|
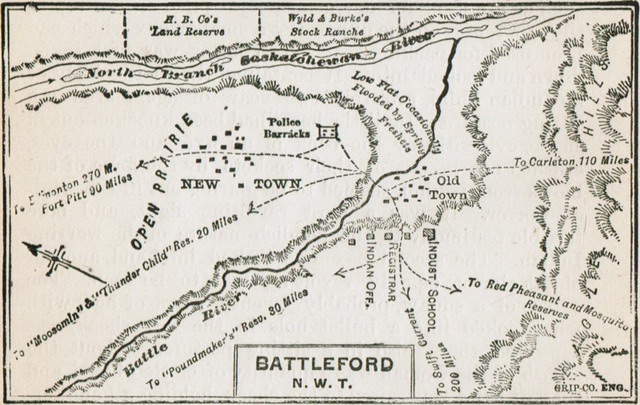
Looting Of Battleford
The Looting of Battleford began at the end of March, 1885, during the North-West Rebellion, in the town of Battleford, Saskatchewan, then a part of the Northwest Territories. Within days of the Métis people (Canada), Métis victory at the Battle of Duck Lake on March 26, 1885 in Canada, 1885. Cree, Cree bands sympathetic to the Métis cause and with grievances of their own began raiding stores and farms in the western part of the District of Saskatchewan for arms, ammunition and food supplies while civilians fled to the larger settlements and forts of the Districts of the Northwest Territories, North-West Territories. Prominent leaders of this uprising were Chief Poundmaker and Chief Big Bear. Poundmaker and his band had a Indian reserve, reserve near present-day Battle of Cut Knife, Cut Knife about 50 km (31 miles) west of Fort Battleford. Big Bear and his band had settled near Frog Lake Massacre, Frog Lake about 55 km (34 miles) northwest of Battle of Fort Pitt, For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North-West Rebellion
The North-West Rebellion (), was an armed rebellion of Métis under Louis Riel and an associated uprising of Cree and Assiniboine mostly in the District of Saskatchewan, against the Government of Canada, Canadian government. Important events included the Frog Lake Massacre, Frog Lake incident, and the Battle of Batoche, capture of Batoche. The North-West Rebellion began in March 1885 after Louis Riel returned from political exile in the U.S. With the assistance of Métis leader Gabriel Dumont (Métis leader), Gabriel Dumont, Riel declared a Provisional Government of Saskatchewan, provisional government on March 18, and rebel territory was carved out. As government forces responded, fighting broke out, with the last shooting over by the end of June. Rebel forces included roughly 250 Métis and 250 Indigenous Peoples of North America, First Nations men, largely Cree and Assiniboine, who were led by Big Bear and Poundmaker and other First Nations chiefs. A non-Indigenous man, Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bear
Big Bear, also known as (; – 17 January 1888), was a powerful and popular Cree chief who played many pivotal roles in Canadian history. He was appointed to chief of his band at the age of 40 upon the death of his father, Black Powder, under his father's harmonious and inclusive rule which directly impacted his own leadership. Big Bear is most notable for his involvement in Treaty 6 and the 1885 North-West Rebellion; he was one of the few chief leaders who objected to the signing of the treaty with the Canadian government. He felt that signing the treaty would ultimately have devastating effects on his nation as well as other First Nations in Canada, Indigenous nations. This included losing the free nomadic lifestyle that his nation and others were accustomed to. Big Bear also took part in one of the last major battles between the Cree and the Blackfoot nations, leading fighters in the last, largest battle on the Canadian Plains. Early life Big Bear (, in Cree syllabics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Northern Railway
The Canadian Northern Railway (CNoR) was a historic Canada, Canadian transcontinental railway. At its 1923 merger into the Canadian National Railway , the CNoR owned a main line between Quebec City and Vancouver via Ottawa, Winnipeg, and Edmonton. Manitoba beginnings The network had its start in the independent branchlines that were being constructed in Manitoba in the 1880s and 1890s as a response to the monopoly exercised by Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR). Many such lines were built with the sponsorship of the provincial government, which sought to subsidize local competition to the federally subsidized CPR; however, significant competition was also provided by the encroaching Northern Pacific Railway (NPR) from the south. Two branchline contractors, William Mackenzie (railway entrepreneur), Sir William Mackenzie and Sir Donald Mann, took control of the bankrupt Lake Manitoba Railway and Canal Company in January, 1896. The partners expanded their enterprise, in 1897, by buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Battleford
North Battleford is a city in west-central Saskatchewan, Canada. It is the seventh largest city in the province and is directly across the North Saskatchewan River from the town of Battleford. Together, the two communities are known as "The Battlefords". North Battleford and the greater Battlefords area are a notable stop along the Yellowhead Highway, part of the Trans-Canada Highway, Trans-Canada system, and serve as a commercial and cultural hub for west- and north-central Saskatchewan. Together, the Battlefords are served by the Yellowhead Highway as well as Saskatchewan Highway 4, Highway 4, Saskatchewan Highway 26, Highway 26, Saskatchewan Highway 29, Highway 29, and Saskatchewan Highway 40, Highway 40. The Battlefords Provincial Park, Battlefords Provincial Park is north on Highway 4. History For thousands of years prior to European settlement, succeeding cultures of indigenous peoples lived in the area. The Battlefords area was home to several historic indigenous gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Saskatchewan River
The North Saskatchewan River is a glacier-fed river that flows from the Canadian Rockies continental divide east to central Saskatchewan, where it joins with the South Saskatchewan River to make up the Saskatchewan River. Its water flows eventually into the Hudson Bay. The Saskatchewan River system is the largest shared between the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan. Its watershed includes most of southern and central Alberta and Saskatchewan. Course The North Saskatchewan River has a length of , and a drainage area of . At its end point at Saskatchewan River Forks it has a mean discharge of . The yearly discharge at the Alberta–Saskatchewan border is more than . The river begins above at the toe of the Saskatchewan Glacier in the Columbia Icefield, and flows southeast through Banff National Park alongside the Icefields Parkway. At the junction of the David Thompson Highway (Highway 11), it initially turns northeast for b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle River
Battle River is a river in central Alberta and western Saskatchewan, Canada. It is a major tributary of the North Saskatchewan River. The Battle River flows for and drains a total area of . Its mean discharge at the mouth is 10 m³/s. History The river is said to be named for a battle that took place between the Cree and the Blackfoot. Course The headwaters of Battle River is Battle Lake in west-central Alberta, east of Winfield. The river flows through Alberta and into Saskatchewan, where it discharges into the North Saskatchewan River at Battleford. Over its course, the river flows through Ponoka and by Hardisty and Fabyan within Alberta. Big Knife Provincial Park is situated on the south bank of the river west of Highway 855, about southwest of Forestburg. The Fabyan Trestle Bridge also spans the river. Tributaries *Sunny Creek *Wolf Creek *Pigeon Lake Creek *Stoney Creek * Pipestone Creek *Driedmeat Creek *Meeting Creek *Paintearth Creek * Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Albert, Saskatchewan
Prince Albert is the third-largest city in Saskatchewan, Canada, after Saskatoon and Regina, Saskatchewan, Regina. It is situated near the centre of the province on the banks of the North Saskatchewan River. The city is known as the "Gateway to the North" because it is the last major centre along the route to the resources of northern Saskatchewan. Prince Albert National Park is located north of the city and contains a wealth of lakes, forest, and wildlife. The city itself is located in a ecotone, transition zone between the aspen parkland and boreal forest biomes. Prince Albert is surrounded by the Rural Municipality of Prince Albert No. 461, of which it is the seat, but is politically separate. History The area was named ''kistahpinanihk'' by the Cree, which translates to "sitting pretty place", "great meeting place" or "meeting place". The first trading post set up in the area was built in 1776 by Peter Pond. James Isbister, an Anglo-Métis employee of the Hudson's Bay C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provisional Government Of Saskatchewan
The Provisional Government of Saskatchewan was an independent state declared during the North-West Rebellion of 1885 in the District of Saskatchewan of the North-West Territories. The name was given by Louis Riel. Although Riel initially hoped to rally the Countryborn, Cree, and European settlers of the Saskatchewan Valley to his banner, this did not occur. The government, with the exception of Honoré Jaxon and Chief White Cap, had an entirely French-speaking and Métis leadership. Gabriel Dumont was proclaimed adjutant general in which capacity he became supreme military commander, although Riel could, and did, override his tactical decisions. The Provisional Government was declared by Riel on March 19, 1885. It ceased to exist following the defeat of the Métis militarily during the Battle of Batoche, which concluded on May 20, 1885. During its existence the government only exercised authority over the Southbranch Settlements along the South Saskatchewan River. Oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Riel
Louis Riel (; ; 22 October 1844 – 16 November 1885) was a Canadian politician, a founder of the province of Manitoba, and a political leader of the Métis in Canada, Métis people. He led two resistance movements against the Government of Canada and its first prime minister John A. Macdonald. Riel sought to defend Métis rights and identity as the Northwest Territories came progressively under the Canadian sphere of influence. The first resistance movement led by Riel was the Red River Resistance of 1869–1870. The provisional government established by Riel ultimately negotiated the terms under which the new province of Manitoba entered the Canadian Confederation. However, while carrying out the resistance, Riel had a Canadian nationalist, Thomas Scott (Orangeman), Thomas Scott, executed. Riel soon fled to the United States to escape prosecution. He was elected three times as Member of Parliament (Canada), member of the House of Commons of Canada, House of Commons, but, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southbranch Settlement
Southbranch Settlement () was the name ascribed to a series of French Métis settlements on the Canadian prairies in the 19th century, in what is today the province of Saskatchewan. Métis settlers began making homes here in the 1860s and 1870s, many of them fleeing economic and social dislocation from Red River, Manitoba. The settlements became the centre of Métis resistance during the North-West Resistance when in March 1885, Louis Riel, Gabriel Dumont, Honoré Jackson, and others set up the Provisional Government of Saskatchewan with their headquarters at Batoche. History The Settlements stretched along both sides of the South Saskatchewan River in river lot style from Fish Creek north through Batoche and St. Laurent to St. Louis which was its northern boundary. They included Duck Lake 12 kilometers from St. Laurent accessed by the St. Laurent Ferry. The distance from Fish Creek to St. Louis was less than 50 kilometres. They were proximal to several Cree reserves, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Regina
The University of Regina is a public university located in Regina, Saskatchewan, Canada. Founded in 1911 as a private denominational high school of the Methodist Church of Canada, it began an association with the University of Saskatchewan as a junior college in 1925, and was disaffiliated by the Church and fully ceded to the university in 1934; in 1961 it attained degree-granting status as the Regina Campus of the University of Saskatchewan. It became an autonomous university in 1974. The University of Regina has an enrolment of over 15,000 full and part-time students. The university's student newspaper, ''The Carillon (Regina), The Carillon'', is a member of Canadian University Press, CUP. The University of Regina is a research university reputed for having a focus on experiential learning and offers internships, professional placements and practicums in addition to cooperative education placements in 41 programs. In 2009 the University of Regina launched the UR Guarantee Progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Agent (Canada)
From 1755 to 1830 Indian agent was a representative of the British Indian Department in British North America. From the 1830s (beginning in what was then so-called "Lower Canada") until the 1960s, an Indian agent was the Canadian government's representative on First Nations reserves. The British involvement ended in 1860 when Indigenous affairs were whole Canadian responsibility. The role of the Indian agent in Canadian history has never been fully documented, and today the position no longer exists. The position of Indian agent was established in the early 1870s. Indian agents were responsible for implementing government policy on reserves, enforcing and administering the provisions of the ''Indian Act'', and managing the day-to-day affairs of First Nations people. An Indian agent was the chief administrator for Indian affairs in their respective districts, although the title now is largely in disuse in preference to "government agent". The powers of the Indian agent held swa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |