|
Posterior Humeral Circumflex Artery
The posterior humeral circumflex artery (posterior circumflex artery or posterior circumflex humeral artery) arises from the third part of the axillary artery at the distal border of the subscapularis. Anatomy Course and relations It passes posteriorward with the axillary nerve through the quadrangular space. It winds laterally around the surgical neck of the humerus. Distribution It is distributed to the shoulder joint, teres major, teres minor, deltoid, and (long and lateral heads of) triceps brachii. Anastomoses It forms anastomoses with the anterior humeral circumflex artery, (deltoid branch of) profunda brachii artery, (acromial branches of) suprascapular artery The suprascapular artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk on the neck. Structure At first, it passes downward and laterally across the scalenus anterior and phrenic nerve, being covered by the sternocleidomastoid muscle; it then crosses t ..., (acromial branches of) and thoracoacromial artery. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axillary Artery
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery. After passing the lower margin of teres major muscle, teres major it becomes the brachial artery. Structure The axillary artery is often referred to as having three parts, with these divisions based on its location relative to the pectoralis minor muscle, which is superficial to the artery. * First part – the part of the artery superior to the pectoralis minor * Second part – the part of the artery posterior to the pectoralis minor * Third part – the part of the artery inferior to the pectoralis minor. Relations The axillary artery is accompanied by the axillary vein, which lies medial to the artery, along its length. In the axilla, the axillary artery is surrounded by the brachial plexus. The second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subscapularis
The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the Glenohumeral joint, shoulder-joint. Structure The subscapularis is covered by a dense fascia which attaches to the scapula at the margins of the subscapularis' attachment (origin) on the scapula. The muscle's fibers pass laterally from its origin before coalescing into a tendon of insertion. The tendon intermingles with the Glenohumeral, glenohumeral (shoulder) joint capsule. A Synovial bursa, bursa (which communicates with the cavity of the shoulder jointMilano, Giuseppe and Grasso, AndreaShoulder Arthroscopy: Principles and Practice, Springer Science & Business Media, Dec 16, 2013. . Accessed 2016-11-07. via an aperture in the joint capsule) intervenes between the tendon and a bare area at the lateral angle of the scapula/the neck of the scapula. The subscapularis (supraserratus) bursa separates the subscapu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axillary Nerve
The axillary nerve or the circumflex nerve is a nerve of the human body, that originates from the brachial plexus ( upper trunk, posterior division, posterior cord) at the level of the axilla (armpit) and carries nerve fibers from C5 and C6. The axillary nerve travels through the quadrangular space with the posterior circumflex humeral artery and vein to innervate the deltoid and teres minor. Structure The nerve lies at first behind the axillary artery, and in front of the subscapularis, and passes downward to the lower border of that muscle. It then winds from anterior to posterior around the neck of the humerus, in company with the posterior humeral circumflex artery, through the quadrangular space (bounded above by the teres minor, below by the teres major, medially by the long head of the triceps brachii, and laterally by the surgical neck of the humerus), and divides into an anterior, a posterior, and a collateral branch to the long head of the triceps brachii bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrangular Space
The quadrangular space, also known as the quadrilateral space (of Velpeau) and the foramen humerotricipitale, is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: triangular space and triangular interval. Structure The quadrangular space is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. Boundaries The quadrangular space is defined by: - "Scapular Region: Quadrangular Space of Scapular Region" * ''above/superior:'' teres minor muscle. * ''below/inferior:'' teres major muscle. * ''medially:'' long head of the triceps brachii muscle (lateral margin). * ''laterally:'' surgical neck of the humerus. * ''anteriorly:'' subscapularis muscle. Contents The quadrangular space transmits the axillary nerve, the posterior humeral circumflex artery and the posterior circumflex humeral vein. Clinical significance The quadrangular space is a clinically important anatomic space in the arm as it provides the anterior regions of the axilla a passageway to the poste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Neck Of Humerus
The surgical neck of the humerus is a bony constriction at the proximal end of shaft of humerus. It is situated distal to the greater tubercle and lesser tubercle, and proximal to the deltoid tuberosity. Clinical significance The surgical neck is much more frequently fractured than the anatomical neck of the humerus. This type of fracture takes place when the humerus is forced in one direction while the joint capsule and the rotator cuff muscles remain intact. A fracture in this area is most likely to cause damage to the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery. Damage to the axillary nerve affects function of the teres minor and deltoid muscles, resulting in loss of abduction of arm (from 15-90 degrees), weak flexion, extension, and rotation of shoulder as well as loss of sensation of the skin over a small part of the lateral shoulder. Additional images File:Neck-of-Humerus.jpg, The difference between anatomical neck and surgical neck of the humerus File:Illu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder Joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial joint, synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). Due to the very loose joint capsule, it gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body. Structure The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. The socket of the glenoid fossa of the scapula is itself quite shallow, but it is made deeper by the addition of the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilage, cartilaginous fibre attached to the circumference of the cavity. This ring is continuous with the tendon of the Biceps, biceps brachii above. Spaces Significant joint spaces are: * The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teres Major Muscle
The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle. The teres major muscle (from Latin ''teres'', meaning "rounded") is positioned above the latissimus dorsi muscle and assists in the extension and medial rotation of the humerus. This muscle is commonly confused as a rotator cuff muscle, but it is not, because it does not attach to the capsule of the shoulder joint, unlike the teres minor muscle, for example. Structure The teres major muscle originates on the dorsal surface of the inferior angle and the lower part of the lateral border of the scapula. The fibers of teres major insert into the medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus. Relations The tendon, at its insertion, lies behind that of the latissimus dorsi, from which it is separated by a bursa, the two tendons being, however, united along their lower borders for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
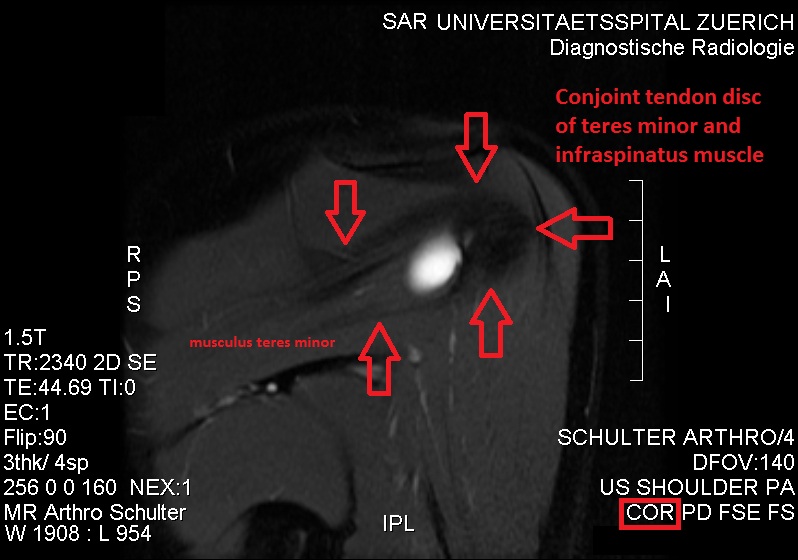
Teres Minor
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule. The primary function of the teres minor is to modulate the action of the deltoid, preventing the humeral head from sliding upward as the arm is abducted. It also functions to rotate the humerus laterally. The teres minor is innervated by the axillary nerve. Structure It arises from the dorsal surface of the axillary border of the scapula for the upper two-thirds of its extent, and from two aponeurotic laminae, one of which separates it from the infraspinatus muscle, the other from the teres major muscle. Its fibers run obliquely upwards and laterally; the upper ones end in a tendon which is inserted into the lowest of the three impressions on the greater tub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltoid Muscle
The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the shoulder, human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the # anterior or clavicular part (pars clavicularis) ( More commonly known as the front delt.) # posterior or scapular part (pars scapularis) ( More commonly known as the rear delt.) # intermediate or acromial part (pars acromialis) ( More commonly known as the side delt) The deltoid's fibres are pennate muscle. However, electromyography suggests that it consists of at least seven groups that can be independently coordinated by the nervous system. It was previously called the deltoideus (plural ''deltoidei'') and the name is still used by some anatomists. It is called so because it is in the shape of the Greek alphabet, Greek capital letter Delta (letter), delta (Δ). Deltoid is also further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triceps Brachii Muscle
The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of three parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. All three heads cross the elbow joint. However, the long head also crosses the shoulder joint. The triceps muscle contracts when the elbow is straightened and expands when the elbow is bent. The long head gets a further contraction when the arm is behind the torso due to how it crosses the shoulder joint. It is the muscle principally responsible for extension of the elbow joint (straightening of the arm). Structure * The long head arises from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. It extends distally anterior to the teres minor and posterior to the teres major. * The medial head arises proximally in the humerus, just inferior to the groove of the radial nerve; from the dorsal (back) surface of the humerus; from the medial intermuscular septum; and its dista ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Humeral Circumflex
The anterior humeral circumflex artery (anterior circumflex artery, anterior circumflex humeral artery) is an artery in the arm. It is one of two circumflexing arteries that branch from the axillary artery, the other being the posterior humeral circumflex artery. The anterior humeral circumflex artery is considerably smaller than the posterior and arises nearly opposite to it, from the lateral side of the axillary artery. Anatomy Course and relations The anterior humeral circumflex artery passes horizontally posterior to the coracobrachialis muscle and short head of the biceps brachii muscle, in and anterior to of the surgical neck of the humerus. Upon reaching the intertubercular sulcus, it gives off an ascending branch which ascends along the sulcus to supply the head of the humerus and the shoulder-joint. It continues laterally, deep to the long head of the biceps brachii and the deltoideus muscle, before anastomosing with the posterior humeral circumflex artery. Additional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |