|
Positive Computing
Positive computing is a technological design perspective that embraces psychological well-being and ethical practice, aiming at building a digital environment to support happier and healthier users. Positive computing develops approaches that integrate insights from psychology, education, neuroscience, and HCI with technological development. The purpose of positive computing is to bridge the technology and mental health worlds. Indeed, there are computer and mental health workshops that are aimed to bring people from both communities together. Everyone who uses technology is impacted by the way the tool is designed and even if most technologies may have small effects, they still apply to huge populations. Background Well-being in psychology Technology researchers typically focus primarily on technical aspects, paying less attention to the ethical impact and ethical considerations of their products. However, researchers from other fields such as psychology and philosophy studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, industry, communication, transportation, and daily life. Technologies include physical objects like utensils or machines and intangible tools such as software. Many technological advancements have led to societal changes. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used in the prehistoric era, followed by fire use, which contributed to the growth of the human brain and the development of language in the Ice Age. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age enabled wider travel and the creation of more complex machines. Recent technological developments, including the printing press, the telephone, and the Internet have lowered communication barriers and ushered in the knowledge economy. While technology contributes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competence (human Resources)
Competence is the set of demonstrable characteristics and skills that enable and improve the efficiency or performance of a job. The term "competence" first appeared in an article authored by R.W. White in 1959 as a concept for performance motivation. In 1970, Craig C. Lundberg defined the concept in "Planning the Executive Development Program". The term gained traction when in 1973, David McClelland wrote a seminal paper entitled, "Testing for Competence Rather Than for Intelligence". The term was used by McClelland commissioned by the State Department, to extract characteristics common to high-performing agents of embassy, and to help them recruit and develop. It has since been popularized by Richard Boyatzis and many others, such as T.F. Gilbert (1978) who used the concept in relationship to performance improvement. Its use varies widely, which leads to considerable misunderstanding. Some scholars see "competence" as a combination of practical and theoretical knowledge, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nick Bostrom
Nick Bostrom ( ; sv, Niklas Boström ; born 10 March 1973) is a Swedish-born philosopher at the University of Oxford known for his work on existential risk, the anthropic principle, human enhancement ethics, superintelligence risks, and the reversal test. In 2011, he founded the Oxford Martin Program on the Impacts of Future Technology, and is the founding director of the Future of Humanity Institute at Oxford University. In 2009 and 2015, he was included in ''Foreign Policy''s Top 100 Global Thinkers list. Bostrom is the author of over 200 publications, and has written two books and co-edited two others. The two books he has authored are '' Anthropic Bias: Observation Selection Effects in Science and Philosophy'' (2002) and '' Superintelligence: Paths, Dangers, Strategies'' (2014). ''Superintelligence'' was a ''New York Times'' bestseller, was recommended by Elon Musk and Bill Gates among others, and helped to popularize the term " superintelligence". Bostrom believes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superintelligence
A superintelligence is a hypothetical agent that possesses intelligence far surpassing that of the brightest and most gifted human minds. "Superintelligence" may also refer to a property of problem-solving systems (e.g., superintelligent language translators or engineering assistants) whether or not these high-level intellectual competencies are embodied in agents that act in the world. A superintelligence may or may not be created by an intelligence explosion and associated with a technological singularity. University of Oxford philosopher Nick Bostrom defines ''superintelligence'' as "any intellect that greatly exceeds the cognitive performance of humans in virtually all domains of interest". The program Fritz falls short of superintelligence—even though it is much better than humans at chess—because Fritz cannot outperform humans in other tasks. Following Hutter and Legg, Bostrom treats superintelligence as general dominance at goal-oriented behavior, leaving open whether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Engineering
Computer engineering (CoE or CpE) is a branch of electrical engineering and computer science that integrates several fields of computer science and electronic engineering required to develop computer hardware and software. Computer engineers not only require training in electronic engineering, software design, and hardware-software integration, but also in software engineering. It uses the techniques and principles of electrical engineering and computer science, but also covers areas such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, computer networks, computer architecture and operating systems. Computer engineers are involved in many hardware and software aspects of computing, from the design of individual microcontrollers, microprocessors, personal computers, and supercomputers, to circuit design. This field of engineering not only focuses on how computer systems themselves work, yet it also demands them to integrate into the larger picture. Robots are one of the appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to practical disciplines (including the design and implementation of hardware and software). Computer science is generally considered an area of academic research and distinct from computer programming. Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and for preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of repositories ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence Explosion
The technological singularity—or simply the singularity—is a hypothetical future point in time at which technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in unforeseeable changes to human civilization. According to the most popular version of the singularity hypothesis, I.J. Good's intelligence explosion model, an upgradable intelligent agent will eventually enter a "runaway reaction" of self-improvement cycles, each new and more intelligent generation appearing more and more rapidly, causing an "explosion" in intelligence and resulting in a powerful superintelligence that qualitatively far surpasses all human intelligence.Vinge, Vernor"The Coming Technological Singularity: How to Survive in the Post-Human Era", in ''Vision-21: Interdisciplinary Science and Engineering in the Era of Cyberspace'', G. A. Landis, ed., NASA Publication CP-10129, pp. 11–22, 1993. The first person to use the concept of a "singularity" in the technological context was John vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
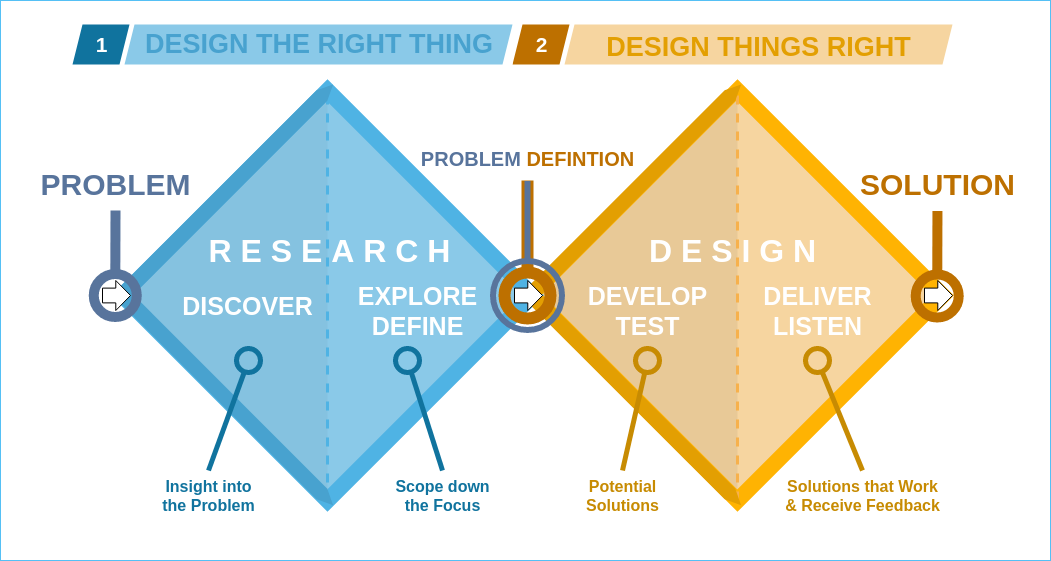
Double Diamond (design Process Model)
Double Diamond is the name of a design process model popularized by the British Design Council in 2005, and adapted from the divergence-convergence model proposed in 1996 by Hungarian-American linguist Béla H. Bánáthy. The two diamonds represent a process of exploring an issue more widely or deeply (divergent thinking) and then taking focused action (convergent thinking). It suggests that the design process A design is a plan or specification for the construction of an object or system or for the implementation of an activity or process or the result of that plan or specification in the form of a prototype, product, or process. The verb ''to design'' ... should have four phases: *Discover: Understand the issue rather than merely assuming it. It involves speaking to and spending time with people who are affected by the issues. *Define: The insight gathered from the discovery phase can help to define the challenge in a different way. *Develop: Give different answers to the clea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Responsible Design Process
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Design
Game design is the art of applying design and aesthetics to create a game for entertainment or for educational, exercise, or experimental purposes. Increasingly, elements and principles of game design are also applied to other interactions, in the form of gamification. Game designer and developer Robert Zubek defines game design by breaking it down into its elements, which he says are the following: * Gameplay, which is the interaction between the player and the mechanics and systems * Mechanics and systems, which are the rules and objects in the game * Player experience, which is how users feel when they're playing the game Games such as board games, card games, dice games, casino games, role-playing games, sports, video games, war games, or simulation games benefit from the principles of game design. Academically, game design is part of game studies, while game theory studies strategic decision making (primarily in non-game situations). Games have historically inspire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)
