|
Prime Knot
In knot theory, a prime knot or prime link is a knot that is, in a certain sense, indecomposable. Specifically, it is a non- trivial knot which cannot be written as the knot sum of two non-trivial knots. Knots that are not prime are said to be composite knots or composite links. It can be a nontrivial problem to determine whether a given knot is prime or not. A family of examples of prime knots are the torus knots. These are formed by wrapping a circle around a torus ''p'' times in one direction and ''q'' times in the other, where ''p'' and ''q'' are coprime integers. Knots are characterized by their crossing numbers. The simplest prime knot is the trefoil with three crossings. The trefoil is actually a (2, 3)-torus knot. The figure-eight knot, with four crossings, is the simplest non-torus knot. For any positive integer ''n'', there are a finite number of prime knots with ''n'' crossings. The first few values for exclusively prime knots and for prime ''or'' composite k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
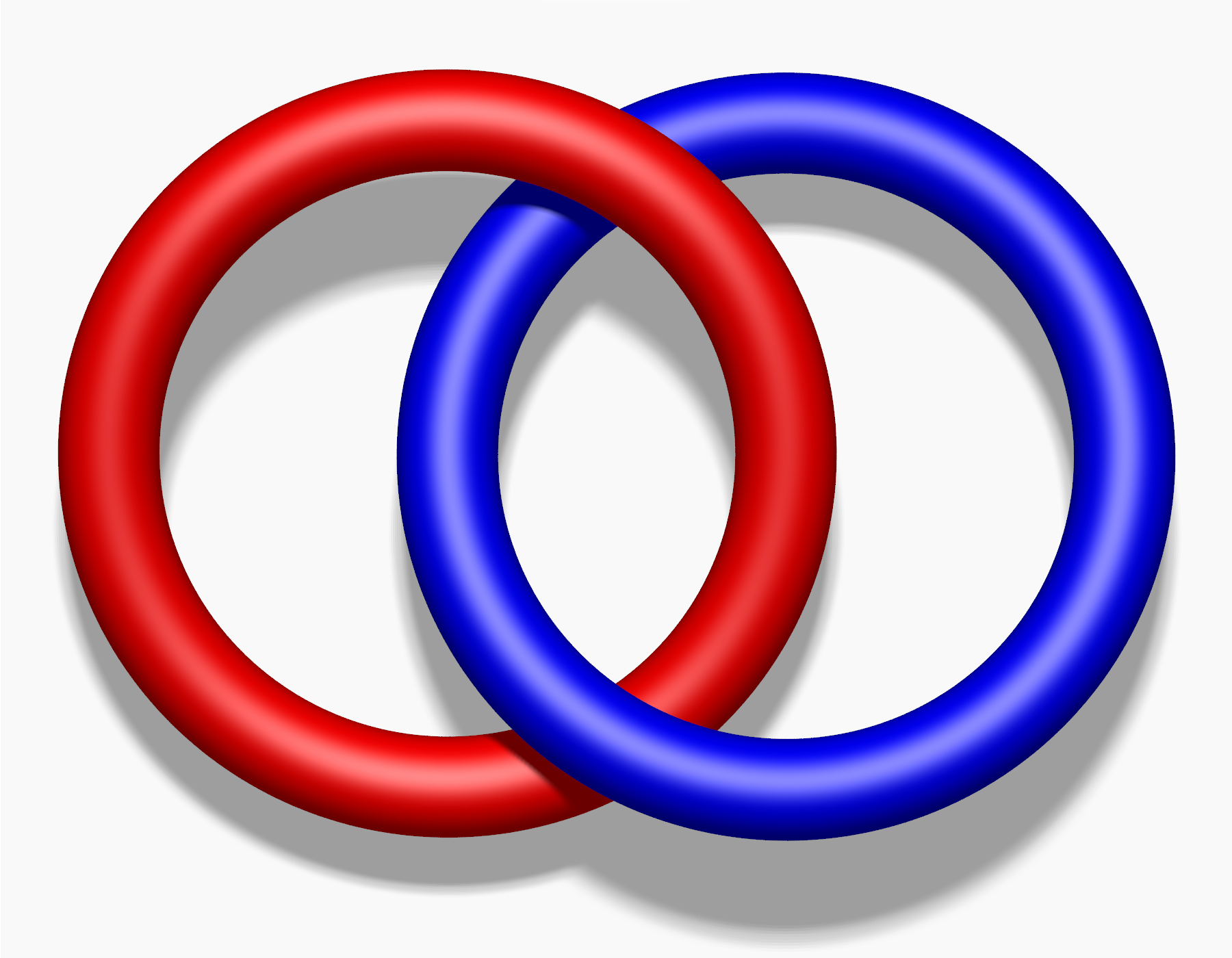
Hopf Link
In mathematics, mathematical knot theory, the Hopf link is the simplest nontrivial link (knot theory), link with more than one component. It consists of two circles linked together exactly once, and is named after Heinz Hopf. Geometric realization A concrete model consists of two unit circles in perpendicular planes, each passing through the center of the other.. See in particulap. 77 This model minimizes the ropelength of the link and until 2002 the Hopf link was the only link whose ropelength was known. The convex hull of these two circles forms a shape called an oloid. Properties Depending on the relative Orientation (geometry), orientations of the two components the linking number of the Hopf link is ±1. The Hopf link is a (2,2)-torus link with the braid word :\sigma_1^2.\, The knot complement of the Hopf link is R × ''S''1 × ''S''1, the Cylinder (geometry), cylinder over a torus. This space has a Geometrization conjecture, locally Euc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative integers. The set (mathematics), set of all integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the set of natural numbers, the set of integers \mathbb is Countable set, countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fraction, fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , 5/4, and Square root of 2, are not. The integers form the smallest Group (mathematics), group and the smallest ring (mathematics), ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot Invariants
In the mathematical field of knot theory, a knot invariant is a quantity (in a broad sense) defined for each knot which is the same for equivalent knots. The equivalence is often given by ambient isotopy but can be given by homeomorphism. Some invariants are indeed numbers (algebraic), but invariants can range from the simple, such as a yes/no answer, to those as complex as a homology theory (for example, "a ''knot invariant'' is a rule that assigns to any knot a quantity such that if and are equivalent then ."). Research on invariants is not only motivated by the basic problem of distinguishing one knot from another but also to understand fundamental properties of knots and their relations to other branches of mathematics. Knot invariants are thus used in knot classification,Purcell, Jessica (2020). ''Hyperbolic Knot Theory'', p.7. American Mathematical Society. "A ''knot invariant'' is a function from the set of knots to some other set whose value depends only on the equiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prime Knots
A list is a Set (mathematics), set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole".Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of ''The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connected Sum
In mathematics, specifically in topology, the operation of connected sum is a geometric modification on manifolds. Its effect is to join two given manifolds together near a chosen point on each. This construction plays a key role in the classification of closed surfaces. More generally, one can also join manifolds together along identical submanifolds; this generalization is often called the fiber sum. There is also a closely related notion of a connected sum on knots, called the knot sum or composition of knots. Connected sum at a point A connected sum of two ''m''-dimensional manifolds is a manifold formed by deleting a ball inside each manifold and gluing together the resulting boundary spheres. If both manifolds are oriented, there is a unique connected sum defined by having the gluing map reverse orientation. Although the construction uses the choice of the balls, the result is unique up to homeomorphism. One can also make this operation work in the smooth categor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horst Schubert
Horst Schubert (11 June 1919 – 2001) was a German mathematician. Schubert was born in Chemnitz and studied mathematics and physics at the Universities of Frankfurt am Main, Zürich and Heidelberg, where in 1948 he received his PhD under Herbert Seifert with thesis ''Die eindeutige Zerlegbarkeit eines Knotens in Primknoten''. From 1948 to 1956 Schubert was an assistant in Heidelberg, where he received in 1952 his habilitation qualification. From 1959 he was a ''professor extraordinarius'' and from 1962 a ''professor ordinarius'' at the University of Kiel. From 1969 to 1984 he was a professor at the University of Düsseldorf. In 1949 he published his proof that every oriented knot in S^3 decomposes as a connect-sum of prime knots in a unique way, up to reordering. After this proof he found a new proof based on his study of incompressible tori in knot complements; he published this work ''Knoten und Vollringe'' in ''Acta Mathematica'', where he defined satellite and companio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot Table
In topology, knot theory is the study of knot (mathematics), mathematical knots. While inspired by knots which appear in daily life, such as those in shoelaces and rope, a mathematical knot differs in that the ends are joined so it cannot be undone, the simplest knot being a ring (or "unknot"). In mathematical language, a knot is an embedding of a circle in 3-dimensional Euclidean space, \mathbb^3. Two mathematical knots are equivalent if one can be transformed into the other via a deformation of \mathbb^3 upon itself (known as an ambient isotopy); these transformations correspond to manipulations of a knotted string that do not involve cutting it or passing it through itself. Knots can be described in various ways. Using different description methods, there may be more than one description of the same knot. For example, a common method of describing a knot is a planar diagram called a knot diagram, in which any knot can be drawn in many different ways. Therefore, a fundamental p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirror Image
A mirror image (in a plane mirror) is a reflection (physics), reflected duplication of an object that appears almost identical, but is reversed in the direction perpendicular to the mirror surface. As an optical phenomenon, optical effect, it results from specular reflection off from surfaces of lustrous materials, especially a mirror or water. It is also a concept in geometry and can be used as a conceptualization process for 3D structures. In geometry and geometrical optics In two dimensions In geometry, the mirror image of an object or 2D geometric model, two-dimensional figure is the virtual image formed by reflection (mathematics), reflection in a plane mirror; it is of the same size as the original object, yet different, unless the object or figure has reflection symmetry (also known as a P-symmetry). Two-dimensional mirror images can be seen in the reflections of mirrors or other reflecting surfaces, or on a printed surface seen inside-out. If we first look at an obje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirality (mathematics)
In geometry, a figure is chiral (and said to have chirality) if it is not identical to its mirror image, or, more precisely, if it cannot be mapped to its mirror image by Rotation (mathematics), rotations and Translation (geometry), translations alone. An object that is not chiral is said to be ''achiral''. A chiral object and its mirror image are said to be enantiomorphs. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (cheir), the hand, the most familiar chiral object; the word ''enantiomorph'' stems from the Greek (enantios) 'opposite' + (morphe) 'form'. Examples Some chiral three-dimensional objects, such as the helix, can be assigned a right or left handedness, according to the right-hand rule. Many other familiar objects exhibit the same chiral symmetry of the human body, such as gloves and shoes. Right shoes differ from left shoes only by being mirror images of each other. In contrast thin gloves may not be considered chiral if you can wear them wiktionary:inside ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A002863
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, '' a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest known ancestor of A is ''aleph''—the first letter of the Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figure-eight Knot (mathematics)
In knot theory, a figure-eight knot (also called Listing's knot) is the unique knot with a crossing number (knot theory), crossing number of four. This makes it the knot with the third-smallest possible crossing number, after the unknot and the trefoil knot. The figure-eight knot is a prime knot. Origin of name The name is given because tying a normal figure-eight knot in a rope and then joining the ends together, in the most natural way, gives a model of the mathematical knot. Description A simple parametric representation of the figure-eight knot is as the set of all points (''x'',''y'',''z'') where : \begin x & = \left(2 + \cos \right) \cos \\ y & = \left(2 + \cos \right) \sin \\ z & = \sin \end for ''t'' varying over the real numbers (see 2D visual realization at bottom right). The figure-eight knot is Prime knot, prime, alternating knot, alternating, rational knot, rational with an associated value of 5/3, and is Chiral kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot Theory
In topology, knot theory is the study of knot (mathematics), mathematical knots. While inspired by knots which appear in daily life, such as those in shoelaces and rope, a mathematical knot differs in that the ends are joined so it cannot be undone, the simplest knot being a ring (or "unknot"). In mathematical language, a knot is an embedding of a circle in 3-dimensional Euclidean space, \mathbb^3. Two mathematical knots are equivalent if one can be transformed into the other via a deformation of \mathbb^3 upon itself (known as an ambient isotopy); these transformations correspond to manipulations of a knotted string that do not involve cutting it or passing it through itself. Knots can be described in various ways. Using different description methods, there may be more than one description of the same knot. For example, a common method of describing a knot is a planar diagram called a knot diagram, in which any knot can be drawn in many different ways. Therefore, a fundamental p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |