|
Polyborate
A borate is any of several boron oxyanions, negative ions consisting of boron and oxygen, such as orthoborate , metaborate , or tetraborate ; or any salt with such anions, such as sodium metaborate, and disodium tetraborate . The name also refers to certain functional groups in molecules consisting of boron and oxygen, and esters with such groups, such as triethyl orthoborate . Natural occurrence Borate ions occur, alone or with other anions, in many borate and borosilicate minerals such as borax, boracite, ulexite (boronatrocalcite) and colemanite. Borates also occur in seawater, where they make an important contribution to the absorption of low frequency sound in seawater. Borates also occur in plants, including almost all fruits. Anions The main borate anions are: * tetrahydroxyborate , found in sodium tetrahydroxyborate . * orthoborate , found in trisodium orthoborate * perborate , as in sodium perborate * metaborate or , found in sodium metaborate * diborate , f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
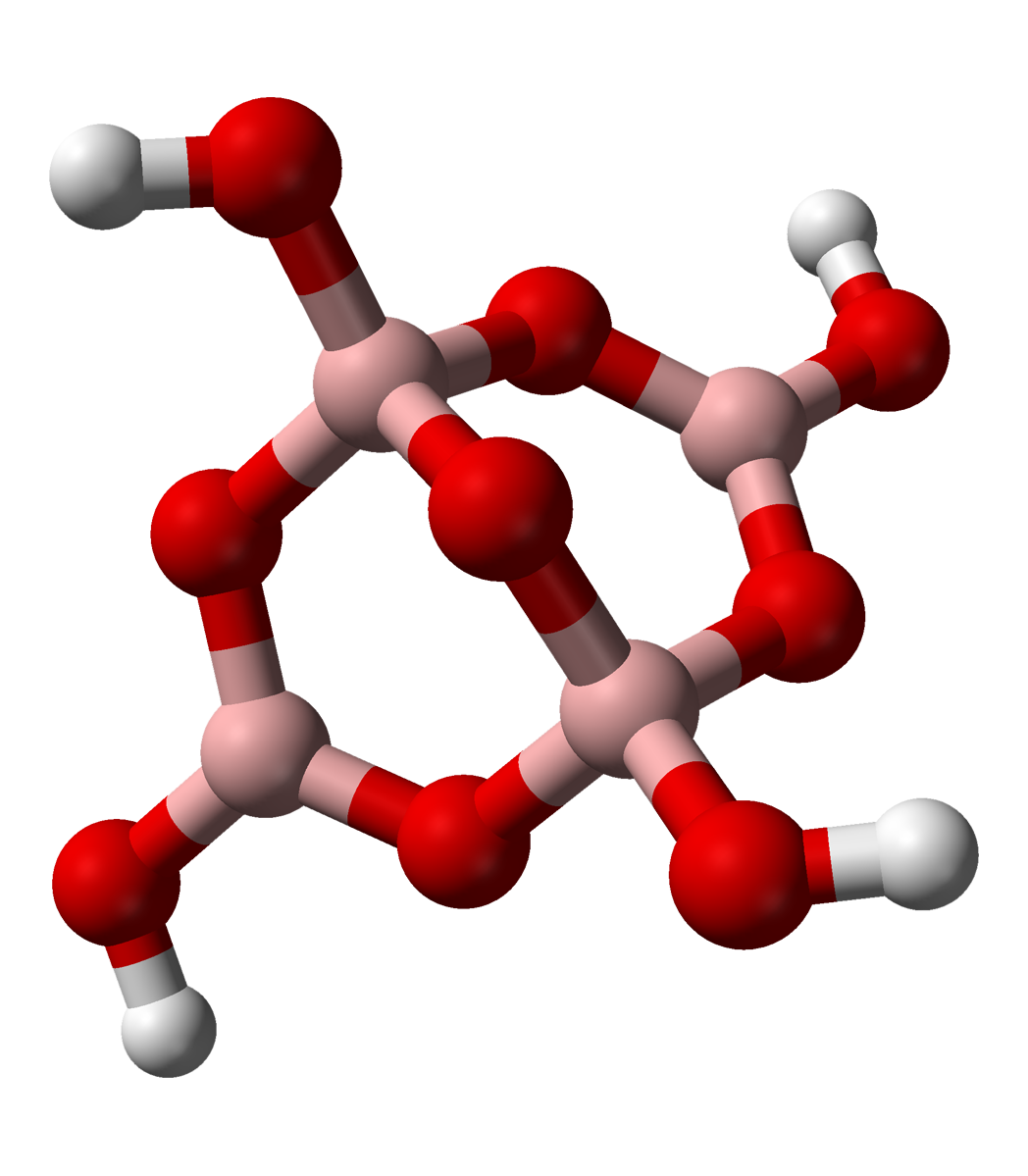
Tetraborate
In chemistry, tetraborate or pyroborate is an anion (negative ion) with formula ; or a salt containing that anion, such as sodium tetraborate, . It is one of the boron oxoacids, that is, a borate. The name is also applied to the hydrated ion as present in borax The ion occurs in boric acid solutions at neutral pH, being formed by condensation of orthoborate and tetrahydroxyborate anions: : 2 B(OH)3 + 2 ⇌ + 5 H2O The tetraborate anion (tetramer) includes two tetrahedral and two trigonal boron atoms symmetrically assembled in a fused bicyclic structure. The two tetrahedral boron atoms are linked together by a common oxygen atom, and each also bears a negative net charge brought by the supplementary OH− groups laterally attached to them. This intricate molecular anion also exhibits three rings: two fused distorted hexagonal (boroxole) rings and one distorted octagonal ring. Each ring is made of a succession of alternate boron and oxygen atoms. Boroxole rings are a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthoborate
In inorganic chemistry, an orthoborate is a polyatomic anion with formula or a salt containing the anion; such as trisodium orthoborate . It is one of several boron oxoanions, or borates. The name is also used in organic chemistry for the trivalent functional group , or any compound (ester) that contains it, such as triethyl orthoborate . Structure The orthoborate ion is known in the solid state, for example, in calcium orthoborate , where it adopts a nearly trigonal planar structure. It is a structural analogue of the carbonate anion , with which it is isoelectronic. Simple bonding theories point to the trigonal planar structure. In terms of valence bond theory, the bonds are formed by using sp2 hybrid orbitals on boron. Some compounds termed orthoborates do not necessarily contain the trigonal planar ion. For example, gadolinium orthoborate contains the planar ion only a high temperatures; otherwise it contains the polyborate anion . Reactions Solution When orthobo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the '' boron group'' it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride. Boron is synthesized entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovae and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, so it is a low-abundance element in the Solar System and in the Earth's crust. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the borate minerals. These are mined industrially as evaporites, such as borax and kernite. The largest known deposits are in Turkey, the largest producer of boron minerals. Elemental boron is a meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boracite
Boracite is a magnesium borate mineral with formula: Mg3 B7 O13 Cl. It occurs as blue green, colorless, gray, yellow to white crystals in the orthorhombic - pyramidal crystal system. Boracite also shows pseudo-isometric cubical and octahedral forms. These are thought to be the result of transition from an unstable high temperature isometric form on cooling. Penetration twins are not unusual. It occurs as well formed crystals and dispersed grains often embedded within gypsum and anhydrite crystals. It has a Mohs hardness of 7 to 7.5 and a specific gravity of 2.9. Refractive index values are nα = 1.658 - 1.662, nβ = 1.662 - 1.667 and nγ = 1.668 - 1.673. It has a conchoidal fracture and does not show cleavage. It is insoluble in water (not to be confused with borax, which is soluble in water). Boracite is typically found in evaporite sequences associated with gypsum, anhydrite, halite, sylvite, carnallite, kainite and hilgardite. It was first described in 1789 for specimens from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suanite
Suanite is a magnesium borate mineral with formula Mg2B2O5. It was first described in 1953 by Japanese scientist Takeo Watanabe from the University of Tokyo. His first contact with the mineral was during analysis of gold- and copper- bearing skarn minerals from the Hol Kol mine, located in North Korea North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and ... obtained in 1939. Due to the small sample size available to him, he was only able to determine the unknown substance's optical properties under a microscope. Watanabe was able to return to the site in 1943 and obtain further samples that permitted him to perform chemical analysis on the material. References Nesoborates Magnesium minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 14 {{mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Diborate
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table) it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and it almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explode as supernovas, much of the magnesium is expelled into the interstellar medium where it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Perborate
Sodium perborate is chemical compound whose chemical formula may be written , , or, more properly, ·. Its name is sometimes abbreviated as PBS (not to be confused with phosphate-buffered saline). The compound is commonly encountered in anhydrous form or as a hexahydrate (commonly called "monohydrate" or PBS-1 and "tetrahydrate" or PBS-4, after the early assumption that would be the anhydrous form).Alexander McKillop and William R Sanderson (1995): "Sodium perborate and sodium percarbonate: Cheap, safe and versatile oxidising agents for organic synthesis". ''Tetrahedron'', volume 51, issue 22, pages 6145-6166. They are both white, odorless, water-soluble solids.B.J. Brotherton "Boron: Inorganic Chemistry" in ''Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry'' (1994) Ed. R. Bruce King, John Wiley & Sons This salt is widely used in laundry detergents, as one of the peroxide-based bleaches. Structure Unlike sodium percarbonate and sodium perphosphate, the compound is not simply an ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trisodium Orthoborate
Trisodium borate is a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen, with formula , or . It is a salt with the orthoborate anion . The compound is also called trisodium orthoborate, sodium orthoborate, or just sodium borate. However, "sodium orthoborate" has been used also for a compound with formula , which would correspond to an equimolar mixture of sodium metaborate and trisodium borate proper. and "sodium borate" is sometimes used in the generic sense, for a sodium salt with any of several other borate anions. Preparation Sodium carbonate will react with sodium metaborate or boric oxide to form the orthoborate and carbon dioxide when heated between 600 and 850 °C: : + → + Difficult to obtain in pure form from melts. Properties Reactions When dissolved in water, the orthoborate anion partially hydrolyzes into metaborate and hydroxide : : + + 3 Electrolysis of a solution of sodium orthoborate generates sodium perborate at the anode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Tetrahydroxyborate
Sodium tetrahydroxyborate is a salt (ionic compound) of with chemical formula or . It is one of several sodium borates. At room temperature it is a colorless transparent crystalline solid. The element ratio corresponds to the oxide mixture , but the structure of the solid is quite different from that suggested by this formula. Structure Sodium tetrahydroxyborate has been crystallized from aqueous solutions in two anhydrous forms. Both contain the tetrahedral tetrahydroxyborate anion, which is formed from (ortho)boric acid in water solutions by binding an hydroxide anion instead of loss of a proton . These anions lie in layers perpendicular to the (010) plane, and form a tridimensional lattice held together by hydrogen bonds between the hydrogen atoms in each anion and the oxygen atoms in adjacent anions. Monoclinic form The first form, described in 1993, crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system with symmetry group ''P''21/''a'' and parameters ''a'' = 588.6 pm, ''b'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |