dinosaurs ncluding birds; Phil Senter">bird">ncluding_bird<_a>s.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing ''Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. These reptiles, which include members of the family Proterosuchidae and more advanced forms, were originally superficially crocodile-like animals with sprawling gaits and long snouts. Unlike the bulk of their therapsid contemporaries, the proterosuchids survived the catastrophe at the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
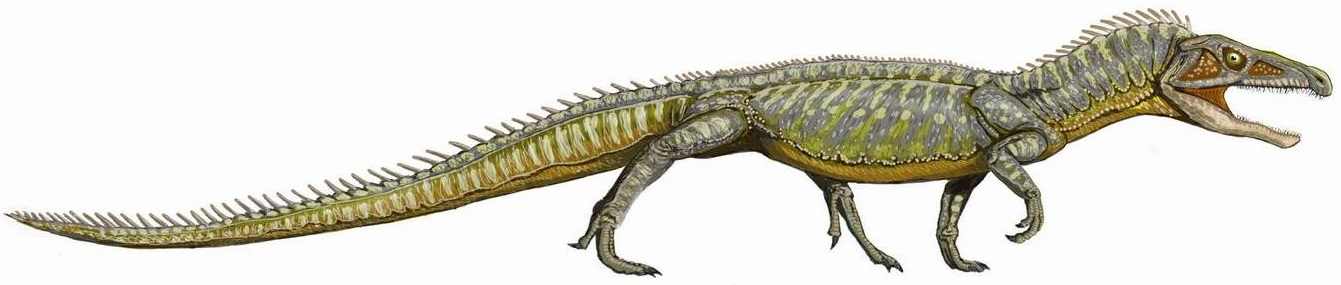
Archosaur
Archosauria () is a clade of diapsids, with birds and crocodilians as the only living representatives. Archosaurs are broadly classified as reptiles, in the cladistic sense of the term which includes birds. Extinct archosaurs include non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and extinct relatives of crocodilians. Modern paleontologists define Archosauria as a crown group that includes the most recent common ancestor of living birds and crocodilians, and all of its descendants. The base of Archosauria splits into two clades: Pseudosuchia, which includes crocodilians and their extinct relatives, and Avemetatarsalia, which includes birds and their extinct relatives (such as non-avian dinosaurs and pterosaurs). Older definitions of the group Archosauria rely on shared morphological characteristics, such as an antorbital fenestra in the skull, serrated teeth, and an upright stance. Some extinct reptiles, such as proterosuchids and euparkeriids, possessed these features yet orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothesis
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can testable, test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained with the available scientific theories. Even though the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, a scientific hypothesis is not the same as a scientific theory. A working hypothesis is a provisionally accepted hypothesis proposed for further research in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to denote the antecedent (logic), antecedent of a proposition; thus in the proposition "If ''P'', then ''Q''", ''P'' denotes the hypothesis (or antecedent); ''Q'' can be called a consequent. ''P'' is the :wikt:assumption, assumption in a (possibly Counterfactual conditional, counterfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lewis Camp
Charles Lewis Camp (March 12, 1893 Jamestown, North Dakota – August 14, 1975 San Jose, California) was a palaeontologist and zoologist, working from the University of California, Berkeley. He took part in excavations at the ' Placerias Quarry', in 1930 and the forty '' Shonisaurus'' skeleton discoveries of the 1960s, in what is now the Berlin-Ichthyosaur State Park. Camp served as the third director of the University of California Museum of Paleontology from 1930 to 1949, and coincidentally as chair of the UC Berkeley Paleontology Department between 1939 and 1949. Camp named a number of species of marine reptiles such as '' Shonisaurus'' and '' Plotosaurus'', as well as the dinosaur ''Segisaurus''. Camp was also an important bibliographer and historian of Western America. This aspect of his career is represented most notably by two works. The first is his biography of American pioneer James Clyman, which Bernard De Voto called "one of the half-dozen classics in the field." The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Younginidae
Younginidae is an extinct family of neodiapsid reptiles from the Late Permian and Early Triassic. In a phylogenetic context, younginids are near the base of the clade Neodiapsida. Younginidae includes the species '' Youngina capensis'' from the Late Permian of South Africa and ''Thadeosaurus colcanapi'' from the Late Permian and Early Triassic of Madagascar. '' Heleosuchus griesbachi'' from the Late Permian of South Africa may also be a member of the family. Younginidae was traditionally assigned to Eosuchia, an order containing an assemblage of basal diapsids now thought to represent an evolutionary grade rather than a true clade. In 1945 paleontologist Alfred Romer reclassified Younginidae within a new group, Younginiformes, grouping it with the families Tangasauridae and Prolacertidae. Romer considered Younginidae to include many genera that are no longer classified as younginids: '' Paliguana'', '' Palaegama'', and '' Saurosternon'' are now considered basal lepidosaurom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

