|
Poundmaker 114-2B
Poundmaker ( – 4 July 1886), also known as ''pîhtokahânapiwiyin'' (), was a Plains Cree chief known as a peacemaker and defender of his people, the Poundmaker Cree Nation. His name denotes his special craft at leading buffalo into buffalo pounds (enclosures) for harvest. In 1885, during the North-West Rebellion, his band was attacked by Canadian troops and a battle ensued. After the rebellion was suppressed, he surrendered and was convicted of treason and imprisoned. He died of illness soon after his release. In May 2019, Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau exonerated the chief and apologized to the Poundmaker Cree Nation. Name According to Cree tradition, or oral history, ''pîhtokahânapiwiyin'', known to English speakers as Chief Poundmaker, gained his name for his special ability to attract buffalo into pounds. A buffalo pound resembled a huge corral with walls covered by the leaves of thick bushes. Usually herds of buffalo were stampeded into this trap. But so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cree
The Cree, or nehinaw (, ), are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people, numbering more than 350,000 in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada, First Nations. They live primarily to the north and west of Lake Superior in the Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces of Alberta, Labrador, Manitoba, the Northwest Territories, Ontario, and Saskatchewan. Another roughly 27,000 live in Quebec. In the United States, the Cree, historically, lived from Lake Superior westward. Today, they live mostly in Montana, where they share Rocky Boy's Indian Reservation with Ojibwe (Chippewa) people. A documented westward migration, over time, has been strongly associated with their roles as traders and hunters in the North American fur trade. Sub-groups and geography The Cree are generally divided into eight groups based on dialect and region. These divisions do not necessarily represent ethnic subdivisions within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Pheasant Band
The Red Pheasant Cree Nation () is a Plains Cree First Nations band government in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The band's sole reserve, Red Pheasant 108, is south of North Battleford. History Chief Wuttunee's people were living along the Battle River when the Numbered Treaties were being negotiated. Wuttunee did not want to sign Treaty 6 but appointed his brother Red Pheasant to sign in his place, and the Department of Indian Affairs henceforth referred to them as the Red Pheasant Band. In 1878, they settled on a reserve in the Eagle Hills. A day school and an Anglican church were opened there within a decade. In 2019, Chief Wuttunee secured the return of the original treaty medal which had been stolen in 1890 off the body of a deceased Chief. In 2020, Chief Clinton Wuttunee was re-elected to the position of Chief. However, his election and that of one other band councillor were annulled amid substantiated allegations of electoral fraud, including vote buying. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state (polity), state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to Coup d'état, overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplomats, its officials, or its secret services for a hostile foreign power, or Regicide, attempting to kill its head of state. A person who commits treason is known in law as a traitor. Historically, in common law countries, treason also covered the murder of specific social superiors, such as the murder of a husband by his wife or that of a master by his servant. Treason (i.e., disloyalty) against one's monarch was known as ''high treason'' and treason against a lesser superior was ''petty treason''. As jurisdictions around the world abolished petty treason, "treason" came to refer to what was historically known as high treason. At times, the term ''traitor'' has been used as a political epithet, regardless of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poundmaker With Woman
Poundmaker ( – 4 July 1886), also known as ''pîhtokahânapiwiyin'' (), was a Plains Cree chief known as a peacemaker and defender of his people, the Poundmaker Cree Nation. His name denotes his special craft at leading buffalo into buffalo pounds (enclosures) for harvest. In 1885, during the North-West Rebellion, his band was attacked by Canadian troops and a battle ensued. After the rebellion was suppressed, he surrendered and was convicted of treason and imprisoned. He died of illness soon after his release. In May 2019, Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau exonerated the chief and apologized to the Poundmaker Cree Nation. Name According to Cree tradition, or oral history, ''pîhtokahânapiwiyin'', known to English speakers as Chief Poundmaker, gained his name for his special ability to attract buffalo into pounds. A buffalo pound resembled a huge corral with walls covered by the leaves of thick bushes. Usually herds of buffalo were stampeded into this trap. But so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Batoche
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Riel
Louis Riel (; ; 22 October 1844 – 16 November 1885) was a Canadian politician, a founder of the province of Manitoba, and a political leader of the Métis in Canada, Métis people. He led two resistance movements against the Government of Canada and its first prime minister John A. Macdonald. Riel sought to defend Métis rights and identity as the Northwest Territories came progressively under the Canadian sphere of influence. The first resistance movement led by Riel was the Red River Resistance of 1869–1870. The provisional government established by Riel ultimately negotiated the terms under which the new province of Manitoba entered the Canadian Confederation. However, while carrying out the resistance, Riel had a Canadian nationalist, Thomas Scott (Orangeman), Thomas Scott, executed. Riel soon fled to the United States to escape prosecution. He was elected three times as Member of Parliament (Canada), member of the House of Commons of Canada, House of Commons, but, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cut Knife Creek
Cut Knife Creek is a river in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The river begins about south of the Highway 40 / Highway 21 intersection and ends at Battle River in the Poundmaker Cree Nation. Battle River is a major tributary of the North Saskatchewan River. The Battle of Cut Knife of the North-West Rebellion took place on Cut Knife Hill near the river on 2 May 1885. The site of the battle was designated a National Historic Site of Canada and is the location of Chief Poundmaker's grave. 'Cut Knife' is named after a Sarcee chief who was killed in a skirmish with the Cree near the area in the 1840s. History In March 1885, Chief Poundmaker and fellow Cree band members travelled to Battleford in search of supplies and rations for famine relief. The local Indian agent refused to meet with Poundmaker and with "a lot of restless Indians wandering the vicinity of the town", the homesteaders fled to the nearby Fort Battleford. With the village deserted, the Indians loote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Dillon Otter
General Sir William Dillon Otter (December 3, 1843 – May 6, 1929) was a professional Canadian soldier who became the first Canadian-born Chief of the General Staff, the head of the Canadian Militia. He led troops in the suppression of the 1885 rebellion. Military career Otter was born near Clinton, Canada West. His parents were Anna Louisa, née de la Hooke (1824–1907) and Alfred William Otter (1815–1866), both English immigrants who married in Ontario on 15 September 1842. He began his military career in the Non-Permanent Active Militia in Toronto in 1864. Captain William Otter was Adjutant of the Queen's Own Rifles of Toronto in 1866. He first saw combat with them at the Battle of Ridgeway during the Fenian Raids. He joined the Permanent Force as an infantry officer when Canada established its own professional infantry unit in 1883. On May 2, 1885, he led a Canadian force of more than 300 in the Battle of Cut Knife against a Cree and Assiniboine camp defended by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakoda (people)
The Nakoda (also known as Stoney, , or Stoney Nakoda) are an Indigenous people in Western Canada and the United States. Their territory used to be large parts of what is now Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Montana, but their reserves are now in Alberta and in Saskatchewan, where they are rarely differentiated from the Assiniboine. They refer to themselves in their language as , meaning 'friend, ally'. The name ''Stoney'' was given to them by Anglophone explorers, because of their technique of using fire-heated rocks to boil broth in rawhide bowls. They are very closely related to the Assiniboine, who are also known as Stone Sioux (from ). The Nakoda First Nation in Alberta comprises three bands: Bearspaw, Chiniki, and Goodstoney. The Stoney were "excluded" from Banff National Park between 1890 and 1920. In 2010 they were officially "welcomed back". Nakoda groups The Nakoda are descendants of individual bands of the Assiniboine, from whom they spun out as an independent gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
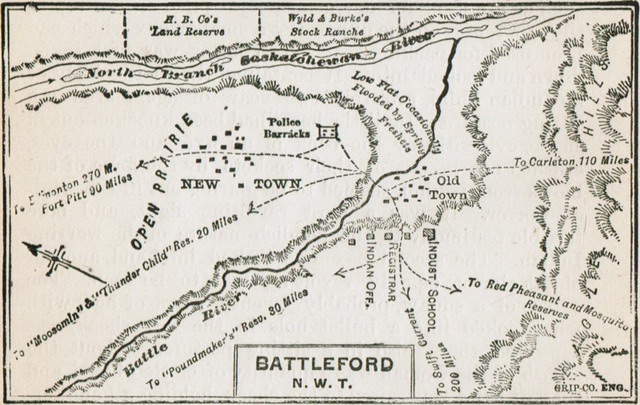
Looting Of Battleford
The Looting of Battleford began at the end of March, 1885, during the North-West Rebellion, in the town of Battleford, Saskatchewan, then a part of the Northwest Territories. Within days of the Métis people (Canada), Métis victory at the Battle of Duck Lake on March 26, 1885 in Canada, 1885. Cree, Cree bands sympathetic to the Métis cause and with grievances of their own began raiding stores and farms in the western part of the District of Saskatchewan for arms, ammunition and food supplies while civilians fled to the larger settlements and forts of the Districts of the Northwest Territories, North-West Territories. Prominent leaders of this uprising were Chief Poundmaker and Chief Big Bear. Poundmaker and his band had a Indian reserve, reserve near present-day Battle of Cut Knife, Cut Knife about 50 km (31 miles) west of Fort Battleford. Big Bear and his band had settled near Frog Lake Massacre, Frog Lake about 55 km (34 miles) northwest of Battle of Fort Pitt, For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Nations In Canada
''First Nations'' () is a term used to identify Indigenous peoples in Canada who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized List of First Nations band governments, First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia. Under Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, Charter jurisprudence, First Nations are a "designated group", along with women, Visible minority, visible minorities, and people with physical or mental disabilities. First Nations are not defined as a visible minority by the criteria of Statistics Canada. North American indigenous peoples have cultures spanning thousands of years. Many of their oral traditions accurately describe historical events, such as the 1700 Cascadia earthquake, Cascadia earthquake of 1700 and the 18th-century Tseax Cone eruption. Writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackfoot
The Blackfoot Confederacy, ''Niitsitapi'', or ''Siksikaitsitapi'' (ᖹᐟᒧᐧᒣᑯ, meaning "the people" or " Blackfoot-speaking real people"), is a historic collective name for linguistically related groups that make up the Blackfoot or Blackfeet people: the '' Siksika'' ("Blackfoot"), the '' Kainai or Blood'' ("Many Chiefs"), and two sections of the Peigan or Piikani ("Splotchy Robe") – the Northern Piikani (''Aapátohsipikáni'') and the Southern Piikani (''Amskapi Piikani'' or ''Pikuni''). Broader definitions include groups such as the ''Tsúùtínà'' ( Sarcee) and ''A'aninin'' ( Gros Ventre) who spoke quite different languages but allied with or joined the Blackfoot Confederacy. Historically, the member peoples of the Confederacy were nomadic bison hunters and trout fishermen, who ranged across large areas of the northern Great Plains of western North America, specifically the semi-arid shortgrass prairie ecological region. They followed the bison herds as they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |