|
Process Parameter
In control theory, a process variable (PV; also process value or process parameter) is the current measured value of a particular part of a process which is being monitored or controlled. An example of this would be the temperature of a furnace. The current temperature is the process variable, while the desired temperature is known as the set-point (SP). Control system use Measurement of process variables is essential in control systems to controlling a process. The value of the process variable is continuously monitored so that control may be exerted. Four commonly measured variables that affect chemical and physical processes are: pressure, temperature, level and flow. but there are in fact a large number of measurement quantities which for international purposes use the International System of Units (SI) The SP-PV error is used to exert control on a process so that the value of PV equals the value of the SP. A classic use of this is in the PID controller PID or Pid ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Theory
Control theory is a field of control engineering and applied mathematics that deals with the control system, control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any ''delay'', ''overshoot'', or ''steady-state error'' and ensuring a level of control Stability theory, stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of Optimal control, optimality. To do this, a controller with the requisite corrective behavior is required. This controller monitors the controlled process variable (PV), and compares it with the reference or Setpoint (control system), set point (SP). The difference between actual and desired value of the process variable, called the ''error'' signal, or SP-PV error, is applied as feedback to generate a control action to bring the controlled process variable to the same value as the set point. Other aspects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
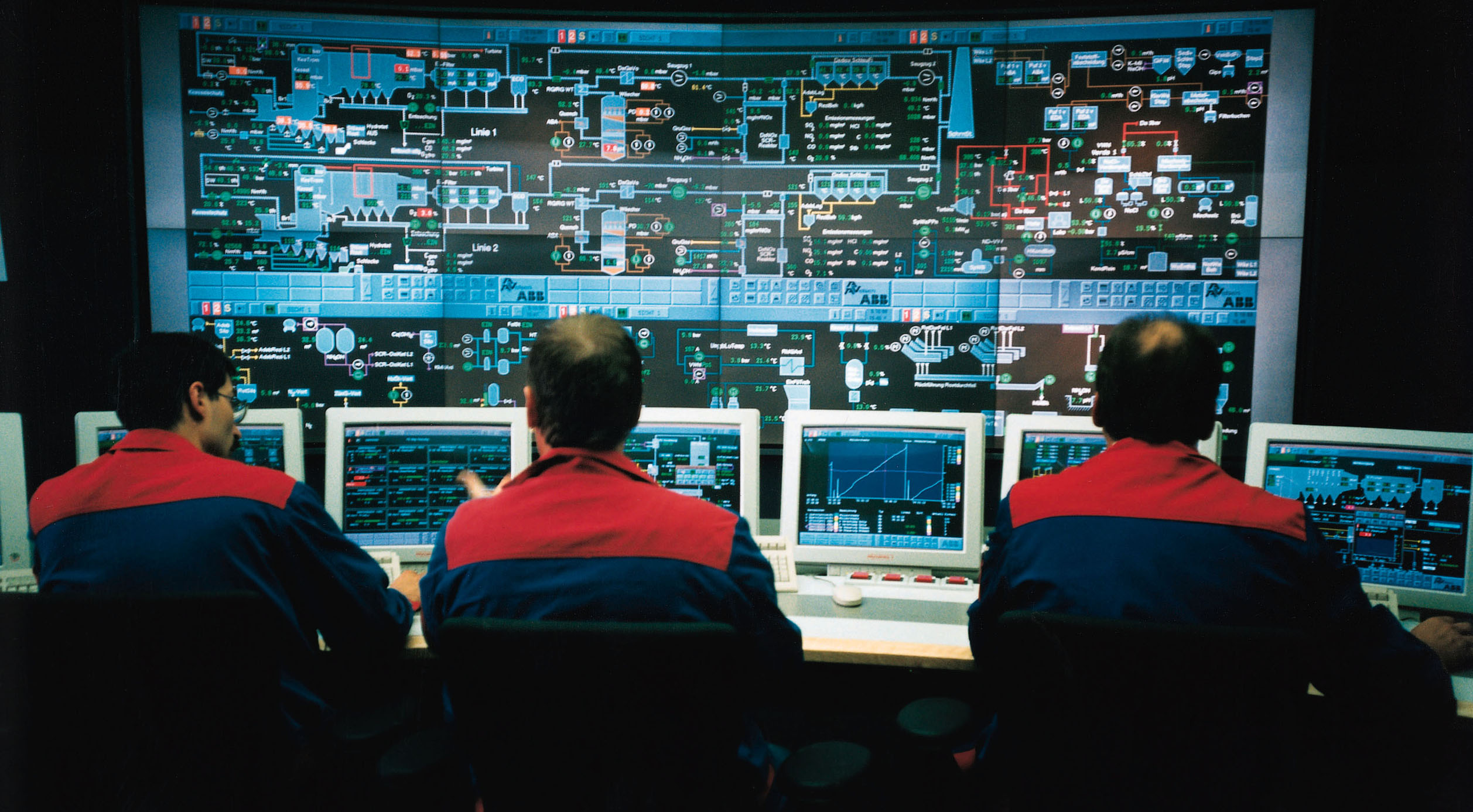
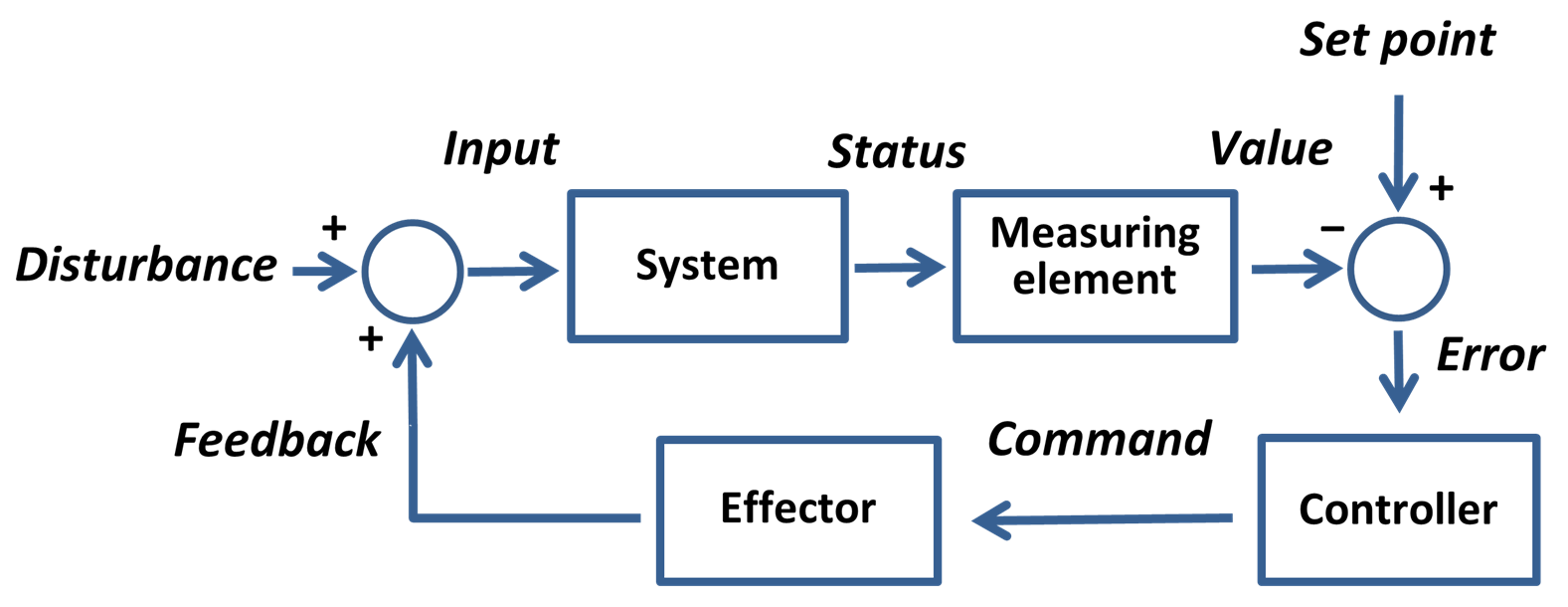
Control System
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial control systems which are used for controlling processes or machines. The control systems are designed via control engineering process. For continuously modulated control, a feedback controller is used to automatically control a process or operation. The control system compares the value or status of the process variable (PV) being controlled with the desired value or setpoint (SP), and applies the difference as a control signal to bring the process variable output of the plant to the same value as the setpoint. For sequential and combinational logic, software logic, such as in a programmable logic controller, is used. Open-loop and closed-loop control Feedback control systems Logic control Logic control systems for indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setpoint (control System)
In cybernetics and control theory, a setpoint (SP; also set point) is the desired or target value for an essential variable, or process value (PV) of a control system, which may differ from the actual measured value of the variable. Departure of such a variable from its setpoint is one basis for error-controlled regulation using negative feedback for automatic control. A setpoint can be any physical quantity or parameter that a control system seeks to regulate, such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, position, speed, or any other measurable attribute. In the context of PID controller, the setpoint represents the reference or goal for the controlled process variable. It serves as the benchmark against which the actual process variable (PV) is continuously compared. The PID controller calculates an error signal by taking the difference between the setpoint and the current value of the process variable. Mathematically, this error is expressed as: :e(t) = SP - PV(t), where e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set-point Control
Set point or setpoint may refer to: * Set point (tennis), a tennis term meaning one player is one point away from winning a set * Set point (endocrinology), a term encompassing a number of quantities (e.g. body weight, body temperature) where the endocrine system contributes to regulation and homeostasis. * Setpoint (control system), the target value that an automatic control system, for example PID controller, will aim to reach * Set point theory, a theory describing how the body maintains a consistent weight over time * Set Point (album), ''Set Point'' (album), the fourth studio album by Elka (singer), Yolka {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control System
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial control systems which are used for controlling processes or machines. The control systems are designed via control engineering process. For continuously modulated control, a feedback controller is used to automatically control a process or operation. The control system compares the value or status of the process variable (PV) being controlled with the desired value or setpoint (SP), and applies the difference as a control signal to bring the process variable output of the plant to the same value as the setpoint. For sequential and combinational logic, software logic, such as in a programmable logic controller, is used. Open-loop and closed-loop control Feedback control systems Logic control Logic control systems for indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various #Units, units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the International System of Units, SI unit of pressure, the Pascal (unit), pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton (unit), newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the Pound (force), pound-force per square inch (Pound per square inch, psi, symbol lbf/in2) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial units, imperial and United States customary units, US customary systems. Pressure ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Temperature
Thermodynamic temperature, also known as absolute temperature, is a physical quantity which measures temperature starting from absolute zero, the point at which particles have minimal thermal motion. Thermodynamic temperature is typically expressed using the Kelvin scale, where the unit of measurement is the ''kelvin'' (unit symbol: K). The Kelvin scale uses the same degree interval as the Celsius scale but is offset so that 0 K corresponds to absolute zero. For comparison, a temperature of 295 K corresponds to 21.85 °C and 71.33 °F. Another absolute scale of temperature is the Rankine scale, which is based on the Fahrenheit degree interval. Historically, thermodynamic temperature was defined by Lord Kelvin in terms of a macroscopic relation between Work (thermodynamics), thermodynamic work and Heat, heat transfer as defined in thermodynamics, but the kelvin was redefined by international agreement in 2019 in terms of phenomena that are now understood as man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International System Of Units
The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI (from French ), is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. It is the only system of measurement with official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI system is coordinated by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, which is abbreviated BIPM from . The SI comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantities. These are called coherent derived units, which can always be represented as products of powers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PID Controller
PID or Pid may refer to: Medicine * Pelvic inflammatory disease or pelvic inflammatory disorder, an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system * Primary immune deficiency, disorders in which part of the body's immune system is missing or does not function properly * Prolapsed intervertebral disc, commonly called a herniated disc Science, technology and engineering * BBC Programme Identifier, a unique identifier for a BBC television or radio programme brand, a season or series, or an individual episode * OBD-II PIDs (on-board diagnostics parameter IDs), requests for data through an OBD connector in automotive repair * Packet Identifier, a field in a MPEG transport stream#Packet Identifier (PID), MPEG transport stream packet * Partial information decomposition, an extension of information theory * Passive infrared detector, a passive infrared sensor * Payload Interface Document (used on space engineering program for example) * Persistent identifier, a long-lastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |